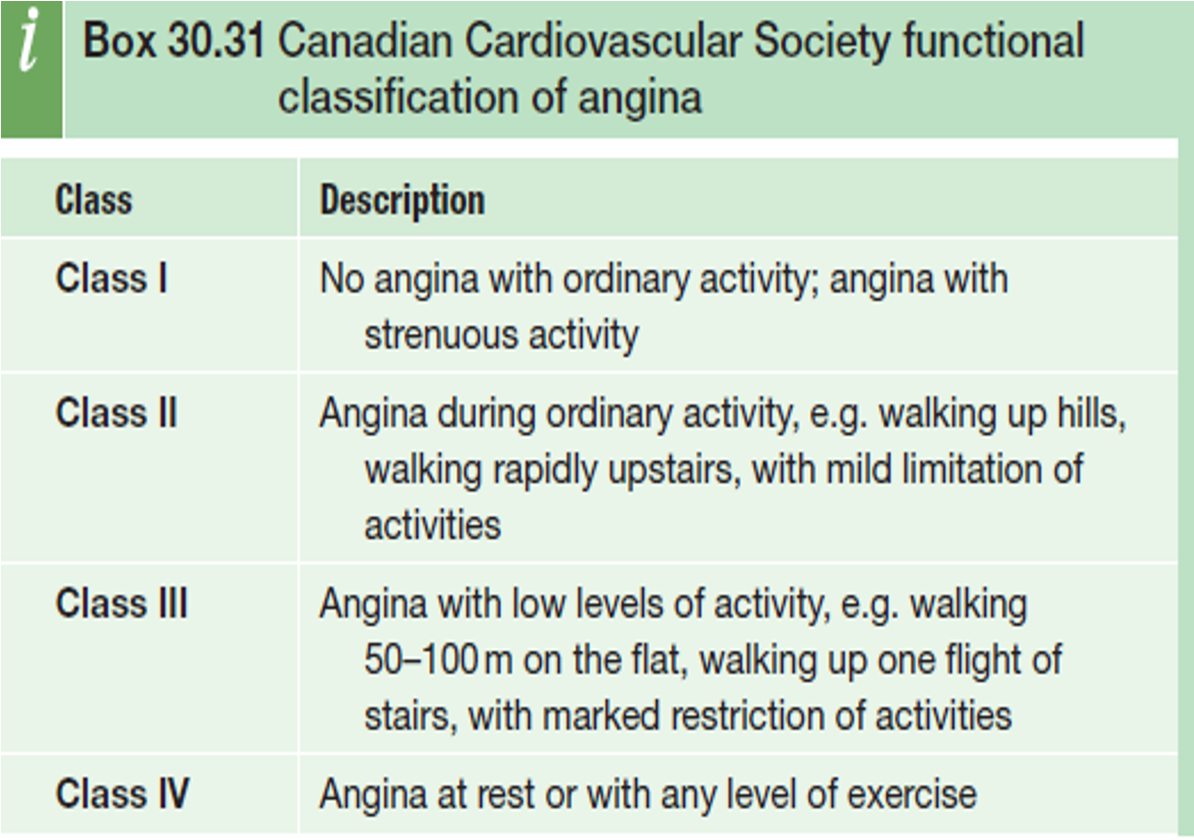
Classification of Angina
 Classical angina or typical angina characterized by chest pain:
Classical angina or typical angina characterized by chest pain:
- • ‘Heavy’, ‘tight’ or ‘gripping’ central or retrosternal radiate to jaw and/or arms.
- • occurs with exercise or emotional stress.
- • Pain eases rapidly with rest or with GTN.
Atypical angina: 2 out of 3
Non-angina chest pain: 1 out of 3 of
spasm =/ bb
Intracoronary acetylcholine may cause coronary spasm. Whilst they have a good prognosis, they are often highly symptomatic and can be difficult to treat. In women with
Investigations (Stable Angina)
- ECG
- 12 lead ECG: normal between attacks
- During attack: transient ST-depression, T-wave inversion.
- 12 lead ECG: normal between attacks
- Cardiac enzymes(Troponin T & I): Normal
- Exercise (Stress) ECG – ST- depression of 2 mm is taken as positive test
- CT – coronary angiography (accurate - noninvasive)
- Non-invasive functional test; coronary calcium index
- Cardiac Catheterization
Need to confirm or exclude CAD
- Medical therapy fails to relieve anginal symptoms
- History and noninvasive testing suggest high-risk coronary anatomy
Stress ECG
Evaluation of patients with known or suspected coronary heart disease (CHD). Diagnosis & risk assessment and prognosis.
Types
- Exercise electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Exercise with imaging
- Pharmacologic stress testing with imaging: physical ability to perform exercise.
