Alopecia CS-OSPE
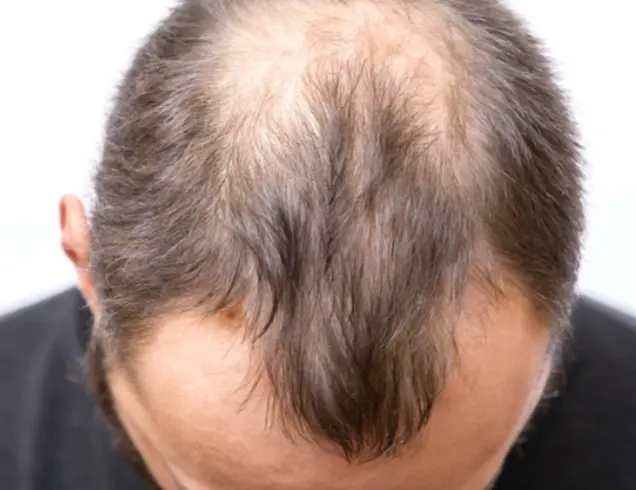
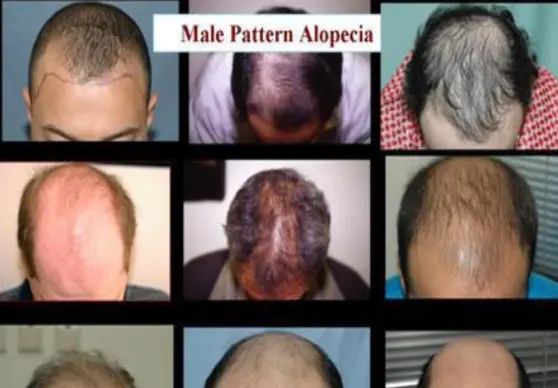
Androgenic alopecia
Diagnosis:
- Androgenic alopecia.
Causes (Differential Diagnosis/Associated Conditions):
- Neoplastic disorders: Basal Cell Carcinoma.
- Trauma: 2nd & 3rd degree burns.
- Lichen planus: It’s a common cause of scarring hair loss.
- Discoid lupus erythematosus.
Treatment: Topical:
- Minoxidil:
- 2% for females.
- 5% for males.
- Used twice per day.
- Note: For females, it shouldn’t be used during pregnancy. Systemic:
- Finasteride:
- Side effects:
- In males: feminization.
- In females: contraindicated in pregnant women carrying a male infant (it can affect the gonads of the infant).
- Side effects:
- Spironolactone: Has an anti-adrenergic effect. Surgical:
- Hair transplantation.
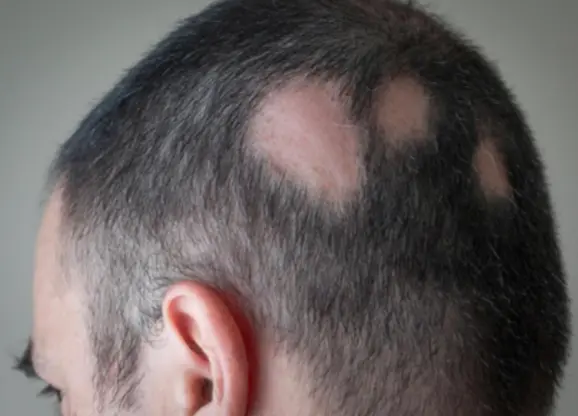
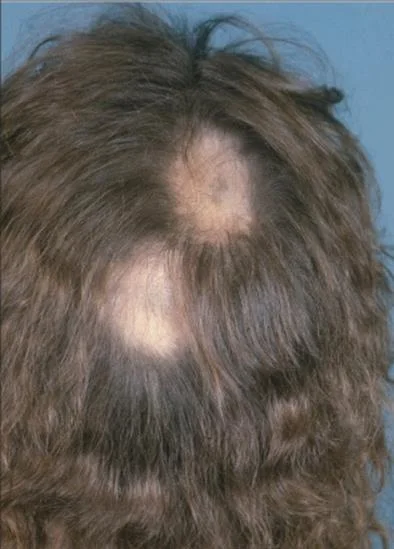
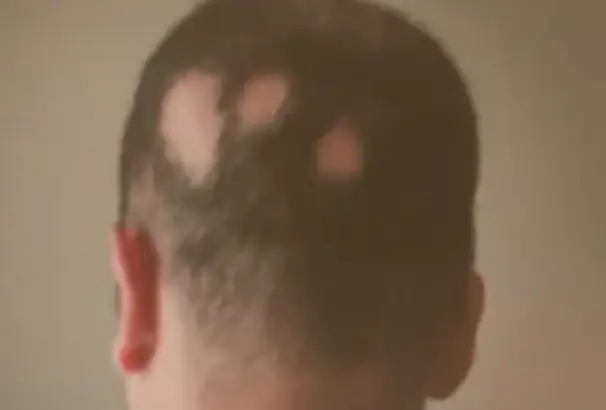
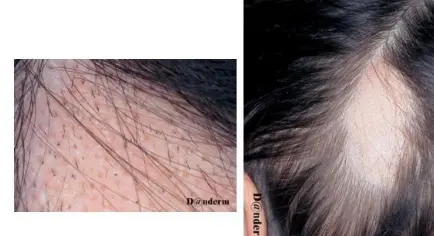
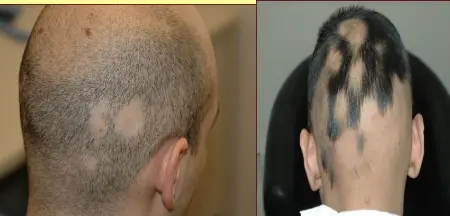
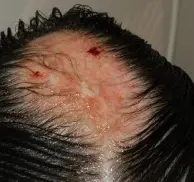
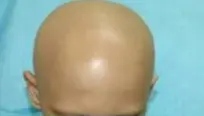

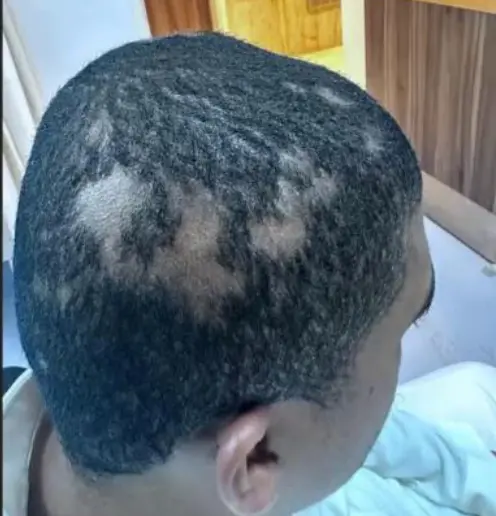
Alopecia Areata
A 32 y/o male presented with 4 months duration non-pruritic on-scaly scalp lesion. Sudden hair loss (localized or generalized), Well demarcated, Exclamation point? Normal scalp, Nail: pitting, ridges. (Grey hair present usually) Diagnosis: Alopecia Areata
Characteristic Features/Clinical Presentation:
- Rapid and complete loss of hair in one or several patches, Patches of 1-5 cm in diameter its well demarcated.
- The characteristic feature or the primary lesion is Exclamation point hairs.
- Nail changes: pitting, ridges.
Differential Diagnosis:
- Tinea capitis.
- Trichotillomania.
- Secondary syphilis.
Associated diseases/Higher incidence/Cause/Predisposing factors:
- Atopic dermatitis.
