Skin Bacterial Infections CS-OSPE
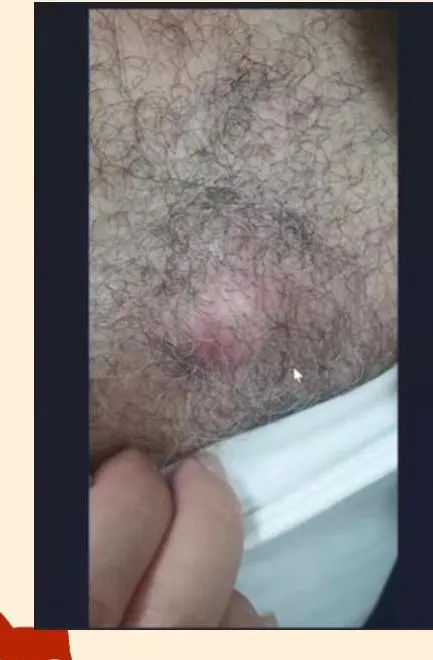
Boil or furuncle
- If eczema happened around it, itchy = infective eczema
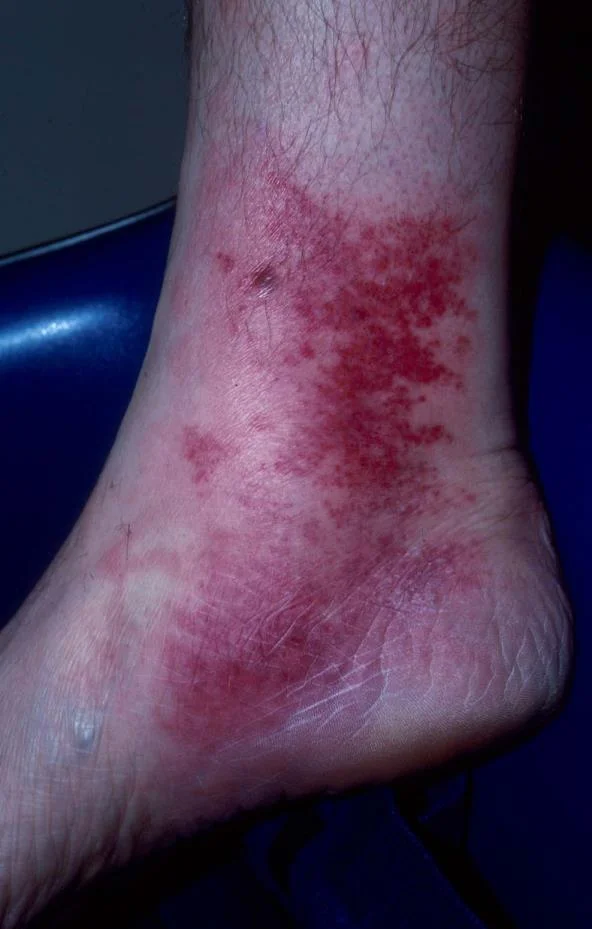
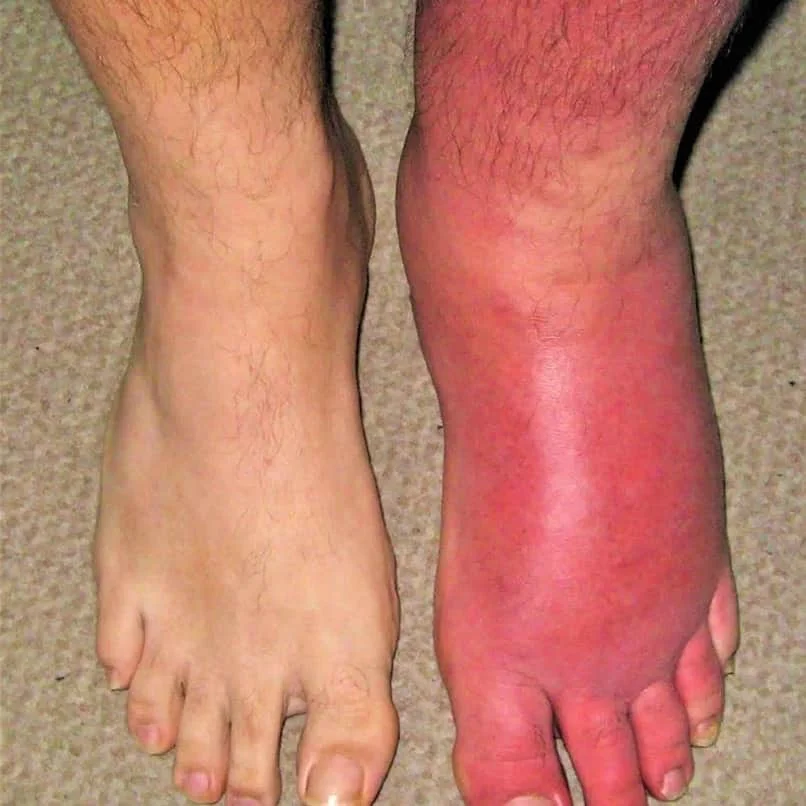
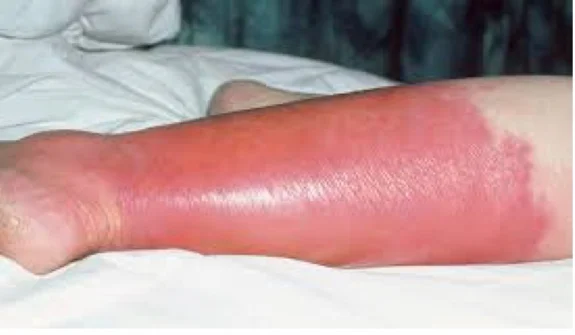
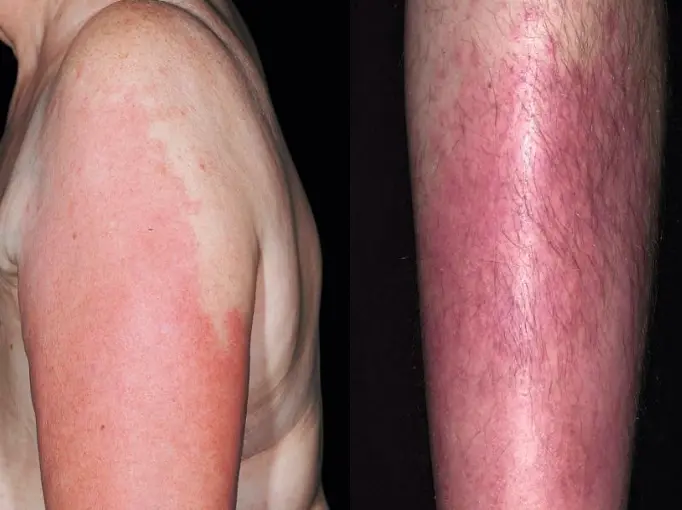
Cellulitis
Case Description/History:
- There is erythema, edema, and tenderness
- History of fever, chills, wound
Diagnosis:
- Cellulitis
Responsible Organism/Cause:
- Group A streptococcus and Staphylococcus aureus (gram +)
Describe/Characteristics:
