Serous Otitis Media (Otitis Media with Effusion)
Definition:
- Persistence of fluid in the middle ear space without evidence of acute inflammation as in AOM..
Pathophysiology:
- Consequence of acute otitis media
- secondary to Eustachian tube dysfunction.
Risk Factors:
- Age (<2 y).
- Gender (Male).
- Adenoids (reservoir of infection & mechanical ET obstruction)
- ET dysfunction (short, horizontal, compliant)
- Cleft palate, Craniofacial abnormality, Down’s
- Immune deficiency
- Atopy (disputed)
- +ve family Hx
- Daycare attendance.
- Season (Fall/Winter).
- URTIs.
- Older siblings
- Parental history of OM.
- Passive smoking.
- Low socioeconomic status.
- Lack of breastfeeding.
- bottle feeding (horizontal position).
- Pacifier use.
Most common cause of pediatric hearing loss, associated with language delay and behavioral issues
Presentation:
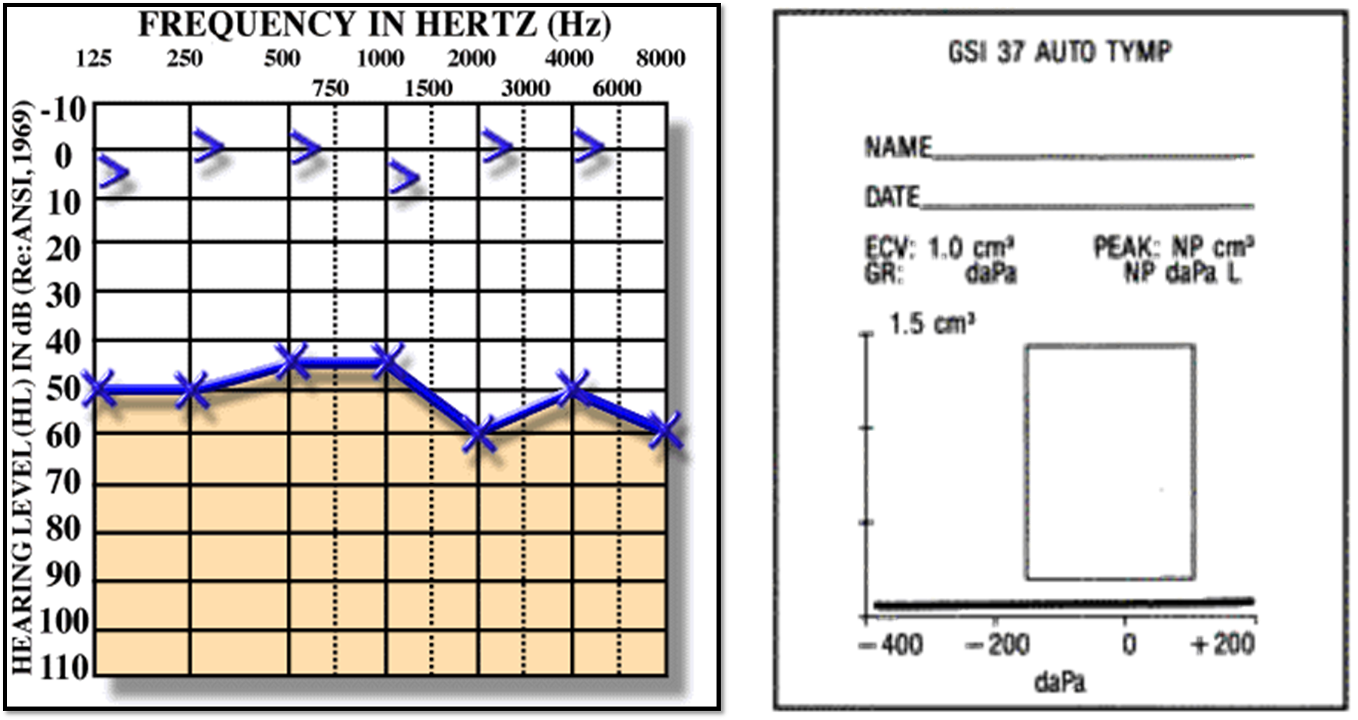
- Hearing loss, earache, ear fullness.
- In children: Ear itching and pulling.
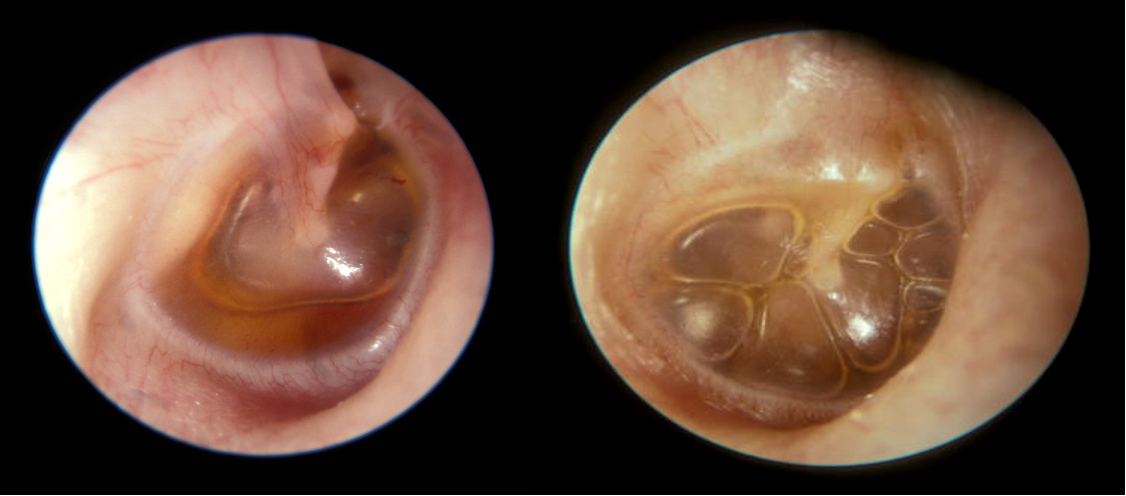
- OE: Fluid in the middle ear, loss of cone of light.
- Tests: PTA, Tympanometry.
Management:
- Observation for 3 months in non “at risk” patients.
- Management of risk factors. (allergic rhinitis, bottle feeding)
- Consider myringotomy with ventilation tube, and/or adenoidectomy.
- Antibiotics.
- Note: Adults with unilateral, persistent middle ear effusion should be inspected for nasopharyngeal tumors.