Examination of the Higher Functions
Alertness
Level of Consciousness (GCS)
Orientation Person, Place, Time, & Situation
Appearance & Behavior
Cognitive function
- Attention
- Perception -Illusions = misinterpretations of real external stimuli -Hallucinations = subjective sensory perceptions in the absence of stimuli
Memory
- Immediate, Short-term & long-term
Speech
- Rate & rhythm
- Spontaneity
- Fluency
- Simple vs. complex
Cognitive = content, sequence, logic, coherence, and relevance Attention = ability to focus or concentrate (over time) on one task or activity; “serial 7’s Varies with the patient’s age
1) Speech
Speech is communication between individuals
2) Dysphonia or aphonia
Dysphonia is the impairment or inability to phonate.
3) Dysarthria or anarthria
Dysarthria is the inability to articulate spoken words.
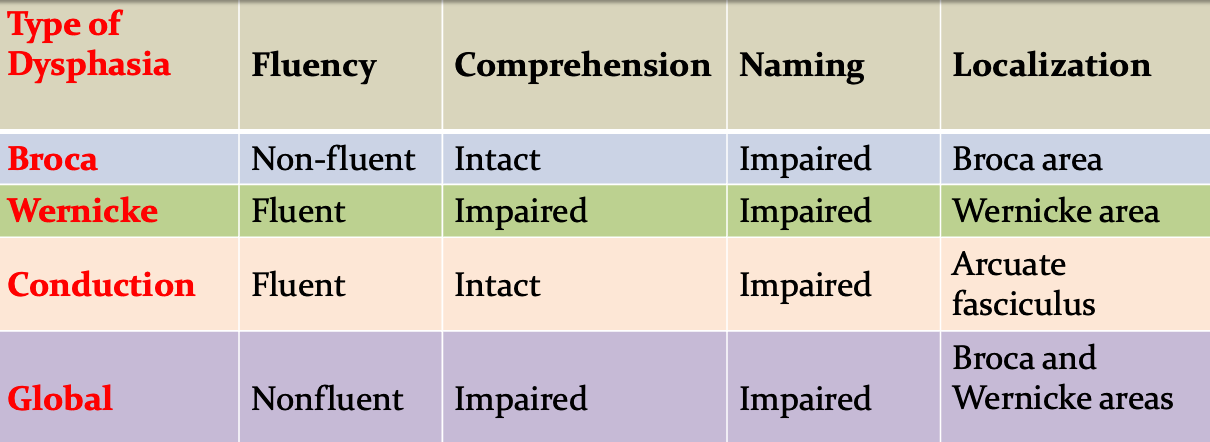
4) Dysphasia or aphasia:
In dysphasia, the ability to process language is impaired
Essential Features of Common Dysphasias
Scores
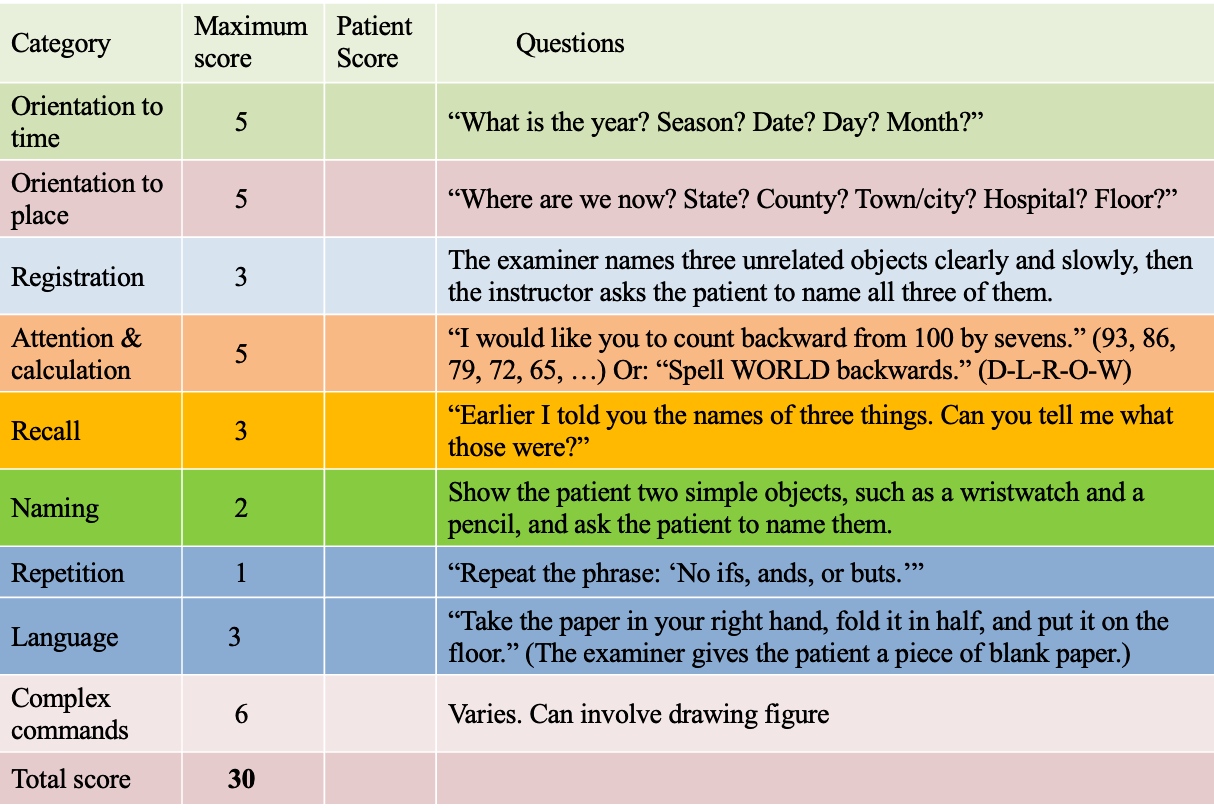
1) Mini–mental state examination
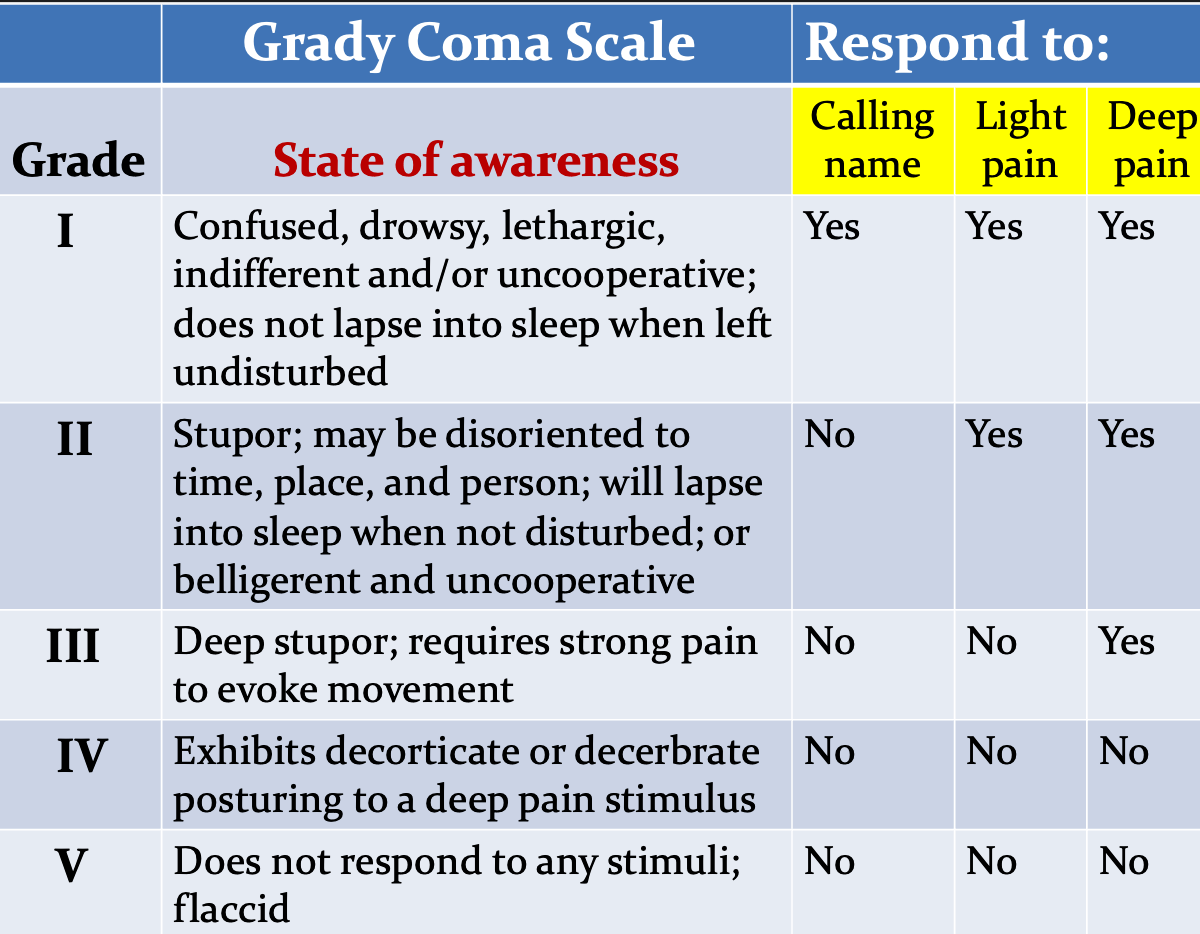
2) Grady Coma Scale
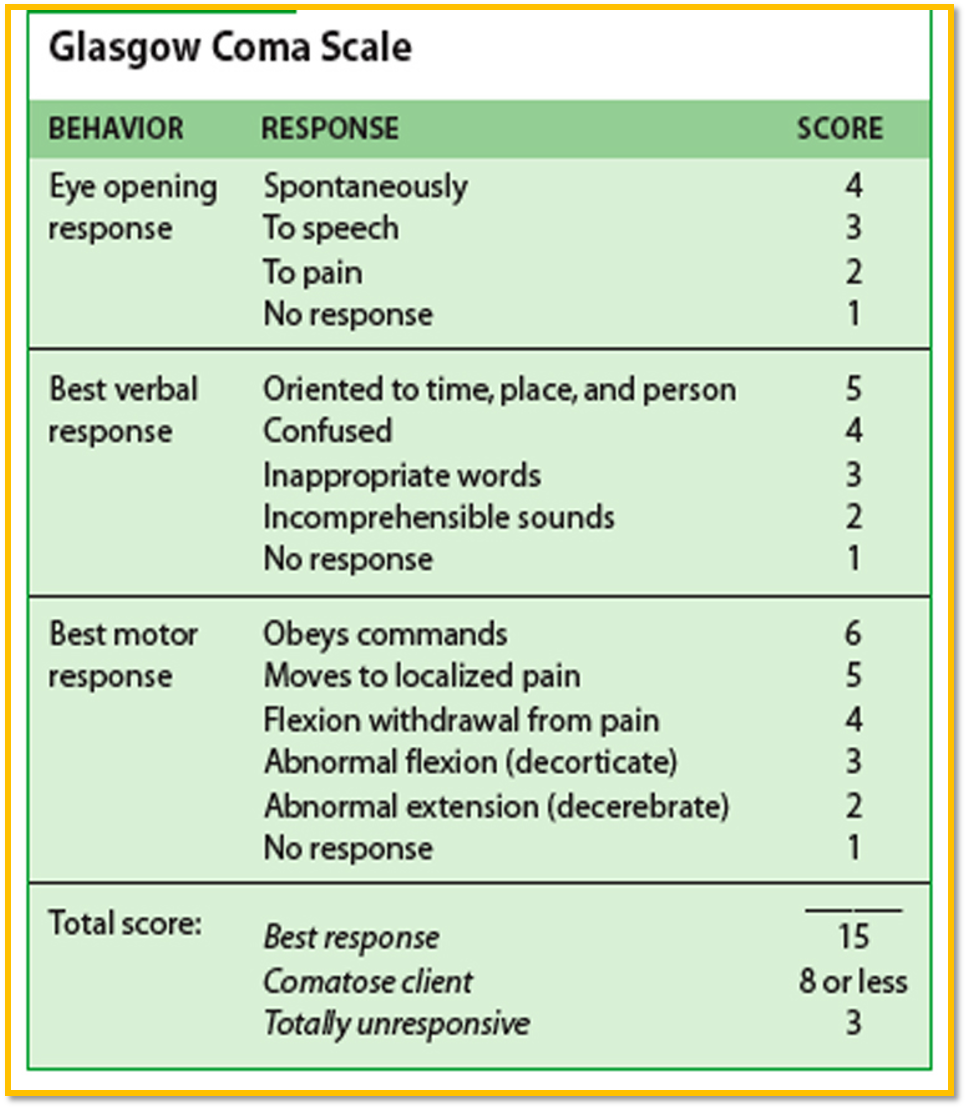