- The subcutaneous tissues are involved and the area is more raised and swollen, and the erythema less marginated.
Differential Diagnosis:
- Necrotizing fasciitis
- Superficial Thrombophlebitis
- Contact dermatitis (CNS)
Superficial Cellulitis:
- Erysipelas, it’s marked with dermal lymphatic involvement.
Risk Factors:
- Local trauma
- Underlying skin lesion
- Inflammation
- Edema and impaired lymphatics in the affected area
Management & Treatment:
- Full history
- Examination
- Education
- Elevation and rest / Elevation of the area to decrease edema / Elevation of involved area
- Systemic antibiotics oral or I.V / IV Antibiotic / Systemic Broad spectrum Antibiotic
- Hospitalization
- Cold-wet dressing
- Rest
- Topical steroids (note: often not primary treatment for cellulitis, but listed in source)
Impetigo
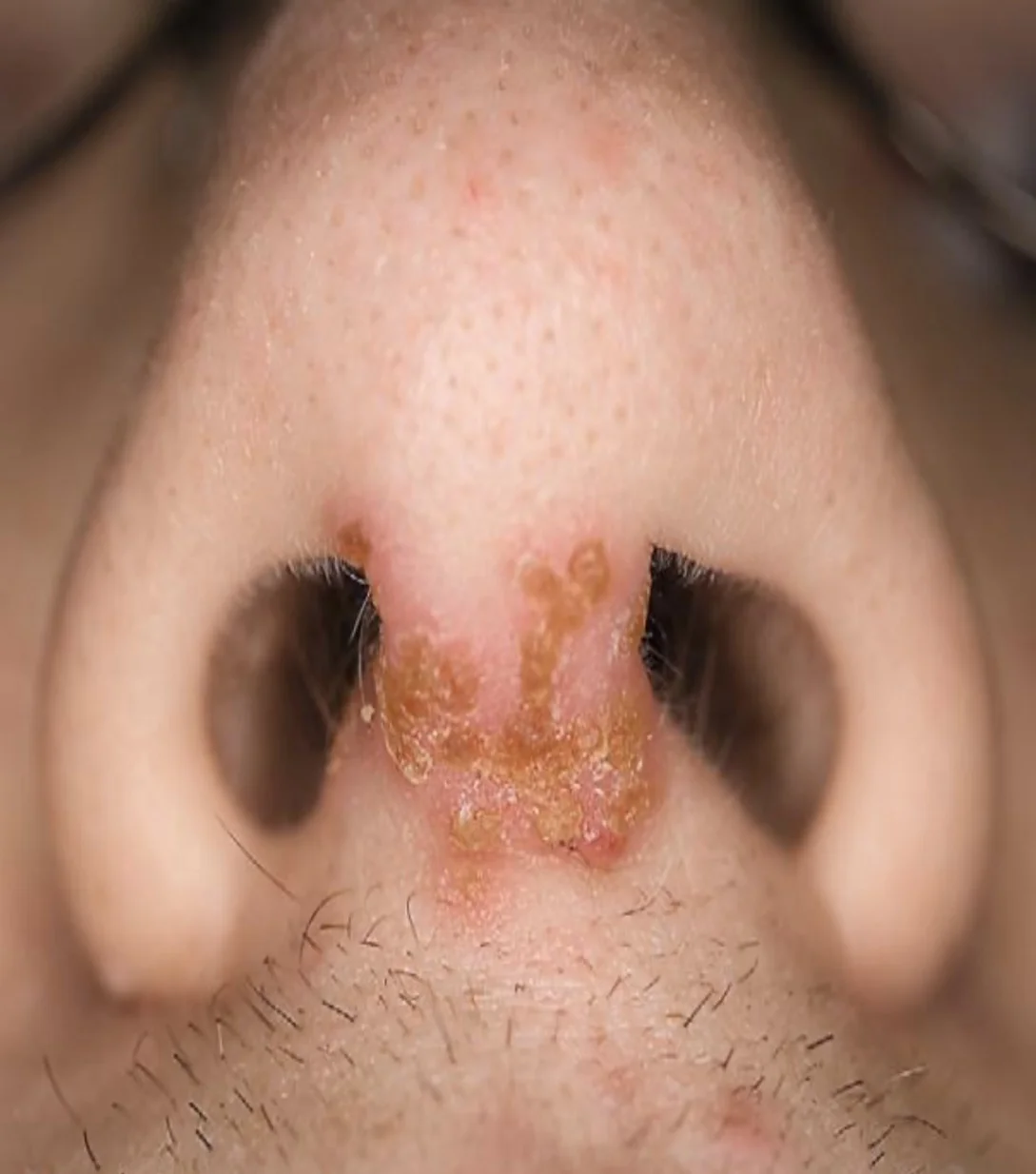
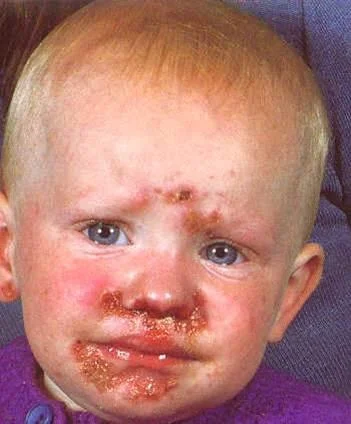
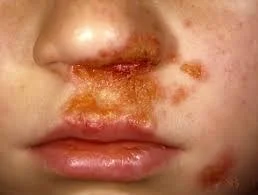
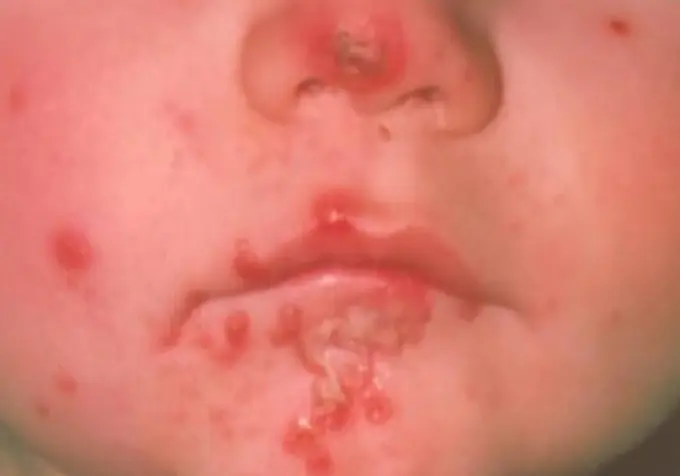
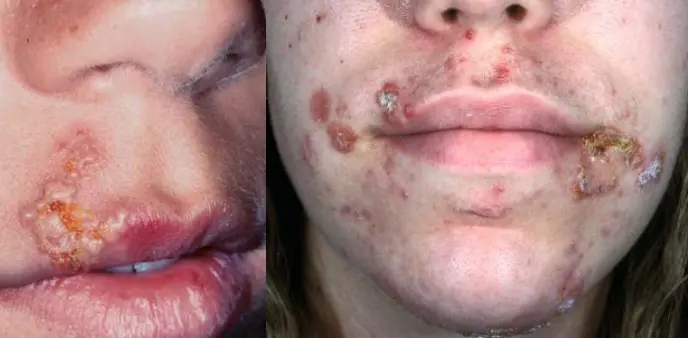
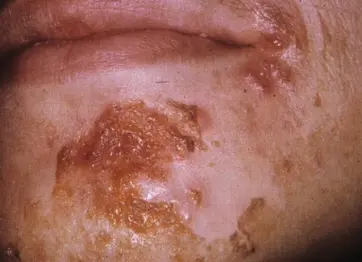
Case Description/History:
- Facial rash. The rash is not painful, but occasionally burns and itches
- An 8 Y\O girl with 2 days history of erythema on the upper cutaneous lip extending onto the nose, no elsewhere.
