Vascular Malformations CS-OSPE
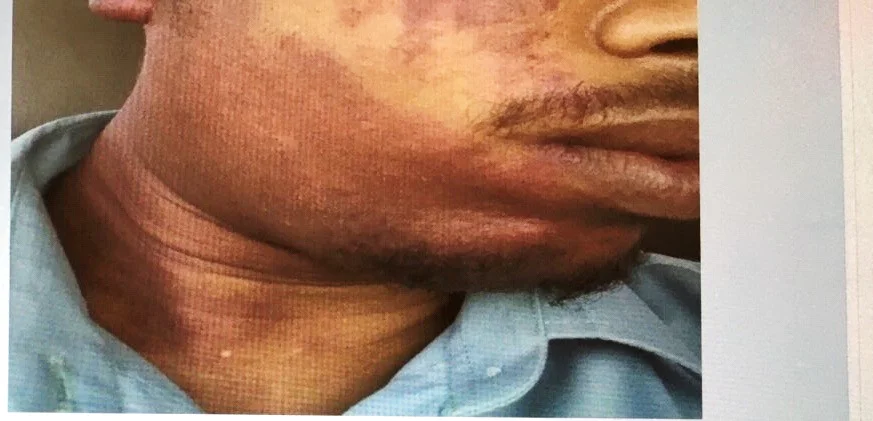
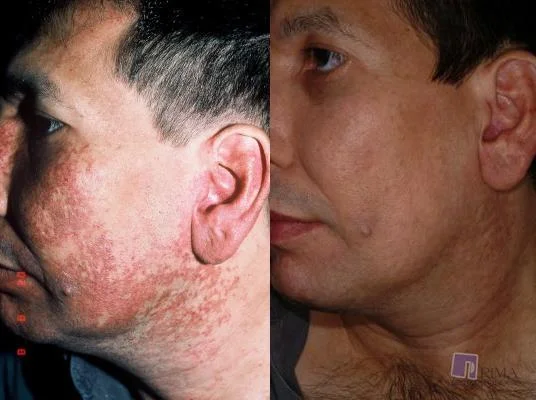
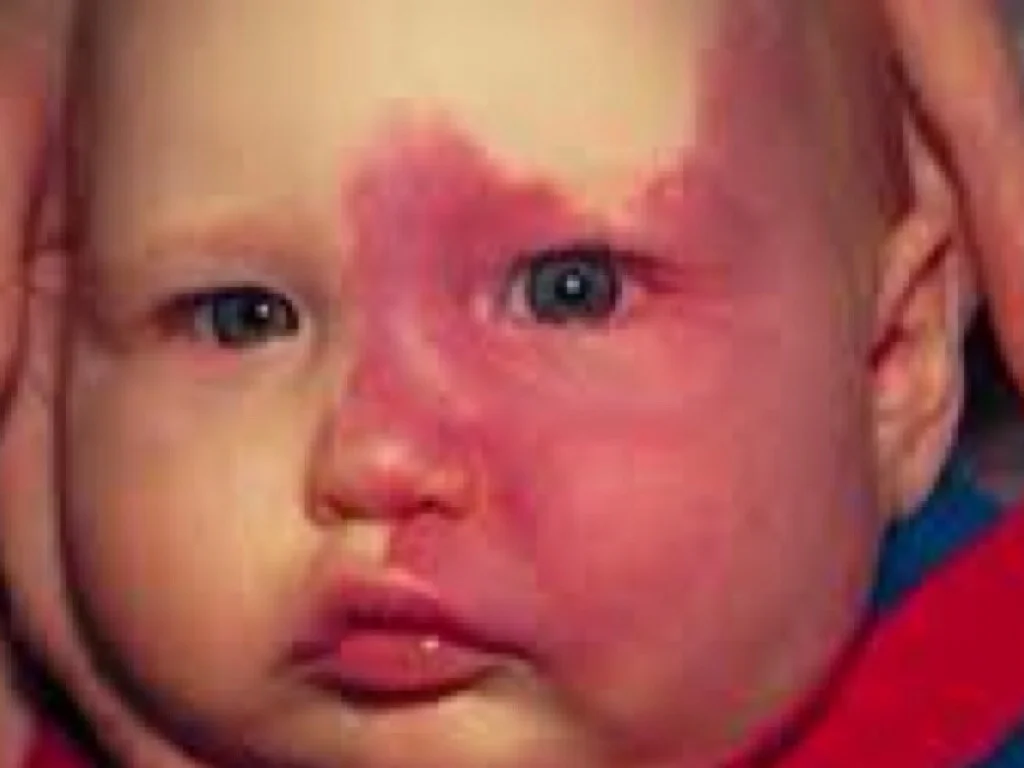
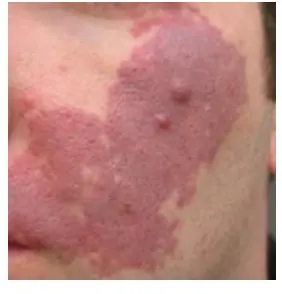
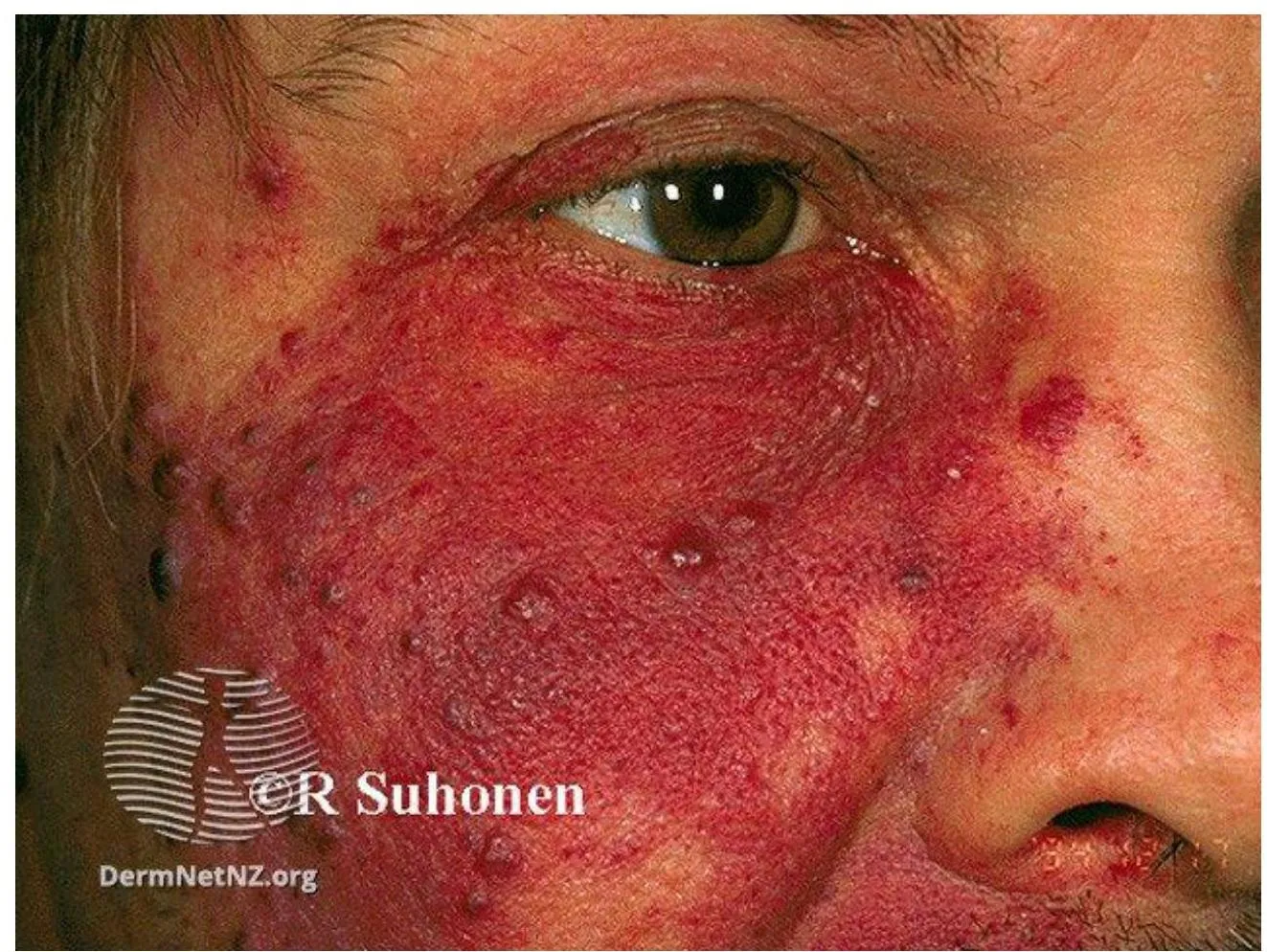
Port Wine Stain (Capillary Malformation)
Case Description/Presentation: baby who presents with a lesion on her face that has been present since birth and has been growing in size. The lesion is not itchy or painful. This is a 30-year-old fellow