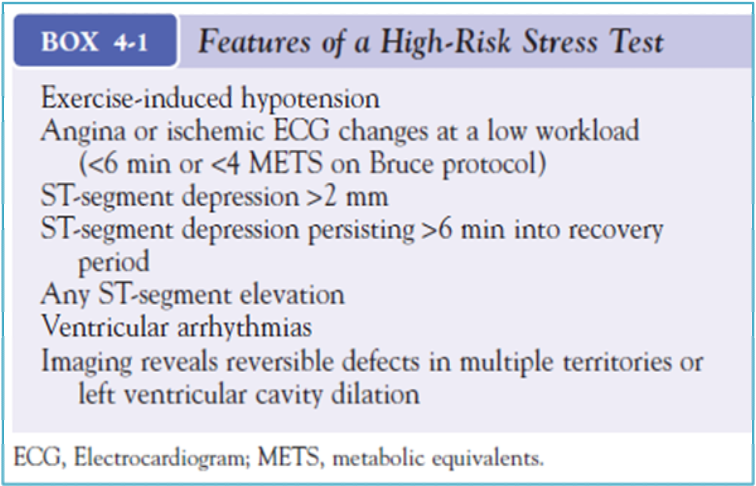
Investigations
- 64-slice CTCA; Chest pain with ST changes or Q waves ⇒
- non-invasive functional tests; SPECT, stress echocardiography, stress MRI). ⇒
- Alternative diagnosis/ tests
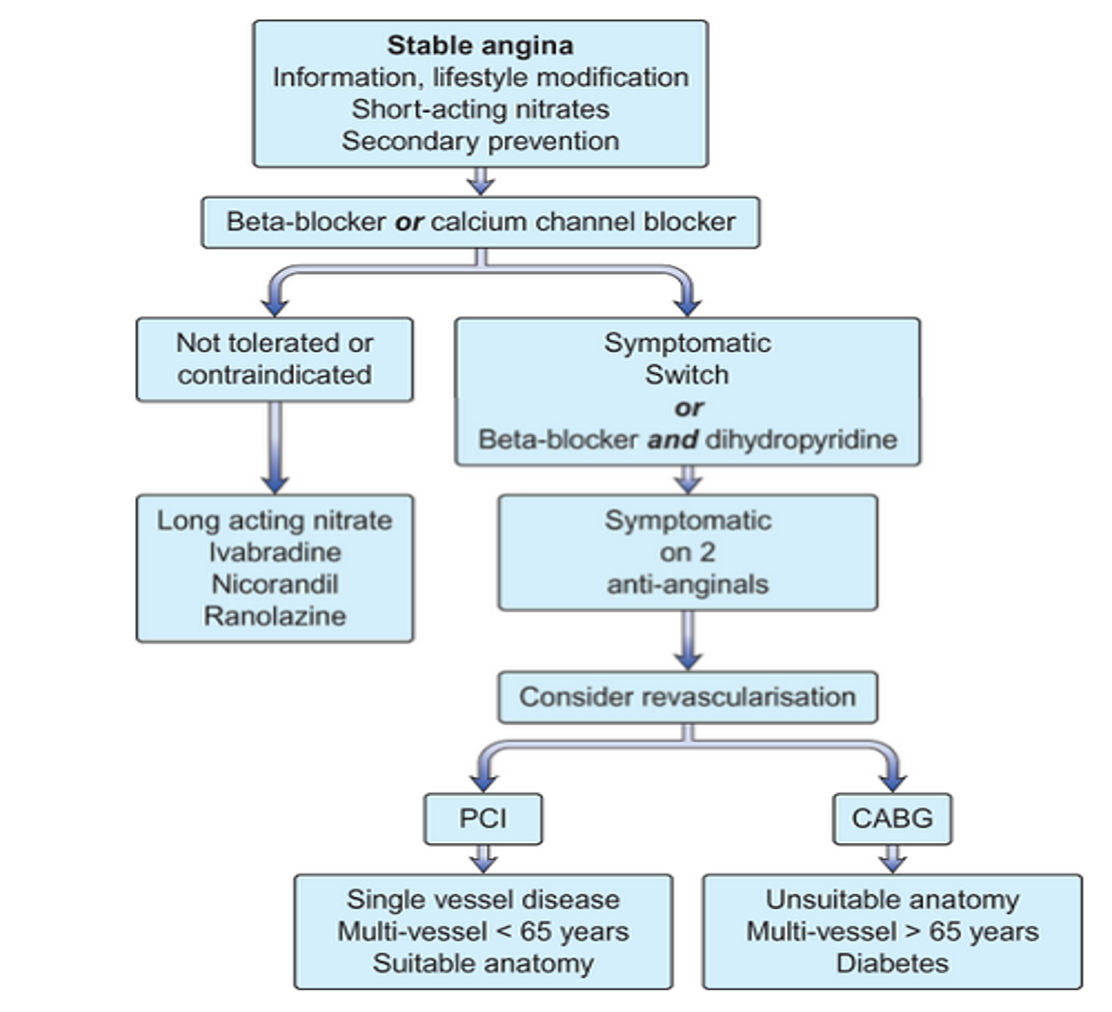
Algorithm for Management of Patient’s with Stable Angina