- This child got this infection from daycare.
- A five – year - old boy developed vesicles on his face that were not painful or pruritic, but some of the ruptured and crusted.
Diagnosis:
- Impetigo
Differential Diagnosis:
- Contact dermatitis
- Herpes simplex
- Discoid dermatitis
- chickenpox
- measles
Responsible Organisms/Cause:
- Superficial Bacterial Infection
- Crusted ulcerated by Group A streptococcus and bullous type by Staphylococcus aureus.
Describe/Morphology:
- Thin-walled clear .
- Rupturing to leave area of exudation and yellowish crusting.
- Papules and plaques with overlying honey- colored crust.
- Minimal surrounding erythem
Types/Clinical Variants:
- Non-bullous impetigo contagiosum (golden appearance)
- Bullous impetigo (flaccid bullae with clear yellow fluid, which later becomes purulent)
- Ecthyma deep impetigo (“punched out” ulcers covered with yellow crust surrounded by raised margins)
Diagnostic Question:
- If any one have the same Symptoms of his family / If any one have the same Symptoms in family
Management & Treatment:
- Full history
- Examination
- Education
- Topical or oral antibiotics
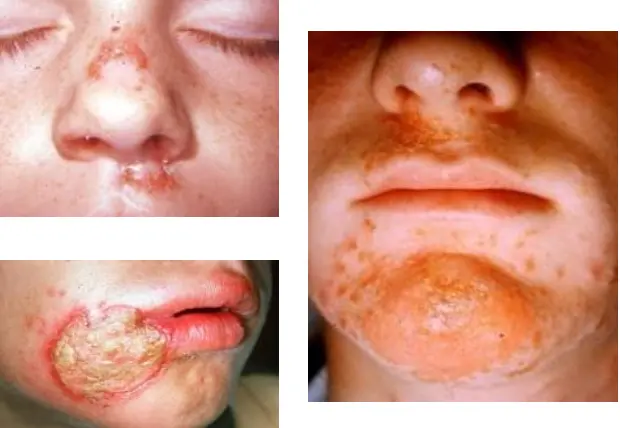
What is the diagnosis?
- Non-bullous Impetigo (contagiosum).
How does it clinically present?
- Lesions begin as papules surrounded by erythema.
- They progress to form pustules that enlarge and break down to form thick, adherent crusts with a characteristic golden appearance.
What are the key pathological agents and their characteristics?
- Staphylococcus aureus: cleaves cell adhesion molecules, often associated with bullous forms.
- Streptococci pyogenes: commonly results in crusted, ulcerated lesions.
What is the recommended treatment?
- For localized lesions?
- Topical antibiotics.
- For widespread lesions or more severe infection?
- Oral Flucloxacillin/Erythromycin.
- What general measures are recommended?
- Hand washing to reduce spread.
- Wash the affected area with antibacterial soap.
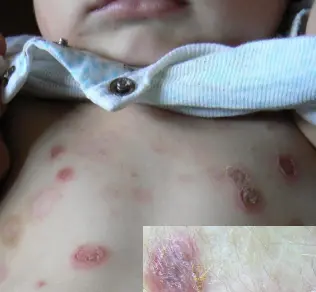
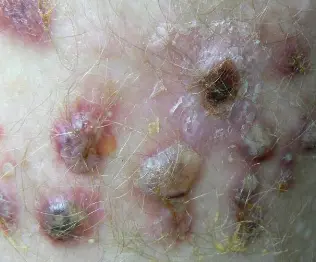
Bullous Impetigo
Diagnosis:
- Bullous Impetigo
Clinical Presentation:
- flaccid bullae with clear yellow fluid, which later becomes purulent.
