Pediatrics-2
INTUSSUSCEPTION
DR. ELFADIL EISA IDRIS SULIMAN
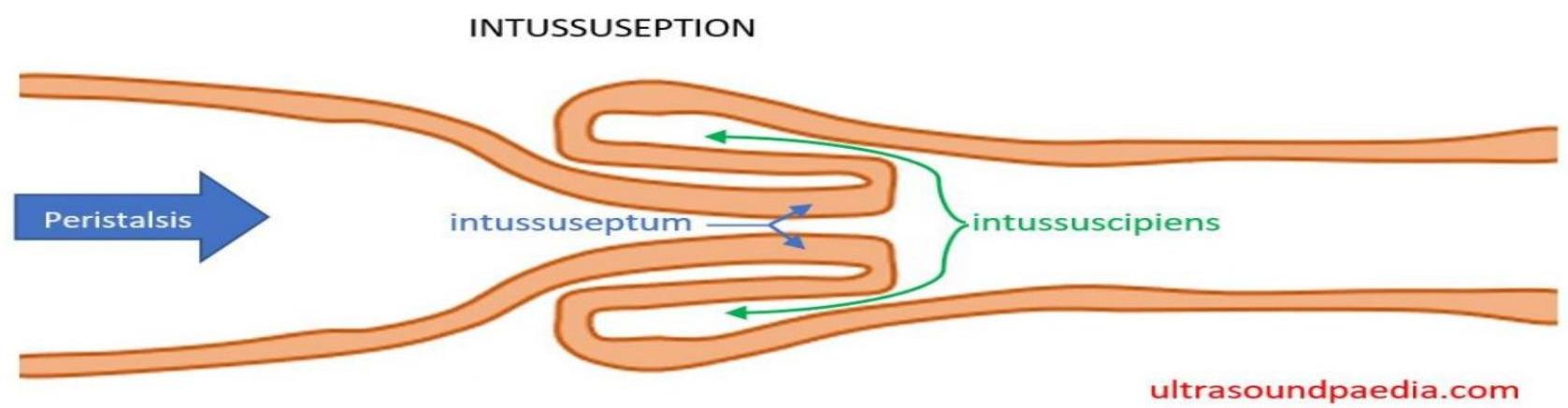
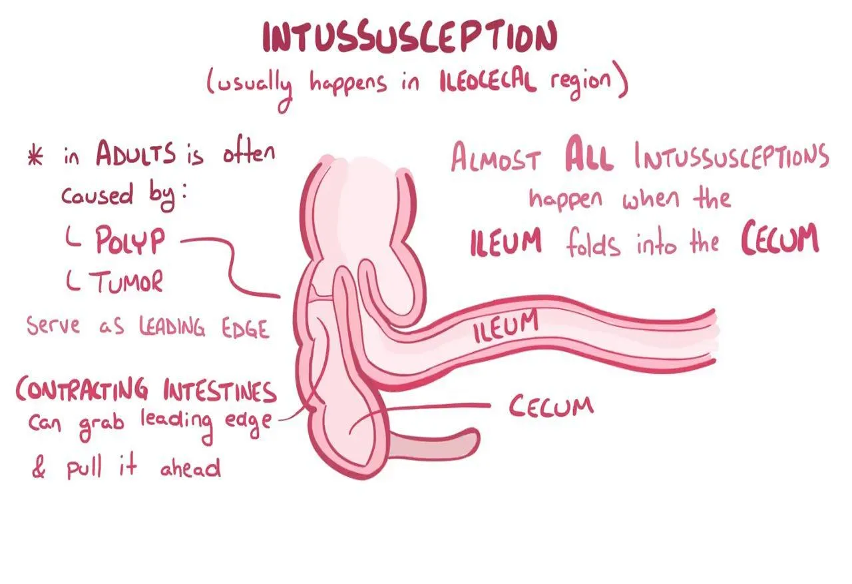
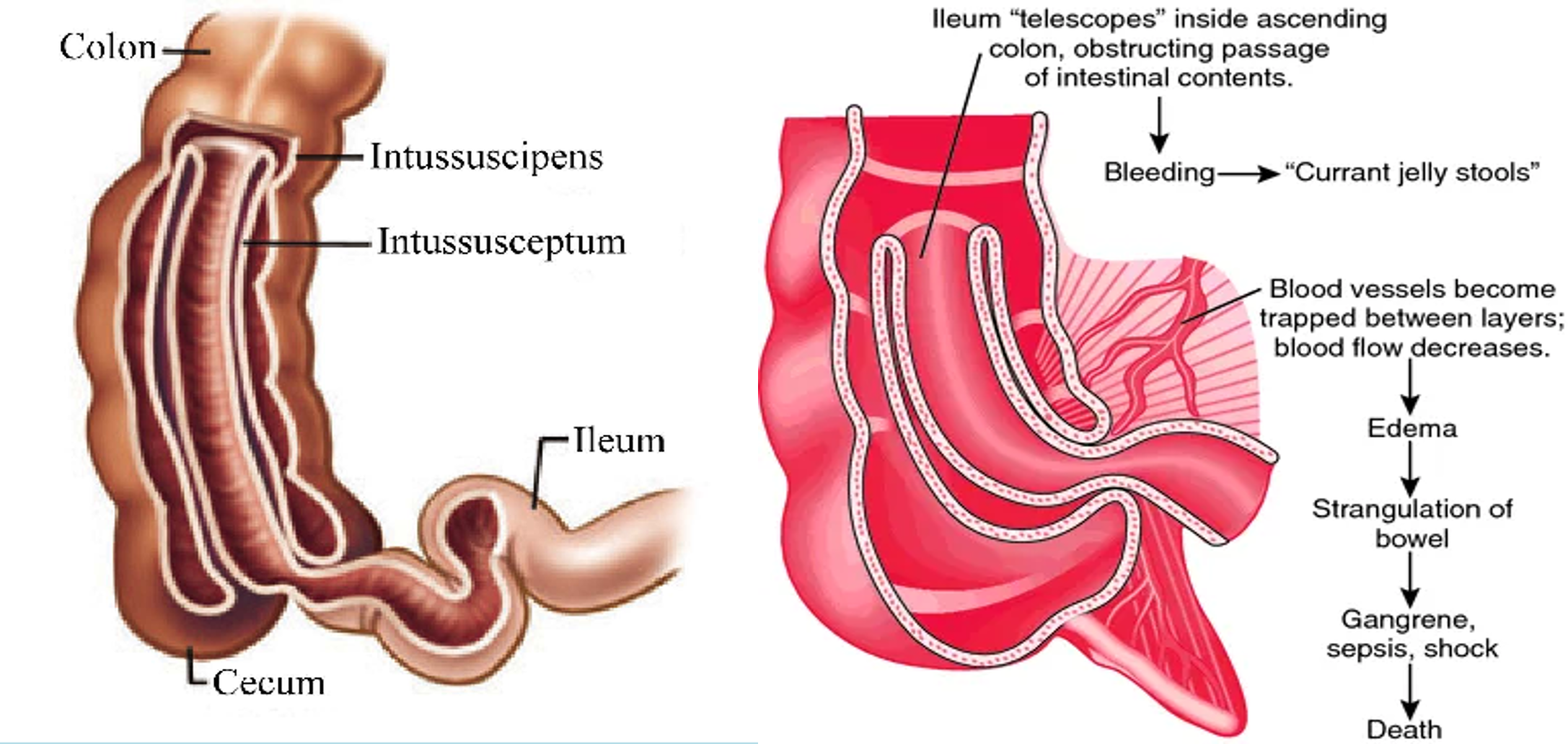
It occurs when a part of the a alimentary tract is telescoped into an adjacent segment.
- It is the most common cause of intestinal obstruction between 5 month and 3 year of age.
- Male affected more than female 3:1.
Etiology and epidemiology
- 90% of cases are idiopathic.
- It is common during winter due to increase incidence of viral infection, e.g gastroenteritis, otitis media, Henoch-Schonlein purpura and other upper respiratory tract infections.
- Very rarely, it can follow Rota virus vaccine especially after the first dose by 3 weeks.
- Gastrointestinal infection results in swollen peyer’s patches in the terminal ilium → intussusception.
- Prominent lymph tissues lead to mucosal prolapse of the ileum into the colon causing an intussusception.
- Recognizable leading points of the intussusception include Meckel’s diverticulum, intestinal polyp, hemangioma and lymphoma.
