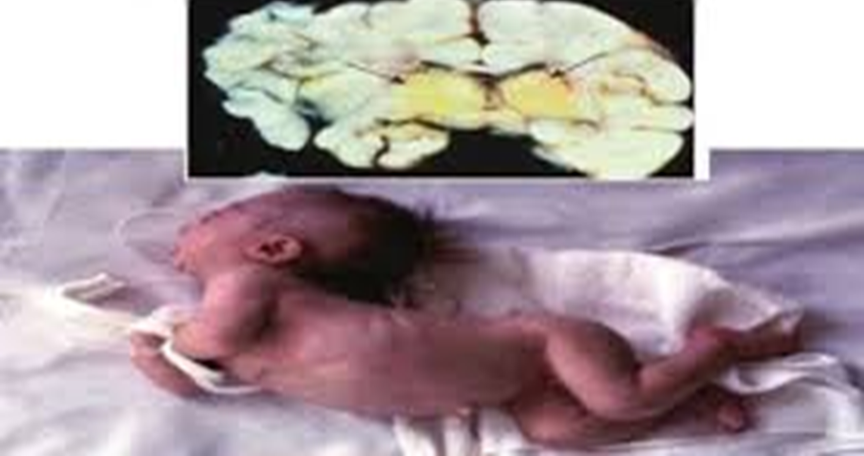
Kernicterus complications
Kernicterus is brain damage caused by unconjugated bilirubin deposition in basal ganglia and brain stem nuclei.
Bilirubin can cross the blood-brain barrier and enter the brain tissue if it is unconjugated and unbound to albumin, or if there is damage to the blood-brain barrier.
Acute bilirubin toxicity in a term infant if: No signs of hemolysis and the TSB concentration is greater than 25 mg/dL. TSB concentration is above 20 mg/dL, in a term infant who has hemolysis
Premature infants are more liable to kernicterus at a lower level of bilirubin because:
- Low serum albumin
- No subcutaneous fat, so most bilirubin passes the blood brain barrier to lipids of CNS
- More liable to asphyxia & acidosis leads to decrease binding of bilirubin to albumin and increase permeability of brain cell membranes to bilirubin
- More liable to hypoglycemia leads to excess free fatty acids in circulation & decrease binding of bilirubin
Clinical presentation
- Poor suck
- High-pitched cry
- Stupor, hypotonia
- Seizures
- Hypertonia of extensor muscles
- Opisthotonos
- Retrocollis
- Fever
- Choreoathetotic cerebral palsy
- Sensorineural hearing loss
- Tremor
- Upward gaze
- Dental dysplasia