- Ruptured bullae leave a thick brown crust
Pathology:
- Staphylococcus aureus: cleave the cell adhesion molecule = bullous.
- Streptococci pyogenes: crusted ulcerated.
Treatment: For localized lesions:
- Topical antibiotics. For widespread lesions or more severe infection:
- Oral Flucloxacillin/ Erythromycin.
- Hand washing to reduce spread.
- Wash the affected area with antibacterial soap.
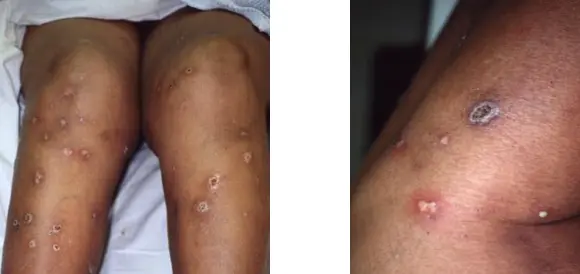
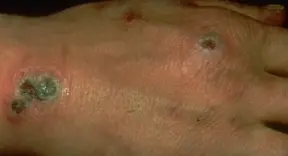
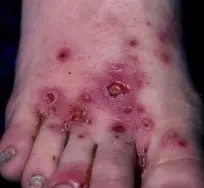
Ecthyma
Diagnosis
- Ecthyma (deep impetigo).
Clinical Presentation
- Ulcers forming under a crusted surface infection.
- Ulcer is full thickness and heals with scarring and pigmentation.
Pathology
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Streptococci
Treatment
- For localized lesions:
- Topical antibiotics.
- For widespread lesions or more severe infection:
- Oral Flucloxacillin/ Erythromycin.
- Hand washing to reduce spread.
- Wash the affected area with antibacterial soap.
Secondary Syphilis
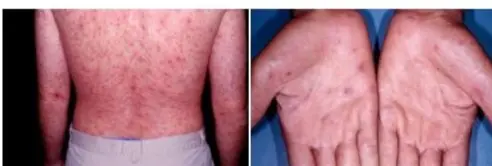 Secondary Syphilis
Secondary Syphilis
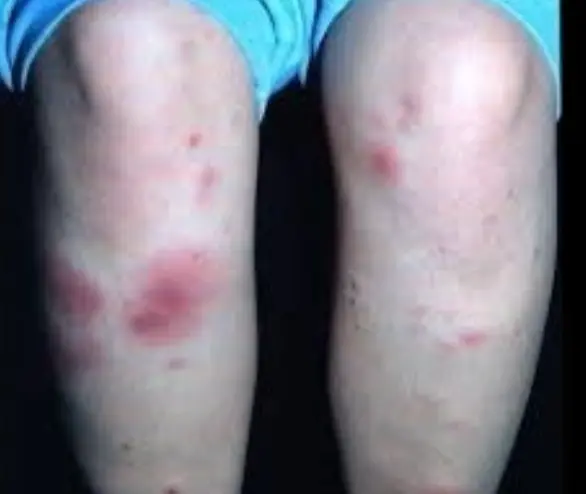
Erythema Nodosum
What is the diagnosis?
- Erythema nodosum
What are two diseases associated with Erythema Nodosum?
- Panniculitis
- Crohn’s disease
Clinical Presentation
- Multiple, bilateral, erythematous nodules typically found in the shins.
Pathology
- Characterized by panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutis).
- Can be idiopathic or a reaction to infections, medications, or an underlying autoimmune disease (e.g., Crohn’s disease).
Treatment
- The condition is often self-limited.
- Painkillers can be administered for symptomatic relief.