- Also diseases that can cause chronic diarrheas e.g: cystic fibrosis, celiac disease and crohn’s disease, can cause intussusception.
Pathology
- Is most often ileocolic, less commonly colocolic.
- The upper portion of the bowel, the intussusceptum, into the lower, the intussuscipiens.
- Constriction of the mesentery, obstructs venues return, leading to edema, bleeding (some times necrosis and perforation) from the mucus of the intussusception and causing bloody stool with mucus (Current Jelly stool).
Clinical manifestation
- Age less than 3 year.
- More common in males.
- Sudden onset of paroxysmal colicky pain in a previously well child.
- During pain there is straining effort with legs and knees flexed and loud cries.
- Patient is normal between the attack (intermittent abdominal pain).
- Vomiting start as non bilious then becomes bilious.
- Passage of red-current Jelly stool.
- Palpation reveals slightly tender sausage- shaped mass with increase in size and firmness during a paroxysm of pain, and is usually in the right upper abdomen.
Diagnosis
- From history and examination.
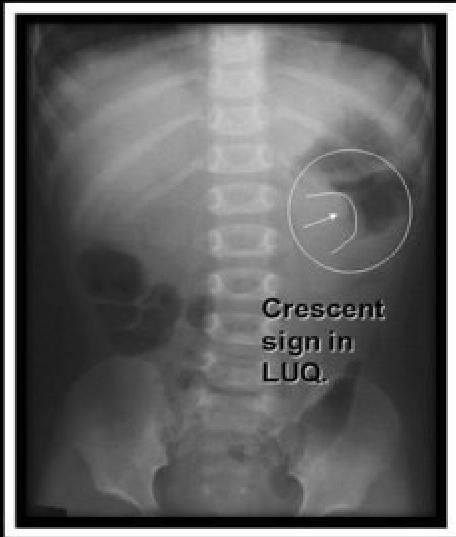
- X-ray → density in the area of the intussusception → crescent sign.
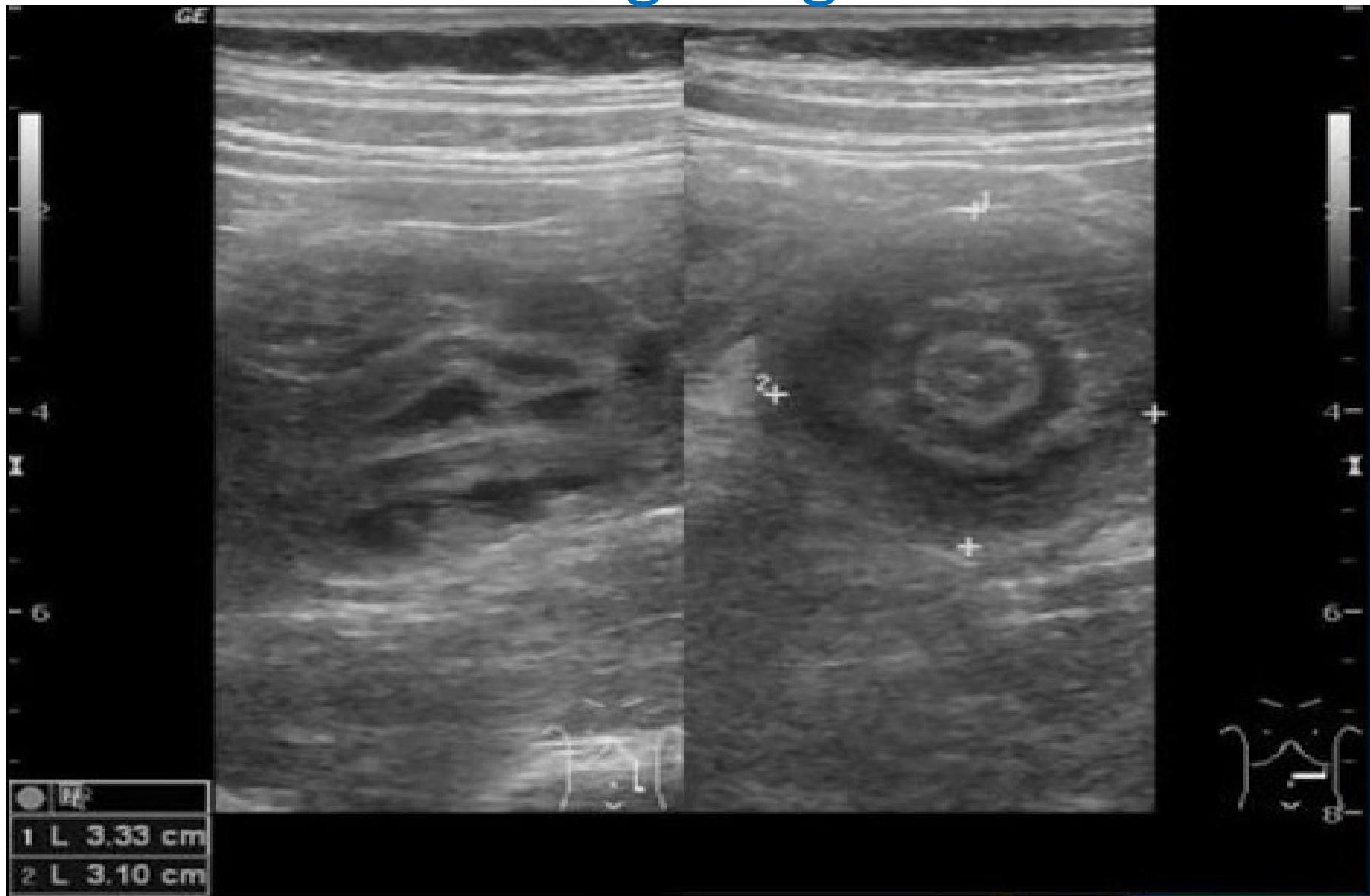
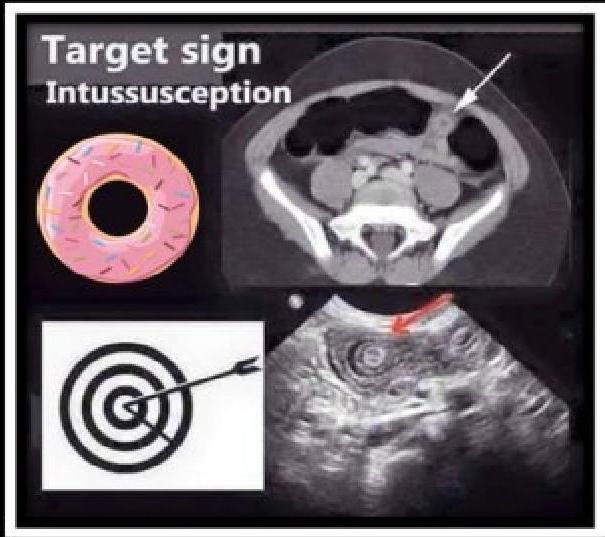
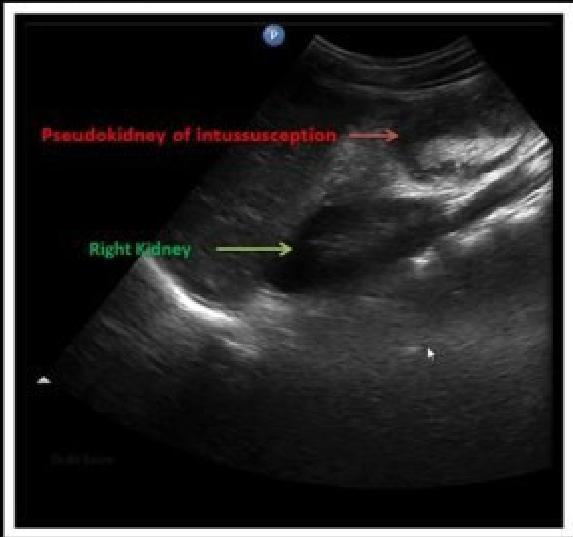
- Ultrasound is the method of choice and diagnostic → target sign.