who presented to your clinic with this skin condition, which appeared since birth. Patient came to the clinic with this lesion since birth.
Diagnosis: Cutaneous or mucosal CM (capillary malformation) (“Port-wine” stain) Port Wine Stain / Portwine
Underlying Cause/Problem: Capillary Capillary malformation (sometimes specified as “with midline cut off”)
Description: Dull red patch on the face involving the upper eyelid, forehead, temple and scalp
Differential Diagnosis:
- Nevus simplex
- Infantile Hemangiomas (IH)
Management/Treatment:
- Full history
- Examination
- Education
- Conservative management – no treatment or use of cosmetics to conceal the lesions
- Pulse dye laser (PDL) – causes intravascular coagulation in abnormal vasculature without damaging surrounding structures
Prognosis/Progression: May develop papules, skin hypertrophy, and nodules over time.
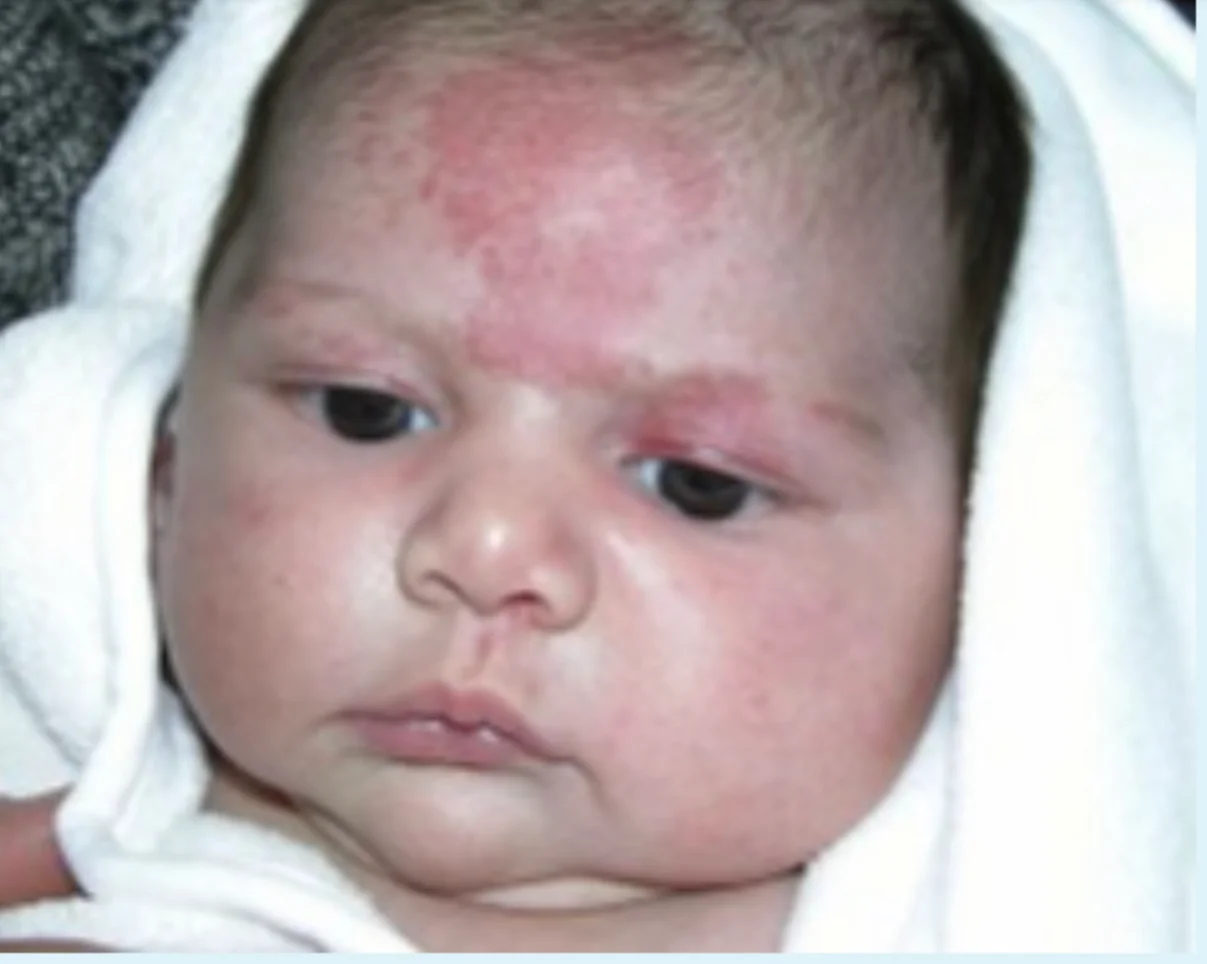
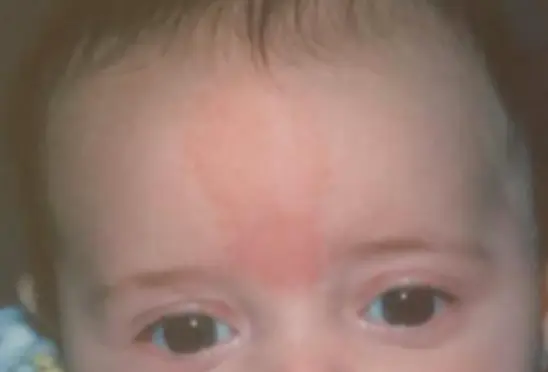
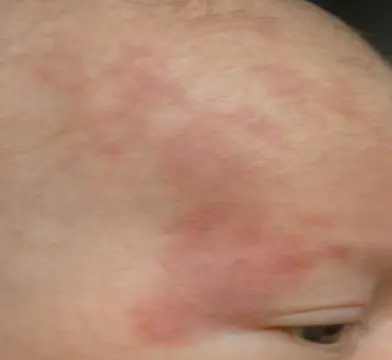
Nevus Simplex / Salmon patch
Look at this birthmark and answer the following questions.
-
What is the most likely diagnosis and what is the underlying cause?
- Diagnosis: Nevus Simplex
- Underlying Cause: Capillary malformation
- Describe: Flat, pink to bright red patches typically on the midline forehead
-
What is the treatment of choice and what is the prognosis?
- Treatment: facial lesions fade within 1-2 years making treatment unnecessary.