Panniculitis
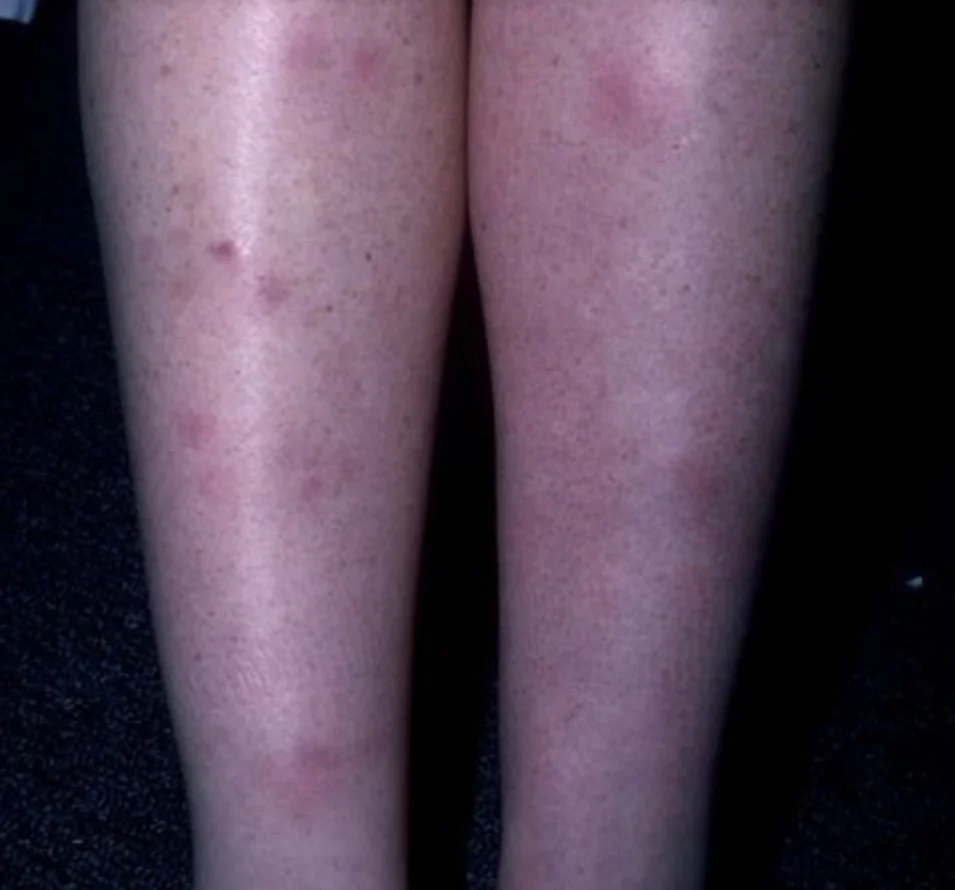
What is the name of this condition?
- Panniculitis
Mention one condition that could be associated with this condition?
- Addison disease
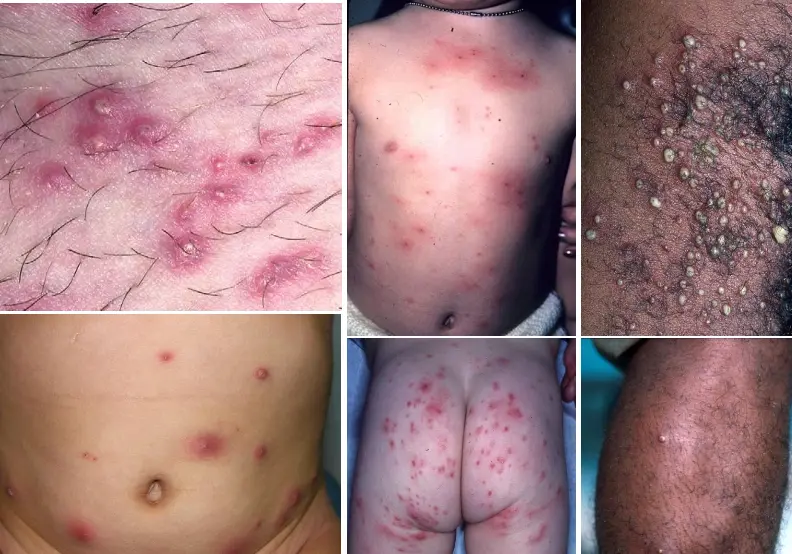
Folliculitis
What is the diagnosis?
- Folliculitis.
What is the clinical presentation?
- Painless or tender pustule that eventually heals without scarring.
What is the pathology/causative agent?
- Staphylococcus aureus.
What is the treatment?
- Solitary small furuncle: warm compresses to promote drainage may be sufficient.
- Localized lesions:
- Antiseptics or
- Topical antibiotics.
- Widespread lesions or more severe infection:
- Oral Erythromycin.
- Stop shaving that area.
- Wash the area daily (antibacterial soap may be used).
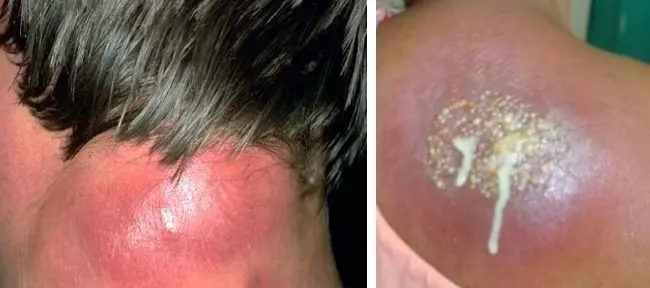
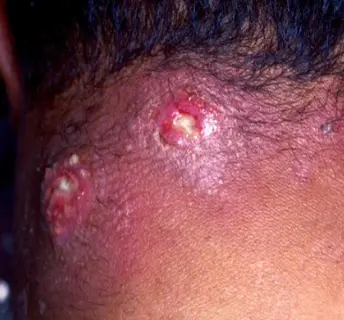
Carbuncle
What is the diagnosis?
