Calculation of the daily dose: 1-Trial method: - Begin with 10 units of regular insulin before each meal and examine the response of the patient biochemically and clinically then ↑or ↓ till adjustment. - Calculate the total daily dose required for the patient (the average daily requirement of insulin is about 40 U) then 2/3 of the calculated dose is given as follow: - Give the 2/3 of the calculated dose before breakfast and the 1/3 before dinner (split method) or - Give 1/3 of the dose regular insulin and 2/3 NPH as a single daily dose before breakfast.
2-Fasting blood glucose divided by 5: (e.g.200/5= 40 units).
3-Multiple daily injections= Basal-Bolus regimen : give one injection of long acting insulin (ultralente) at bed time; plus three daily injection of short acting insulin before each meal. The ultralente insulin provides basal level of insulin that controls blood glucose during night and between meals, and the other three injections control postprandial hyperglycemia. Commonly used for patients with Type-1 DM and in pregnant women with diabetes.
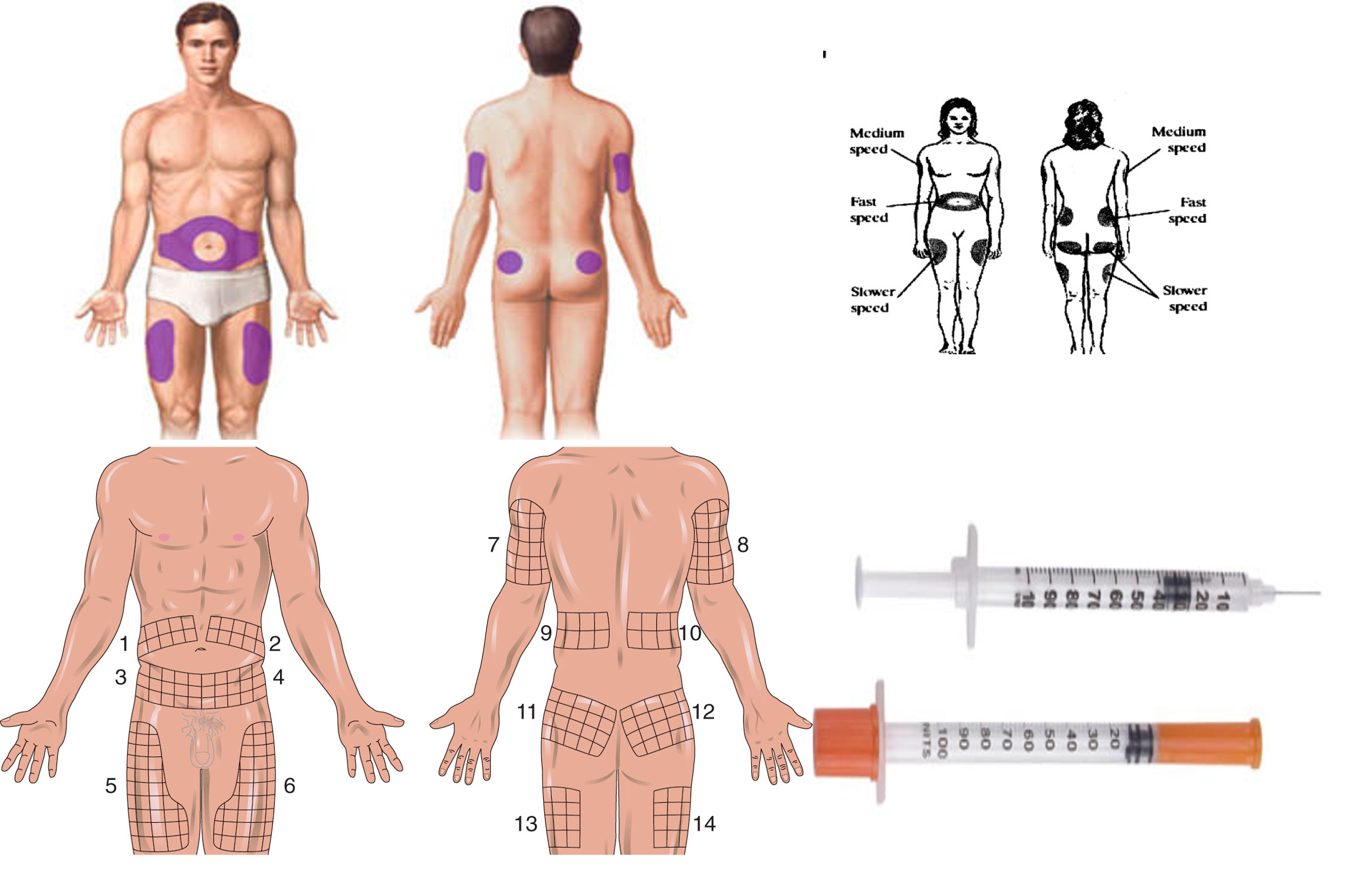
Sites of injection - any site
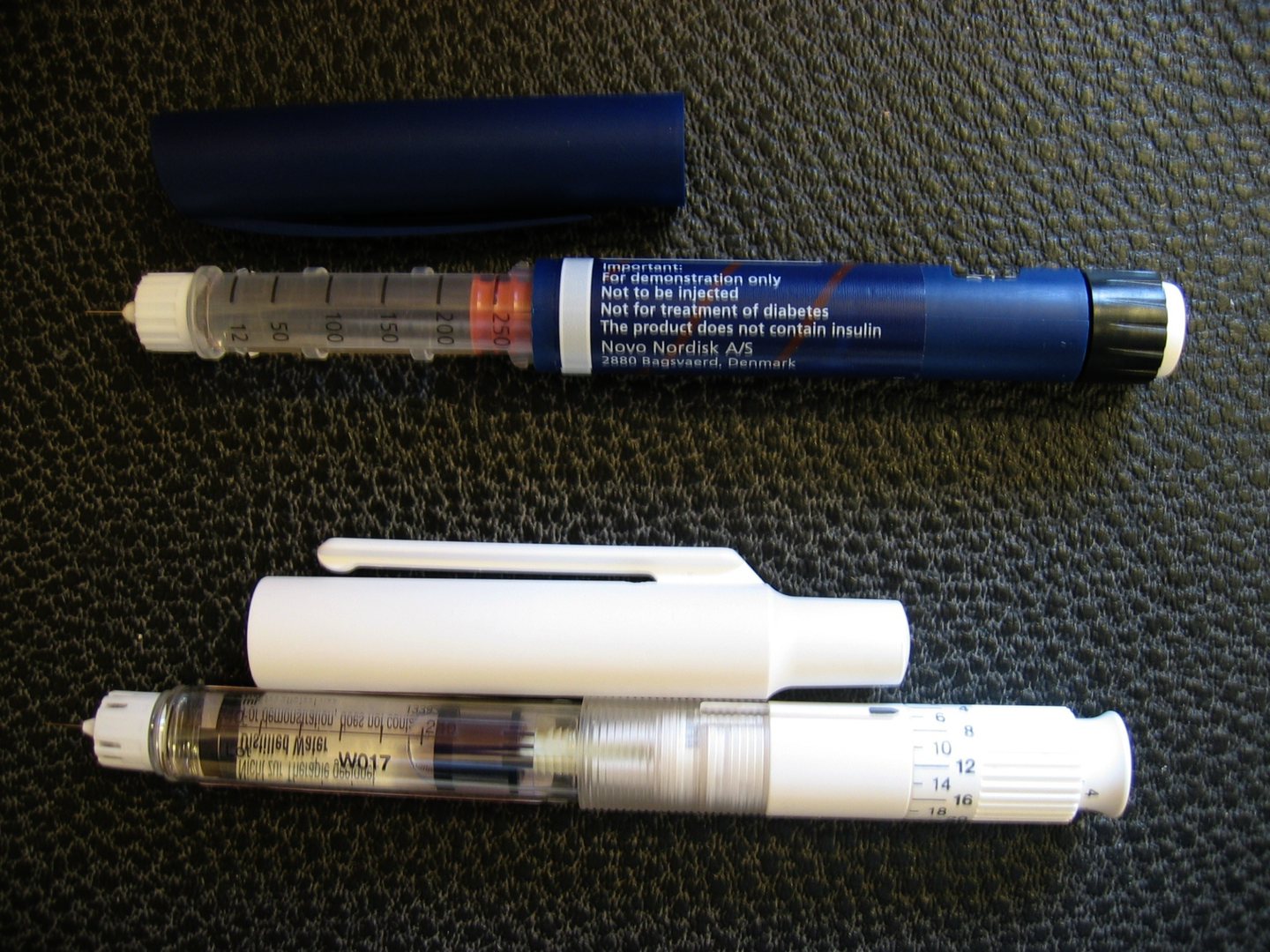
Methods of administration:
- Subcutaneous injection (commonest method).
- Portable pen injector.
- Continuous Insulin Infusion (Artificial pancreas) (insulin pump = artificial pancreas): Not Recommended, high side effects and risks
- See below…………………..
- Intranasal administration:
- Oral………………………