Common Neck Swellings
Dr. Shaheer
Presentations
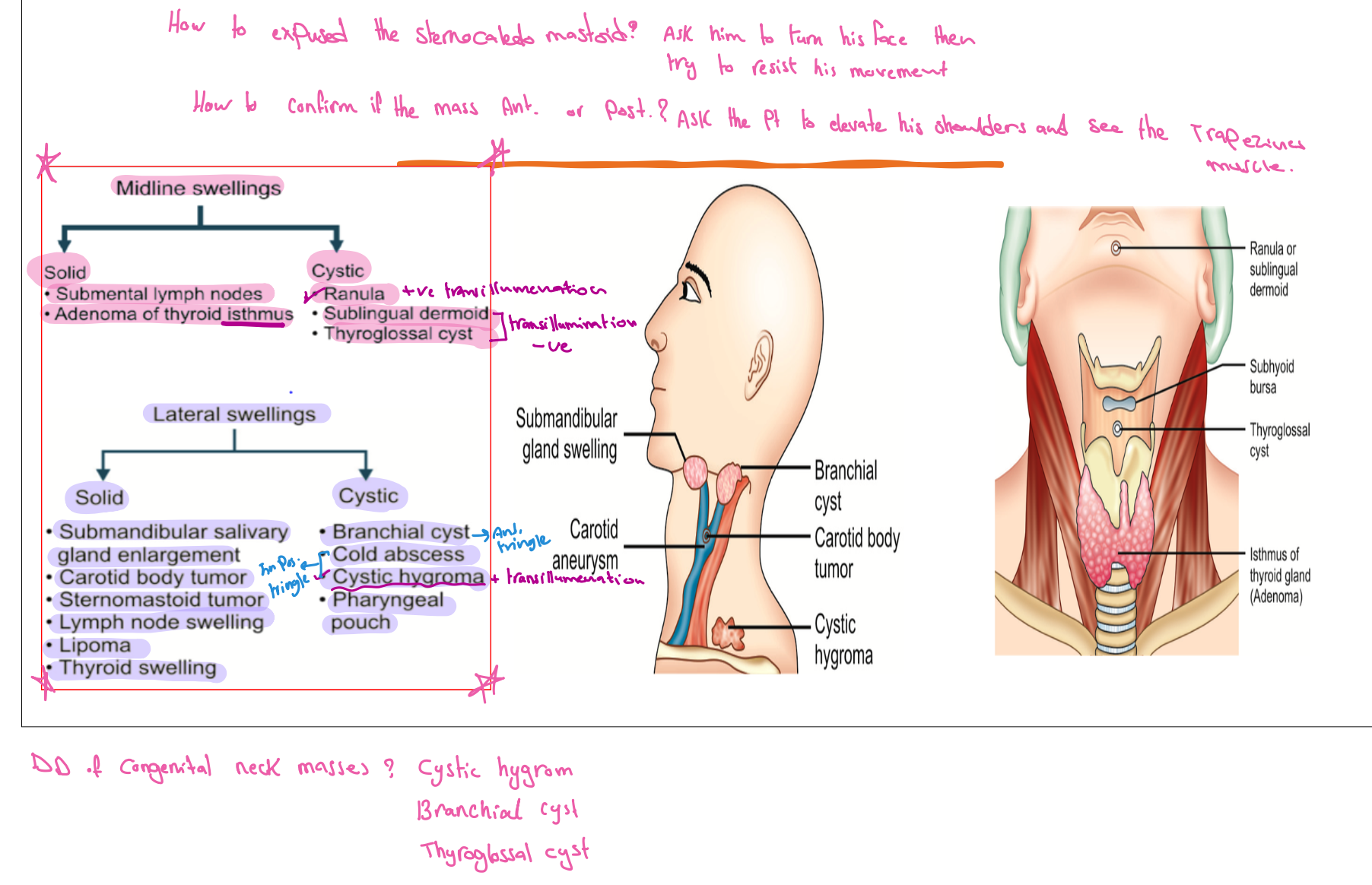
Midline swelling
Solid
- Submental lymph nodes
- Adenoma of thyroid isthmus
- Calcular disease (Sialolithiasis)
Cystic
Lateral Swellings
Solid
- Carotid Body Tumour
- Sternomastoid tumor
- Cervical Lymphadenopathy
- Salivary gland swellings - Viral
- Bacterial Infection
- Lipoma
- Thyroid swelling
Cystic
Investigations (General for neck swellings) :
- CBC, Serology, Tuberculin
- Thyroid function (TSH, T3, T4, Antibody) (very important)
- CXR, U/S, CT scan, MRI, Angio.