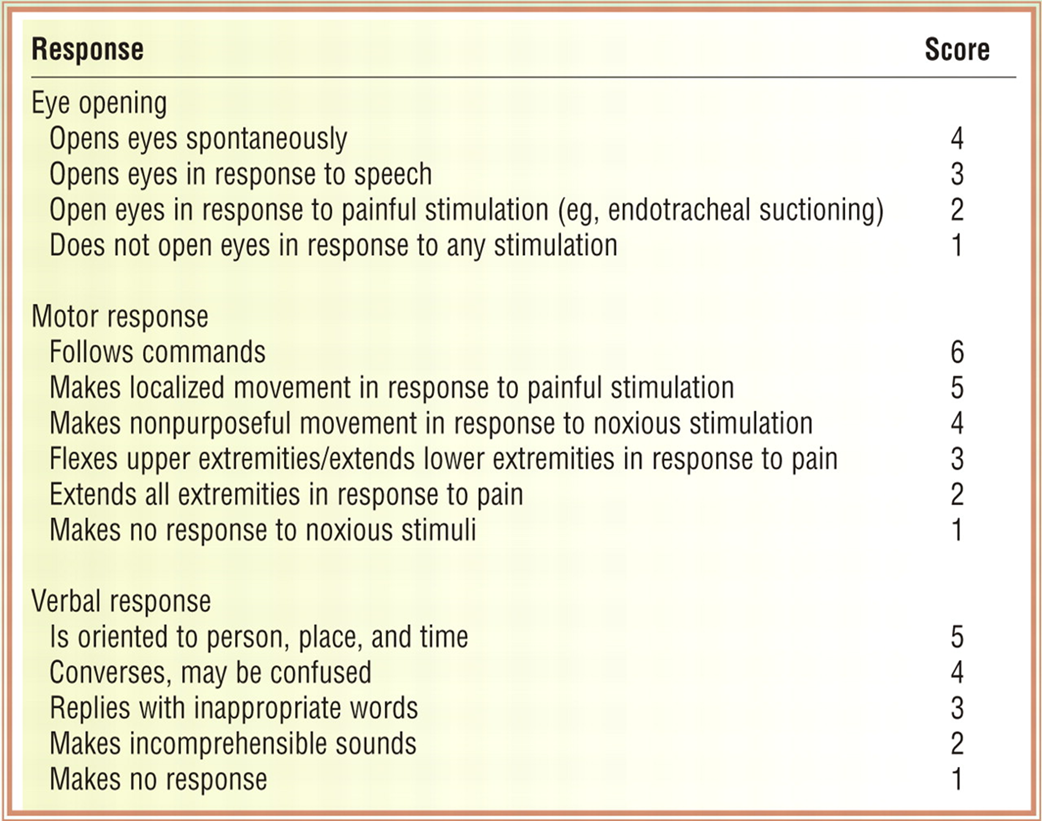
3) Glasgow Coma Scale (GCC) - Assessing LOC
Assesses patient’s neurological condition
Three Categories:
- Eye opening
- Best motor response
- Best verbal response
Score Value range 3 -15
- 3 totally comatose patient - lowest worst possible score
- Score <8 Indicates coma
- 9-12 Moderate altered level of conscious
- 15 fully alert patient - highest possible score