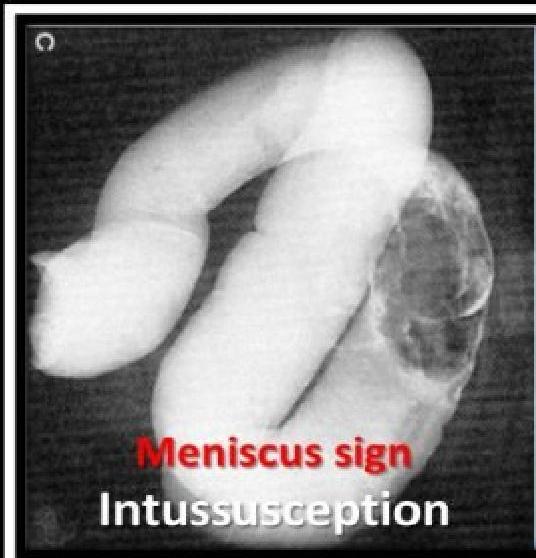
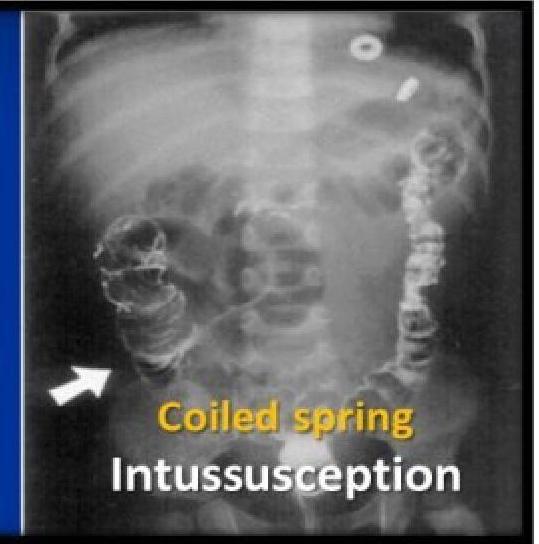
- Contrast enema: air hydrostatic (saline) and water soluble contrast enema → diagnostic and therapeutic. It demonstrates a filling defect in the contrast media (coiled-spring sign) and claw sign.
Target sign
TOPIC SUMMARY
Intussusception
Pediatric In Trauma
Radiological findings
X-ray
- ☑ Crescent sign
Ultrasounds
- ➤ Best initial test
- ☑ Doughnut shape
- ☑ Target sign
- ☑ Pseudkidney sign
Air contrast enema
- ➤ Best diagnostic and therapeutic
- ☑ Coiled spring
- ☑ Meniscus sign
- ☑ Claw sign

Treatment
- Is an emergency treated within 24 hours.
- Use of enema reduction, pneumatic or hydrostatic, (ultrasound guidance) in stable child if there are no complications e.g shock, perforation bowel necrosis.
- Surgical reduction If:
- Failed enema reduction.
- Signs of perforation or peritonitis.
