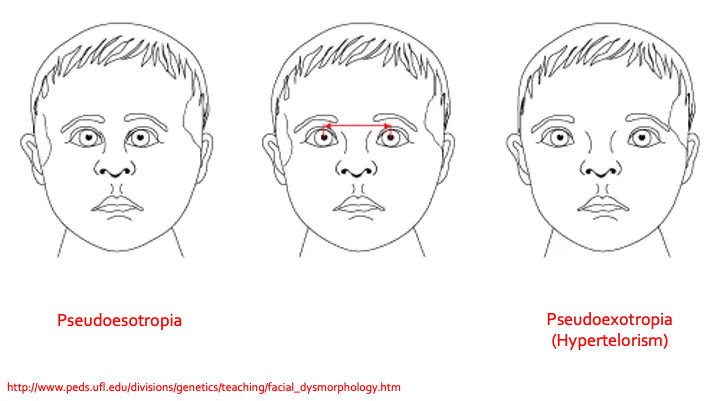
PSEUDOSTRABISMUS (Apparent)
- Pseudoesotropia- in prominent epicanthal folds, high myopia
- Pseudoexotropia- in hypertelorism



Pseudoesotropia
One of the most common reasons that an ophthalmologist is asked to evaluate an infant;
Patient is orthophoric but has an appearance of esotropia
-
Flat, broad nasal bridge
-
Prominent medial epicanthal folds
-
Narrow interpupillary distance
-
Can be differentiated from a true manifest deviation by use of the corneal light reflex and the cover-uncover test; Z
-
When pseudostrabismus has been confirmed, parents can be reassured that the child will outgrow the appearance of esotropia.
-
Look at the corneal light reflex!
 after using torch seeing image of light in center of pupil its normal Z
after using torch seeing image of light in center of pupil its normal Z
Pseudoexotropia (Hypertelorism)
- Appearance of exodeviation when the eyes are in fact the eyes are properly aligned;
- May result from the following:
- Wide interpupillary distance (hypertelorism)