- Carbuncle.
What is the clinical presentation?
- Purulent material from a multiple opening.
- Swollen painful suppurating area discharging pus from several points.
What is the pathology?
- Staphylococcus aureus.
What is the treatment?
- Incision & drainage (I&D) +
- Oral Flucloxacillin +
- Topical antibiotic.
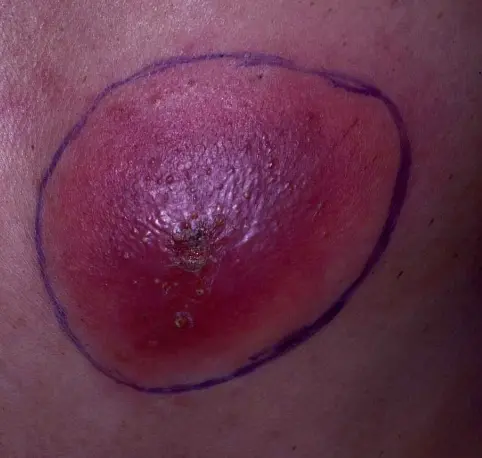
Abscess
What is the diagnosis?
- Abscess.
What is the clinical presentation?
- Erythematous, warm, fluctuant nodule with several small pustules throughout the surface.
- Very tender to palpation.
What is the pathology?
- Staphylococcus aureus.
What is the recommended treatment?
- Incision & drainage.
- Oral Flucloxacillin.
- Offer HIV test.
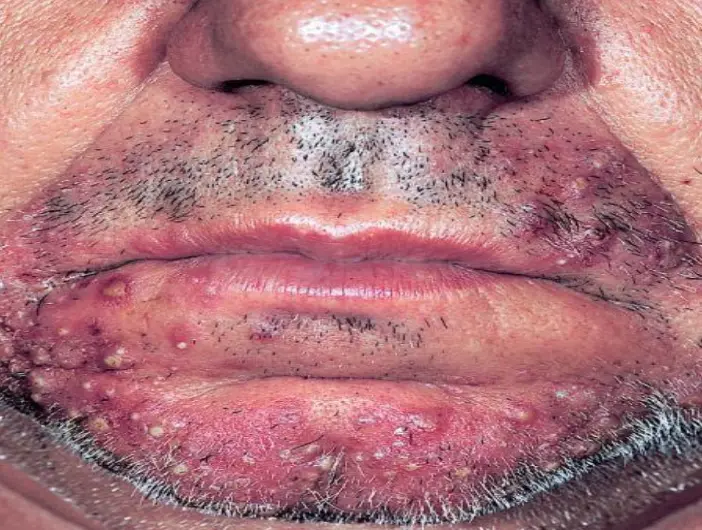
Sycosis barbae
What is the diagnosis?
- Sycosis barbae.
What is the clinical presentation?
- follicular papules or pustules.
What is the causative agent?
- Staphylococcus aureus.
What is the recommended treatment?
- For localized lesions: Topical antibiotics.
- For widespread lesions or more severe infection: Oral Flucloxacillin.
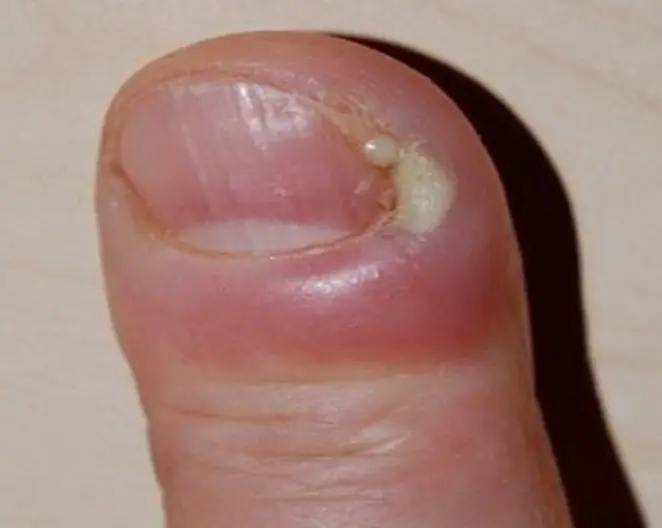
Paronychia
Diagnosis:
- Paronychia.
Clinical Presentation:
- Bright red swelling of the proximal and lateral nailfold.
- Painful.
- Rapid onset.
Pathology:
- Staphylococcus aureus.
Treatment:
- Warm water compresses.
- Topical or systemic antistaphylococcal antibiotic.
