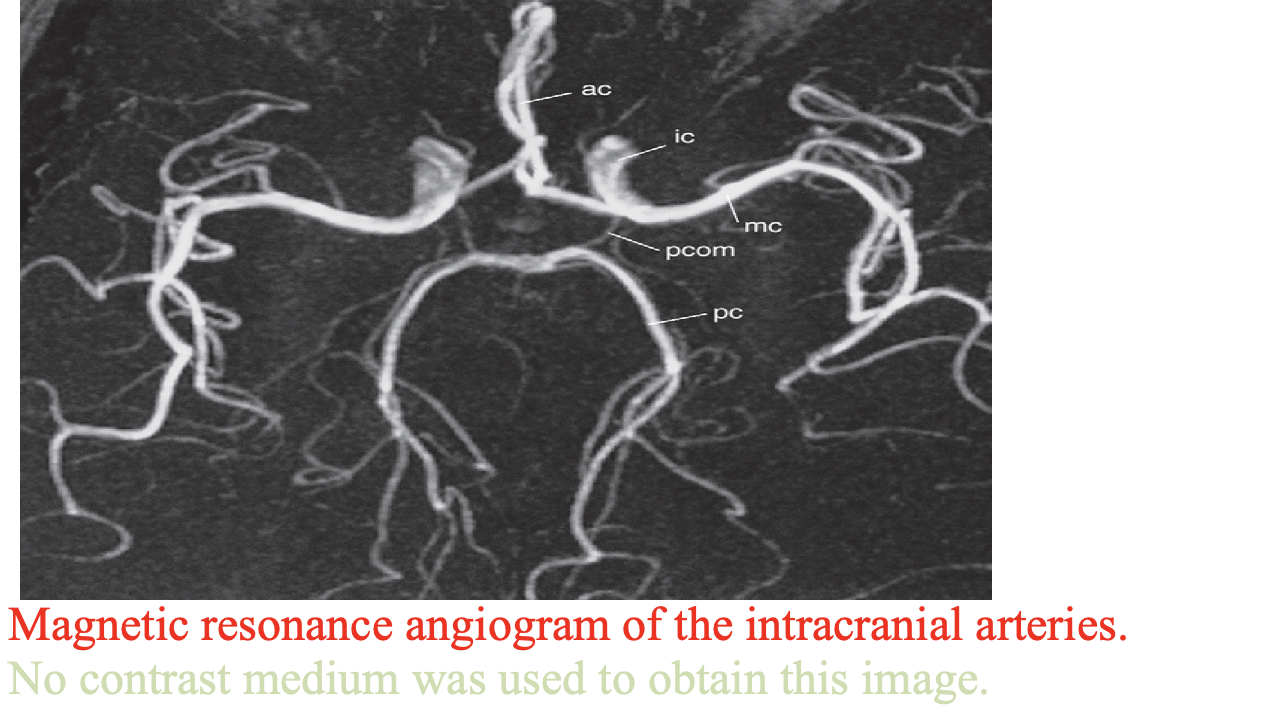
-
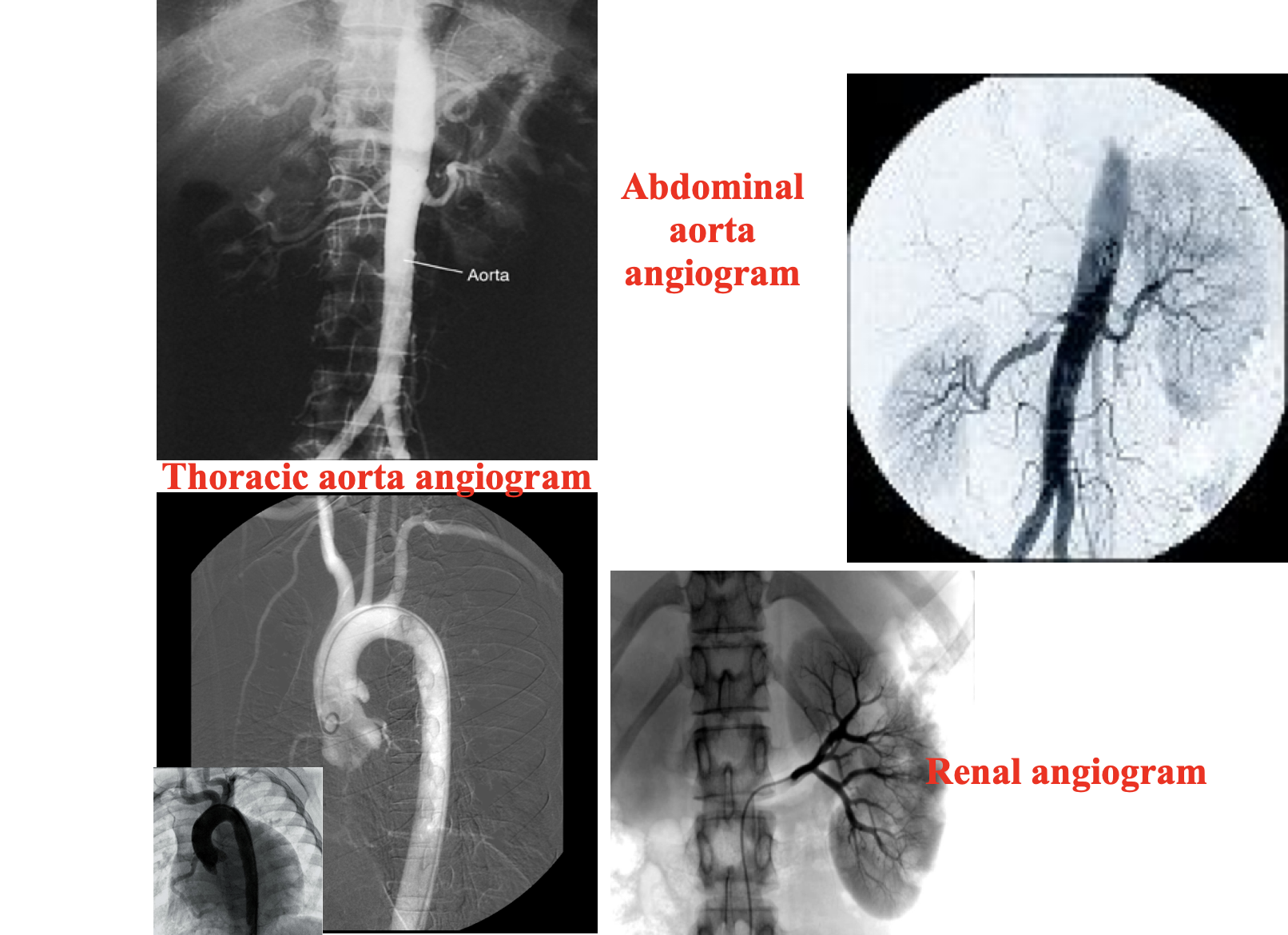
Conventional angiography
Radiographic visualization of blood vessels after injection of radiopaque contrast media into the blood vessels.Contrast is rapidly injected in to the blood vessel and a series of images are taken rapidly to follow the flow of contrast in the blood vessel. It is performed under fluoroscopy.
Angiography is indicated to diagnose vascular pathology. Conventional angiography is diagnostic as well as therapeutic.
-
CT angiography
Rapid intravenous injections of contrast media result in significant opacification of blood vessels, which, with