- Prognosis: Good. 90-95% of lesions resolve/fade after 1-2 years.
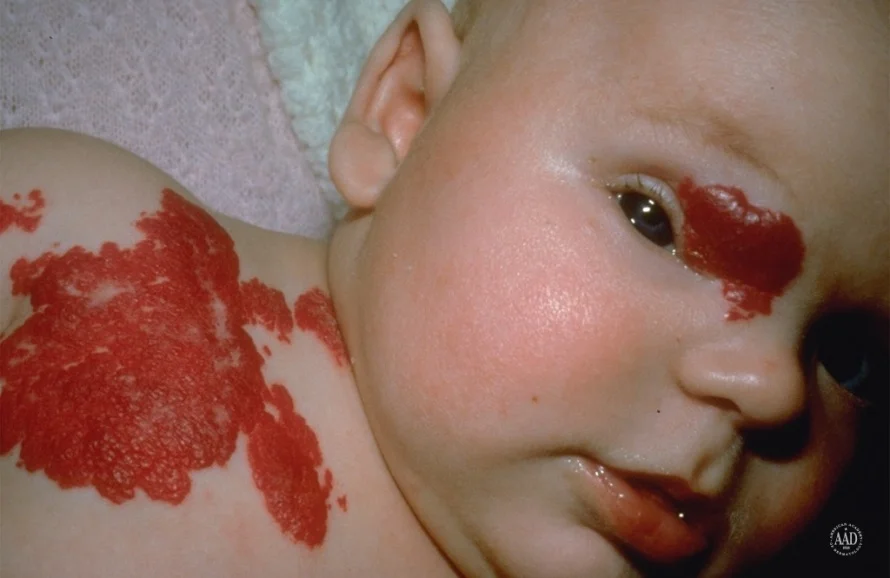
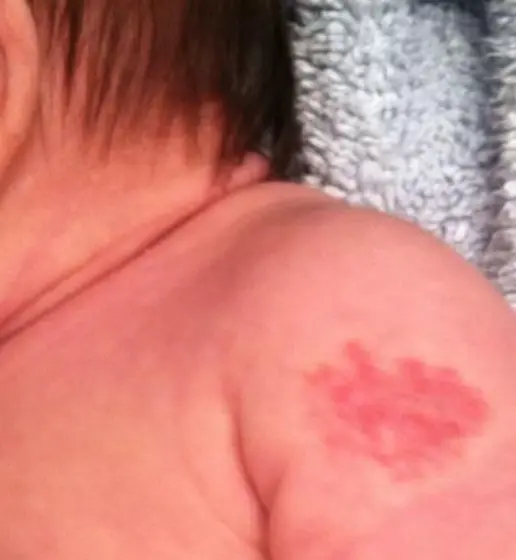
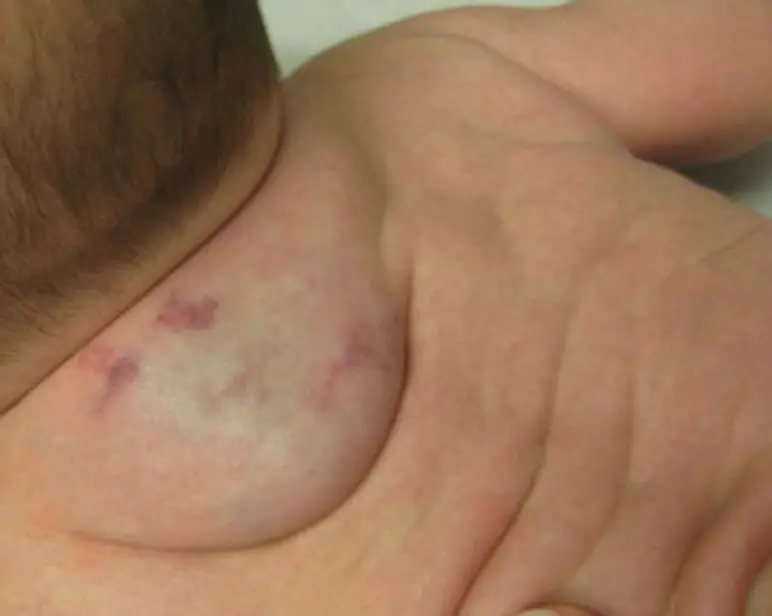
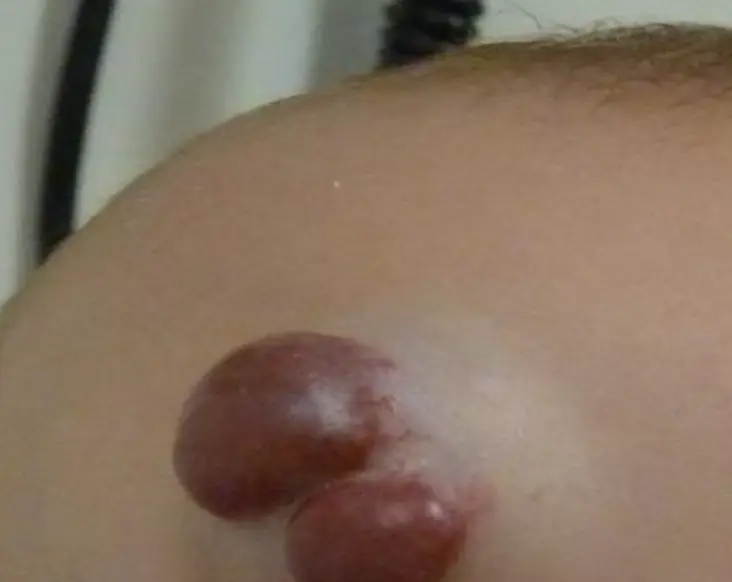
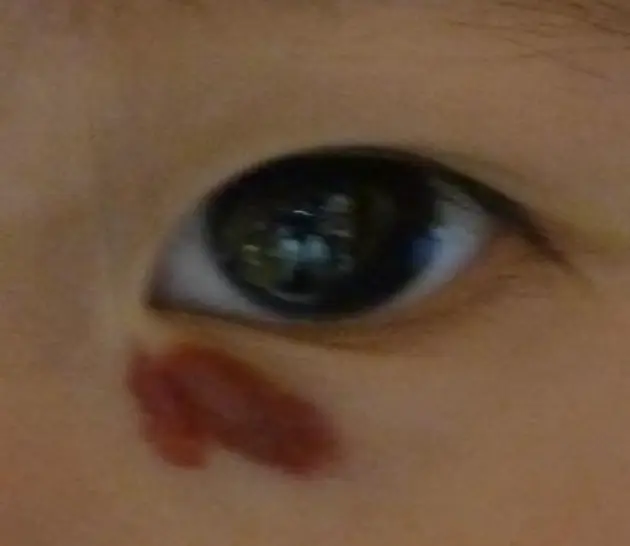
Infantile Hemangioma
This is a six-month-year baby boy who presented to the dermatological clinic with this condition.
What is the diagnosis?
- Infantile hemangioma (IH) (types: Segmental regional, Superficial, Deep, Mixed, Localized).
What are the typical clinical presentations?
- Bruise-like patch, area of vasoconstriction/pallor or telangiectasias.
- Bright red.
- Minimally elevated.
- Large with bluish color.
What are the recommended treatment options?
- Topical therapies:
- Pulsed dye laser: for ulceration or residual lesion.
- Topical corticosteroid: if on the trunk, medium potency or low for 2-3 months.
- Topical beta blocker.
- Interalesional corticosteroid.
- Systemic therapies:
- Immunosuppressive anti-plastic therapies: interferon, vincristine.
- Oral propranolol.
- Systemic corticosteroid.