- Pathological lead point suspected.
Prognosis
- Depends on the duration of the intussusception before reduction.
- Delayed reduction more than 24 hours carries a bad prognosis.

SURGERY
illeoilleal peyers patches enlarged could due in pedia red current jelly stool
illeocecal in adults - polyps & tumour
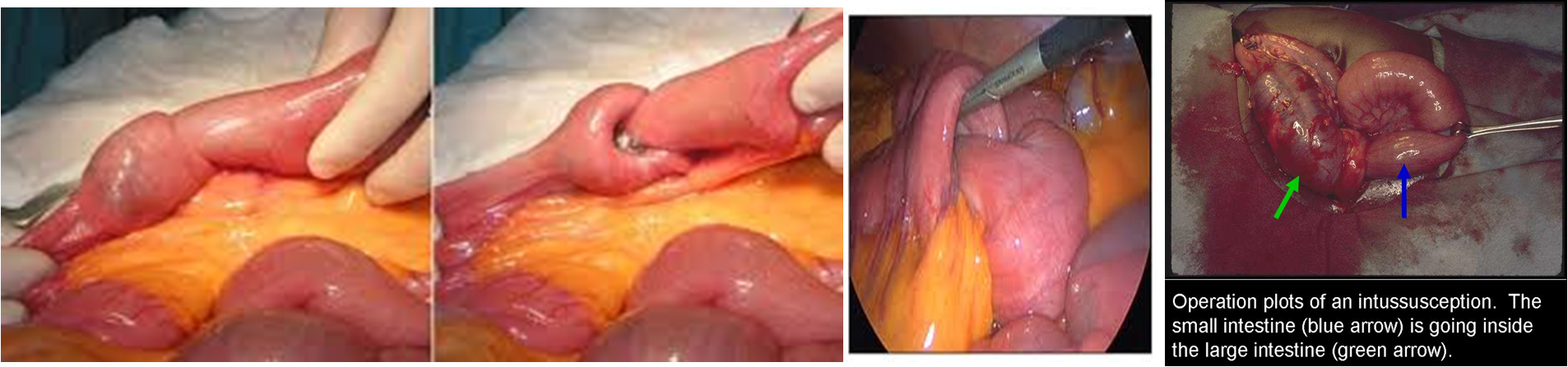
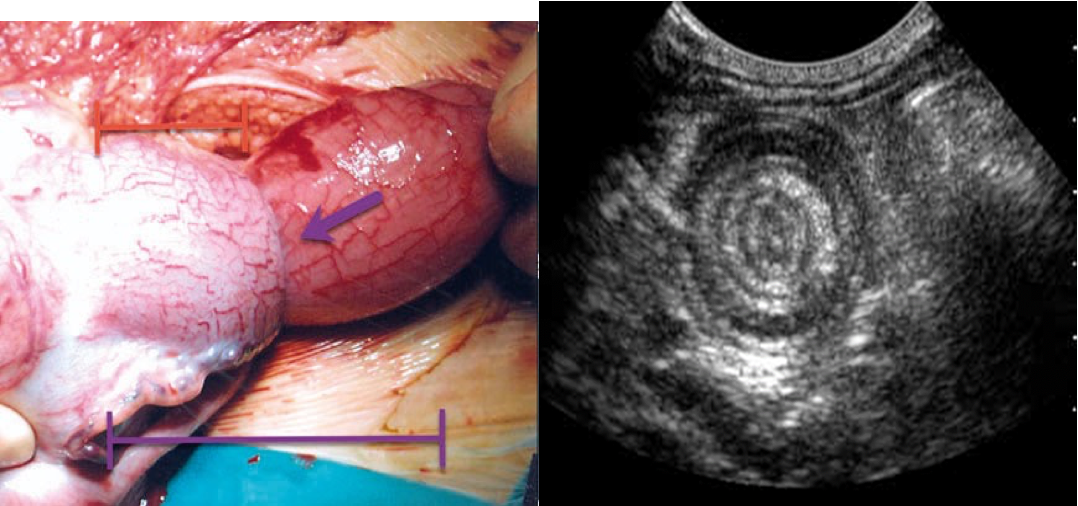
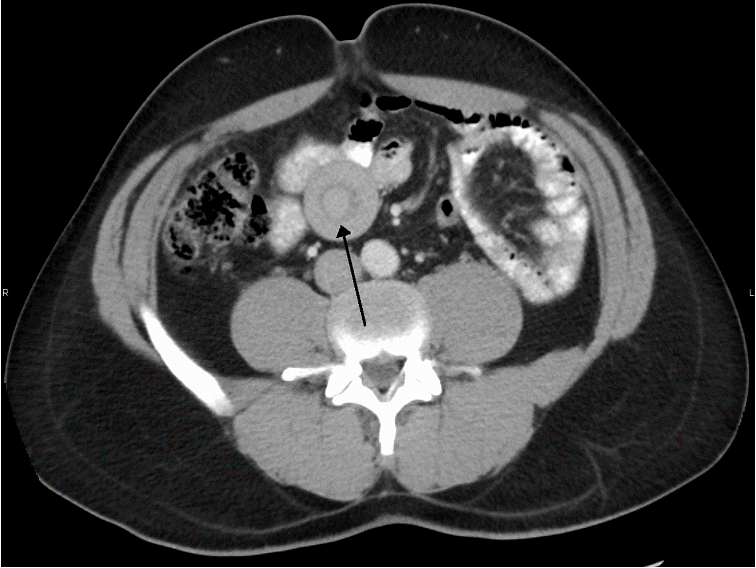
IMAGING
Intussusception occurs when a proximal part of the bowel invaginates into a distal part, leading to a mechanical obstruction and bowel ischemia.
-
Infants aged 3–12 months are most commonly affected.
-
Affected infants are typically present with acute cyclical abdominal pain, knees drawn to the chest, and vomiting (initially nonbilious).
-
A late-onset symptom is “currant jelly” stool (stool with blood and mucus.