multiplanar or 3D reconstructions, can be exploited to produce angiograms. CT angiogram. Reconstruction from many thin axial sections following an intravenous injection of contrast demonstrating an aortic aneurysm Z . Calcification is seen in the wall of the arteries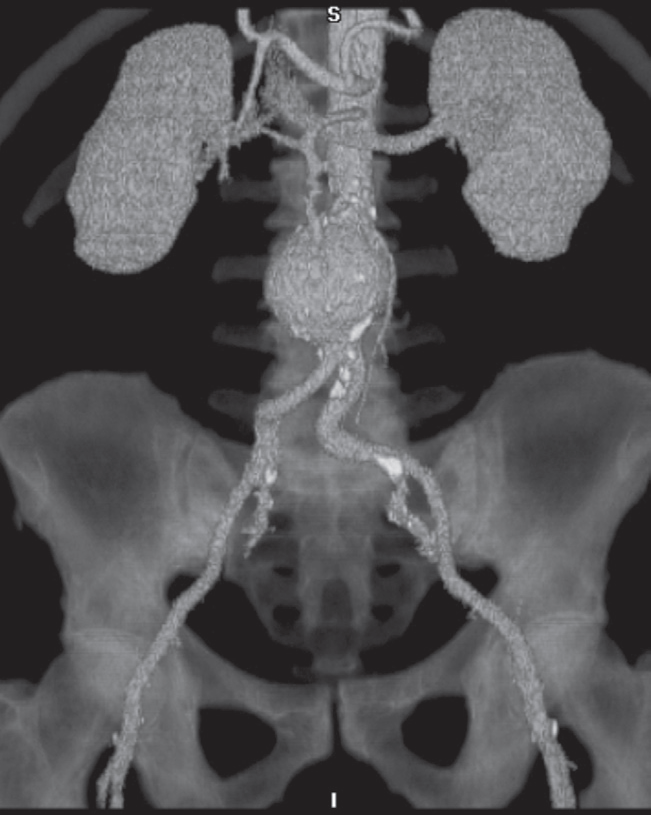
-
MRA angiography is a very useful noninvasive technique, which can demonstrate both arteries and veins. Images of the vascular system can be obtained using special sequences that depend on the signal obtained from flowing blood or via an injection of a contrast agent (gadolinium DTPA (diethylene triamine pentacetic acid) into a peripheral vein