- FNAC
- Laryngoscopy, Endoscopy (preop, to check if both vocal cords are functioning or not)
- Open biopsy
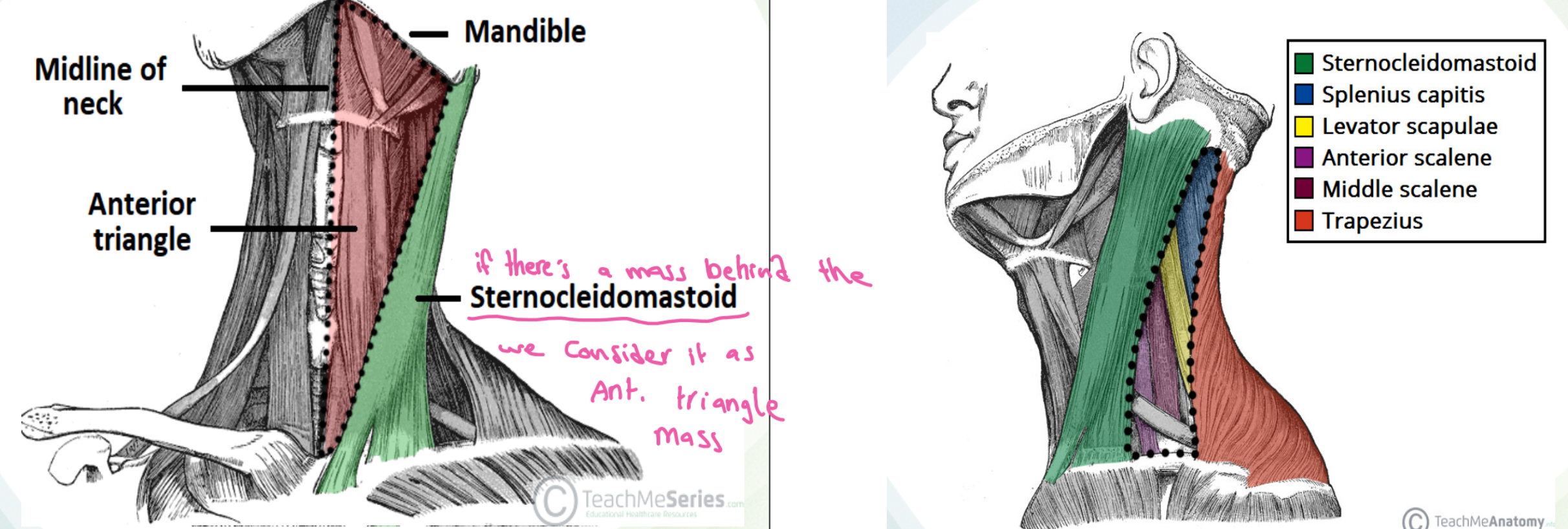
Anatomy:
The anterior triangle is situated at the front of the neck.
- It is bounded:
- Superiorly
- Inferior border of the mandible (jawbone).
- Laterally
- Anterior border of the sternocleidomastoid.
- Medially
- Sagittal line down the midline of the neck from the chin to the manubrium.
- Superiorly
The posterior triangle is situated posterior to SCM
- Its boundaries are as follows:
- Anterior
- Posterior border of the SCM.
- Posterior
- Anterior border of the trapezius muscle.
- Inferior
- Middle 1/3 of the clavicle.
- Anterior
-
Which triangle of the neck is involved
-
Does it move with swallowing? This indicates it is deep to the pretracheal fascia and likely to be thyroid. (thyroid, lymph nodes pretracheal fascia)
-
Does it move with protrusion of the tongue? This applies to upper anterior neck lumps, and the physical sign refers to thyroglossal cysts.
Objectives
- Triangles of the neck, & lymph node distribution
- Clinical presentations, investigation, & management of common neck swellings
- Differentiate the presenting features, use of different investigations and management of neck swellings