- Down syndrome.
- Lichen planus.
- SLE.
- Myasthenia Gravis.
- Hashimoto Thyroiditis.
- Addison’s disease.
- Vitiligo.
- Autoimmune conditions (e.g., DM).
- Psychological stress can be a predisposing factor.
- Genetic background, as 30% have a positive family history.
Types:
- Localized partial
- Localized extensive
- Alopecia ophiasis
- Alopecia totalis
- Alopecia universalis
Bad/Poor prognostic factors? Z
- Young age (Old age is NOT a poor prognosis factor)
- Atopy
- Alopecia totalis, universalis, ophiasis (Extra scalp/ outside scalp involvement / Multiple lesions) (This patient has poor prognosis = multiple lesions)
- Nail changes: pitting or ridges
Management/Treatment:
- Full history
- Examination
- Investigation (Histopathology = swarm bees)
- Education
- Observation
- Intralesional Corticosteroids
- Skin Sensitizers: Anthralin, Diphencyclopropenone (DPCP)
- Hair Transplant
- Topical steroids
- Systemic Steroids
- Cytotoxic Rx
- Phototherapy: Narrow band – UVB – PUVA
- Minoxidil
Other indications for intralesional steroids?
- Keloid
- Vitiligo
- Acne Vulgaris
- Infantile hemangioma
- Alopecia
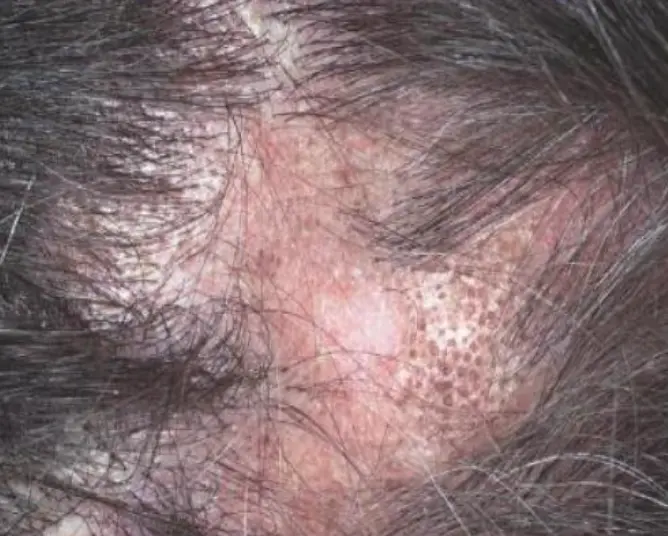
Scarring alopecia
What is the diagnosis?
- Scarring alopecia.
What are the causes?
- Neoplastic disorders: Basal Cell Carcinoma.
- Trauma: 2nd & 3rd degree burns.
- Lichen planus: It’s a common cause of scarring hair loss.
- Discoid lupus erythromatosus.
What is the treatment?
- Topical:
- Minoxidil:
- 2% for females and 5% for males.
- Used twice per day.
- For females, it shouldn’t be used during pregnancy.
- Minoxidil:
- Systemic:
- Fenestride:
- Side effects:
- In males: Feminization.
- In females: If pregnant with a male infant, it may affect the gonads of the infant.
- Side effects:
- Spironolactone: Has an anti-adrenergic effect.
- Fenestride:
- Hair transplantation.