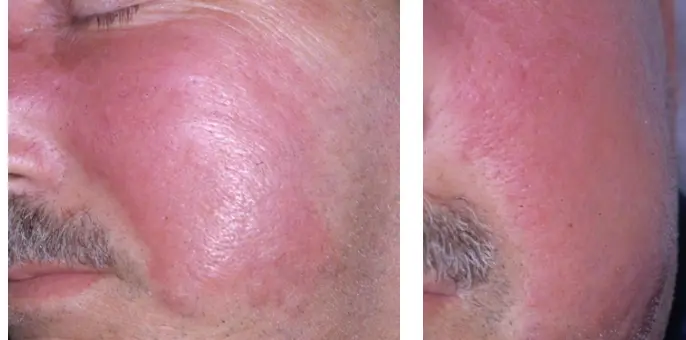
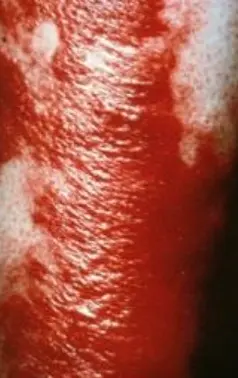
Erysipelas
What is the diagnosis?
- Erysipelas.
What are the clinical presentations?
- Presents with pain, superficial erythema, and plaque-like edema with a sharply defined margin to normal tissue. Plaques may develop overlying blisters (bullae).
What is the pathology?
- Group A streptococci.
What is the treatment?
- Oral Flucloxacillin.
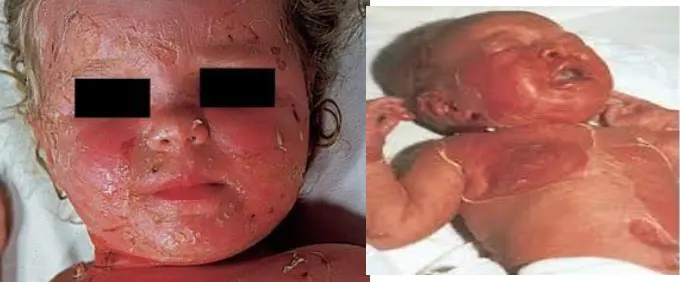
Staphylococcal scalded skin Syndrome SSSS (Ritter’s disease)
What is the diagnosis?
- Staphylococcal scalded skin Syndrome (SSSS), also known as Ritter’s disease.
What is the clinical presentation?
- Erythema and tenderness, followed by the loosening of large areas of overlying epidermis.
- Fluid from bullae is sterile.
What is the pathology?
- Caused by Staphylococcus aureus.
- Leads to acute skin failure.
What is the treatment?
- Admission to a severe burn unit, which involves:
- Nursing care.
- Monitoring hemodynamic changes.
- Maintaining fluid, electrolyte balance, and nutrition.
- Prevention of complications (e.g., sepsis).
- Identification of risk factors.
- Topical therapy.
- Oral or IV flucloxacillin.
- The patient’s skin should be lubricated with light lotions.
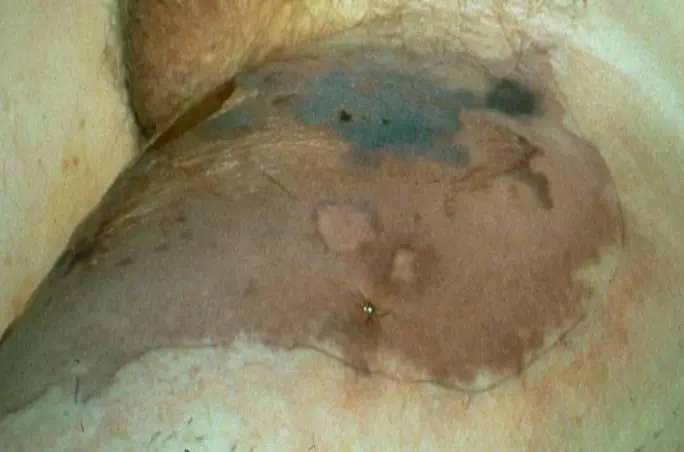
Necrotizing Fasciitis
What is the diagnosis?
- Necrotizing Fasciitis.
What is the clinical presentation?
- Ill-defined, large erythematous plaque with central patches of dusky blue discoloration, which is anesthetic.
- Upon re-examination 60 minutes later, the redness had spread.
What are the common pathogens?
- Staphylococcus aureus.
- Group A streptococci.
What is the recommended treatment?
- Call an urgent surgery consult.
- Give IV fluids and antibiotics.
- Image with stat MRI.
- Obtain a deep skin biopsy.
- Treatment includes widespread debridement and broad-spectrum systemic antibiotics.