Case 1
 A 50-year-old patient has chronic renal failure with end-stage renal disease (ESRD). Now started on dialysis. After 2 dialysis sessions, he developed confusion and mental status changes.
A 50-year-old patient has chronic renal failure with end-stage renal disease (ESRD). Now started on dialysis. After 2 dialysis sessions, he developed confusion and mental status changes.
-
What is the name of this CNS complication which he has developed? Z
- Dialysis Disequilibrium syndrome
-
Mention 1 more complication of hemodialysis?
- Hypotension
- Infection/Thrombosis of the fistula
-
Mention 2 complications of peritoneal dialysis?
- Hyperglycemia and Peritonitis
-
Mention 2 Absolute indications for dialysis?
- Uremic encephalopathy
- Uremic pericarditis
-
Once a fistula is made, after how much time is it ready to be used?
- After few months
-
At what GFR should you start dialysis in a renal failure patient, if he also has diabetes mellitus?
- When GFR reaches below 15
Case 2
 A 20 year old male has a history of “recurrent” urinary tract infection. His urine looks turbid as shown below, and urine analysis shows UTI.
A 20 year old male has a history of “recurrent” urinary tract infection. His urine looks turbid as shown below, and urine analysis shows UTI.
-
Name 3 features in a Urine analysis report that indicate infection?
- +nitrites, +leukocyte esterase, WBC more than 8-10/high power field
-
Name 2 bacteria which commonly cause UTI?
- E.coli and klebsiella
-
Which is the drug of first choice to treat this patient’s UTI? Z
- Bactrim, Ciprofloxacin
-
For how many days will you treat this patient?
- 7 days for man in this case - 3 days for woman 7 if preg
-
Name any 1 investigation which you will do in this patient as a work up for recurrent UTI?
- Urine culture
-
Urine culture should be done in recurrent UTI
Case 3
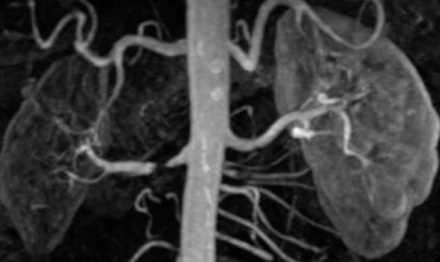
- If it comes to 20y/o man, what is the cause? Z Secondary HTN
- Name 2 etiologies of condition: Z Atherosclerosis, Fibromuscular dysplasia
- Pathology in the image: Renal Artery Stenosis
- Treatment option: Angioplasty + or - stent
Case 4 Z
A patient with chronic renal failure. His blood tests show the following results:
- Hb: 9g/dl.
- Creatinine: 4 mg/dl
- K (potassium): 6 meq/L
- Serum Calcium: low
- ABG: pH 7.28/ pCO2 28mmHg/ HCO3 18mEq/L
-
Name the 2 most common causes of chronic renal failure worldwide?
HTN and DM -
Name any 2 treatments which can be used for hyperkalemia? Z Insulin/glucose, K binding resins (Kay-exalate), calcium - gluconate
-
What is the cause of low serum calcium in chronic renal failure?
Inactivation of vit D - low vit D -
What acid base abnormality is seen in chronic renal failure?
Metabolic acidosis -
Name 2 treatments used to treat anemia of chronic renal failure?
Iron (Fe) and erythropoietin -
Give 2 indications for dialysis in renal failure?
- **Uremic pericarditis
- uremic encephalitis
- Hyperkalemia
- Pericarditis?
-
Name any 2 complications of CRF Uremia, HTN, Osteoprosis
-
How you’re going to treat his hyperkalemia?
- Calcium gluconate
- Oral chelating agent
- Dialysis
Case 6 Z
A 20 year old man known case of sickle cell disease developed nocturia and swollen ankles.