Imaging Procedures
Abdominal ultrasound (best initial test): often sufficient to confirm diagnosis
- Target sign : The invaginated portion of bowel appears as rings on a target on ultrasound.
- Pseudokidney sign: This “pseudokidney” is made up of longitudinal layers of bowel wall.
Contrast or pneumatic enema using ultrasound or fluoroscopy
- Interruption of contrast or air at the site of invagination.
- Pneumatic insufflation (air enema): z air is injected into the intestines to create pressure. is the best confirmatory diagnostic test and nonoperative method. Abdominal x-ray -Inhomogeneous distribution of gas with absence of air at the site of invagination.
Abdominal CT: Perform if ultrasound and abdominal x-ray are inconclusive.
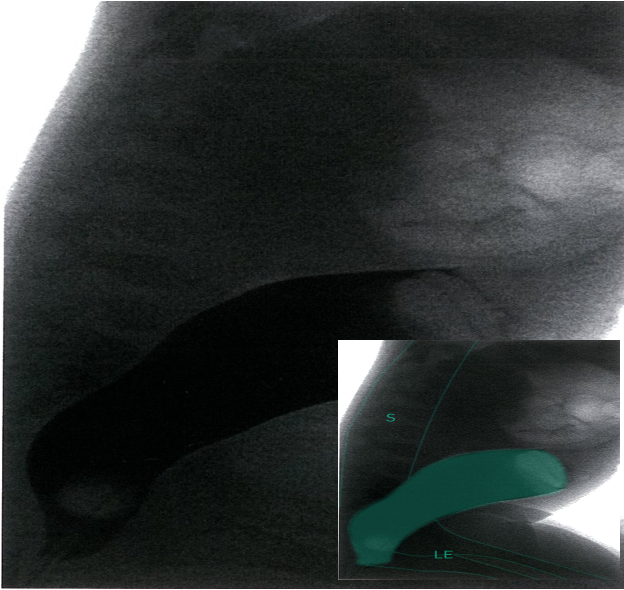 Colosigmoidal intussusception in a 4-year-old girl
Contrast enema; lateral view
Rectum and lower sigmoid are filled with contrast (dark); sudden interruption of contrast in the upper sigmoid (green area).
Colosigmoidal intussusception in a 4-year-old girl
Contrast enema; lateral view
Rectum and lower sigmoid are filled with contrast (dark); sudden interruption of contrast in the upper sigmoid (green area).
- S = spine
- LE = lower extremity
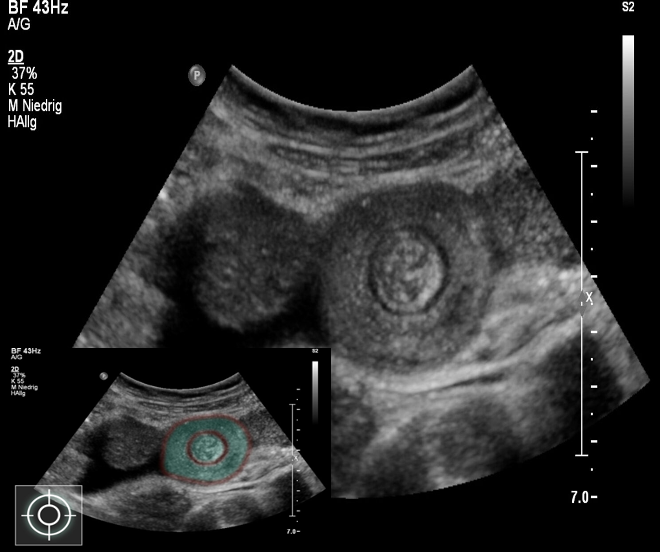 Target sign in intussusception
Ultrasound abdomen (bowel; transverse plane)
Concentric alternating hyperechoic and hypoechoic rings are visible. The hyperechoic rings (green overlay) are formed by mucosa and the hypoechoic rings (red overlay) by submucosa. Together the alternating layers produce a target-like appearance (target sign; bull’s eye sign).
Target sign in intussusception
Ultrasound abdomen (bowel; transverse plane)
Concentric alternating hyperechoic and hypoechoic rings are visible. The hyperechoic rings (green overlay) are formed by mucosa and the hypoechoic rings (red overlay) by submucosa. Together the alternating layers produce a target-like appearance (target sign; bull’s eye sign).