The following blood results were obtained:
-
Plasma urea 8.0 mmol/l
-
Sodium 145 mmol/l
-
Potassium 4.0 mmol/l
-
Bicarbonate 22 mmol/l
-
Phosphate 0.9 mmol/l
-
Serum Albumin 21 g/l
-
24 hour urinary protein 10 g
-
Early morning urine osmolality 310 mOsm/kg
-
Name 2 laboratory abnormalities? a. low serum albumin (hypoalbuminemia) b. urine protein is high (hyperprotienuria)
-
What is the clinical diagnosis? a. nephrotic syndrome
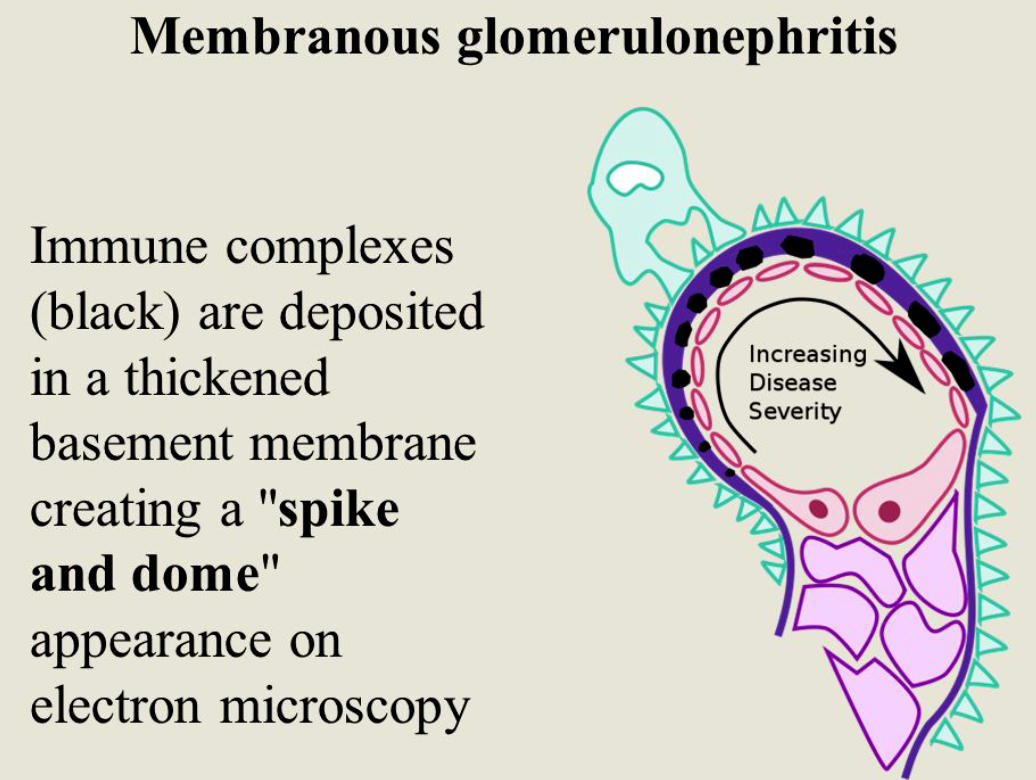
M.N. (spike pattern)
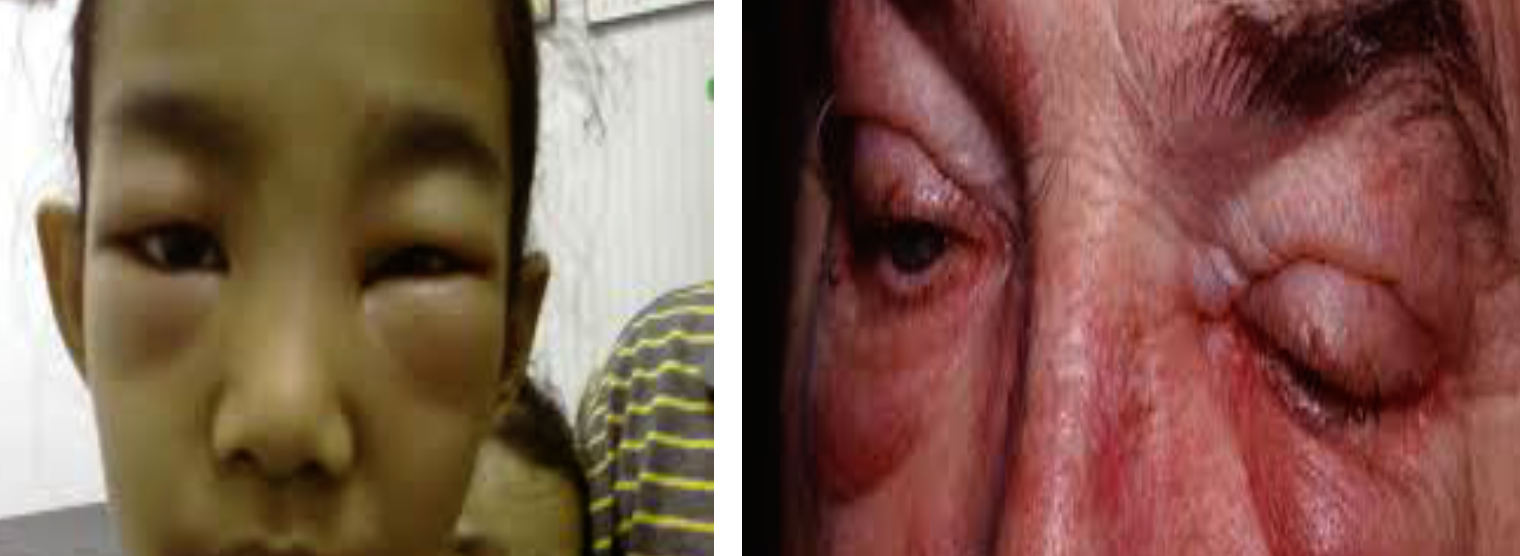
Peri-Orbital Edema in Nephrotic