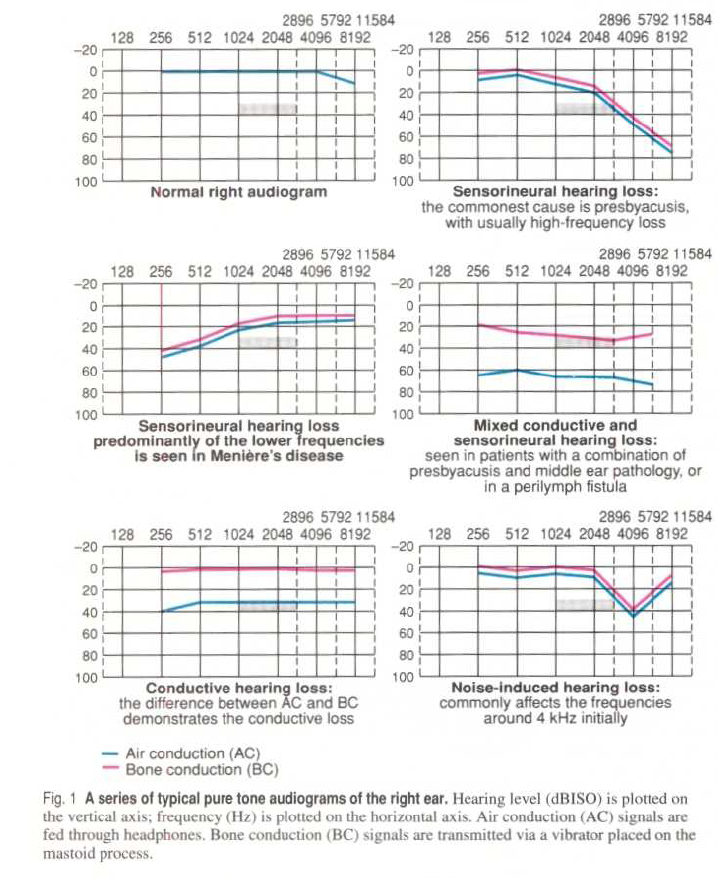
Value of Audiograms
- Type of Hearing Loss: Site of the lesions
- Degree of Hearing Loss: Threshold
- Configuration of Hearing Loss: Etiology
- Pre and Post Operation: Success
- Hearing Aid Fitting: Rehabilitation
- Hearing Screening: Prevention of hearing loss in noisy environments
- Medico-Legal Purpose
Reading PTA
-
Types.
-
Degree.
-
Air conduction assesses entire system.
-
Bone conduction assesses cochlea.
-
Air-bone gap (>10)
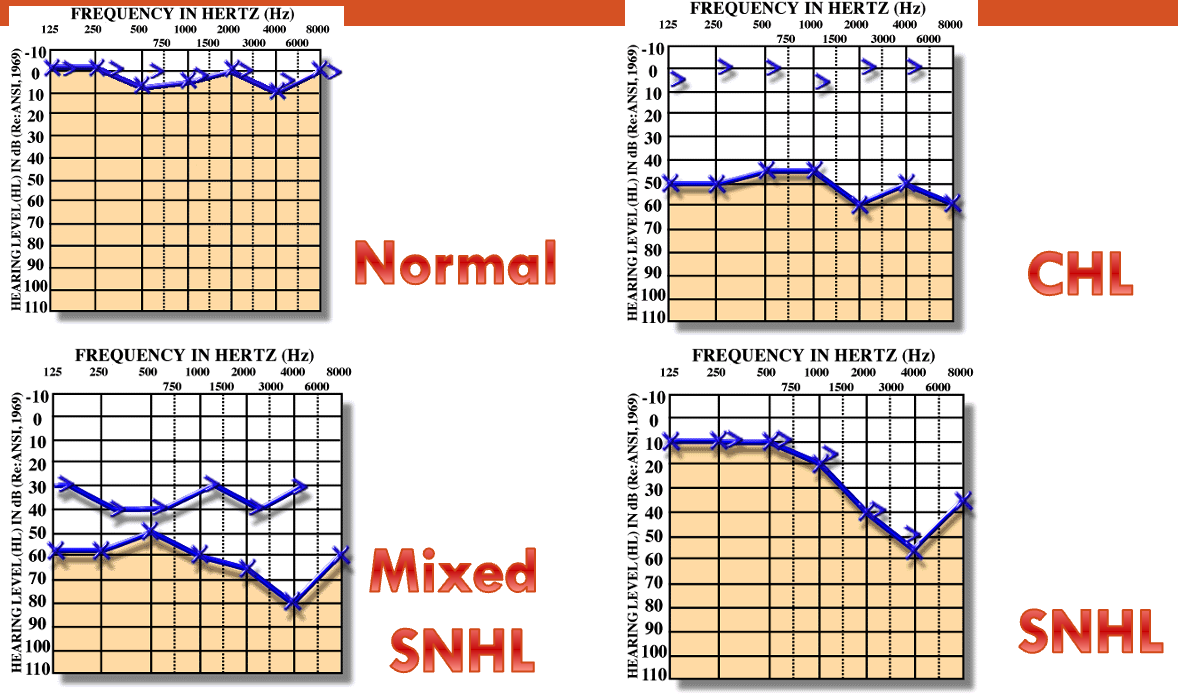
Types of Hearing Loss Z
- Normal Hearing
- positive renne, negative = conductive
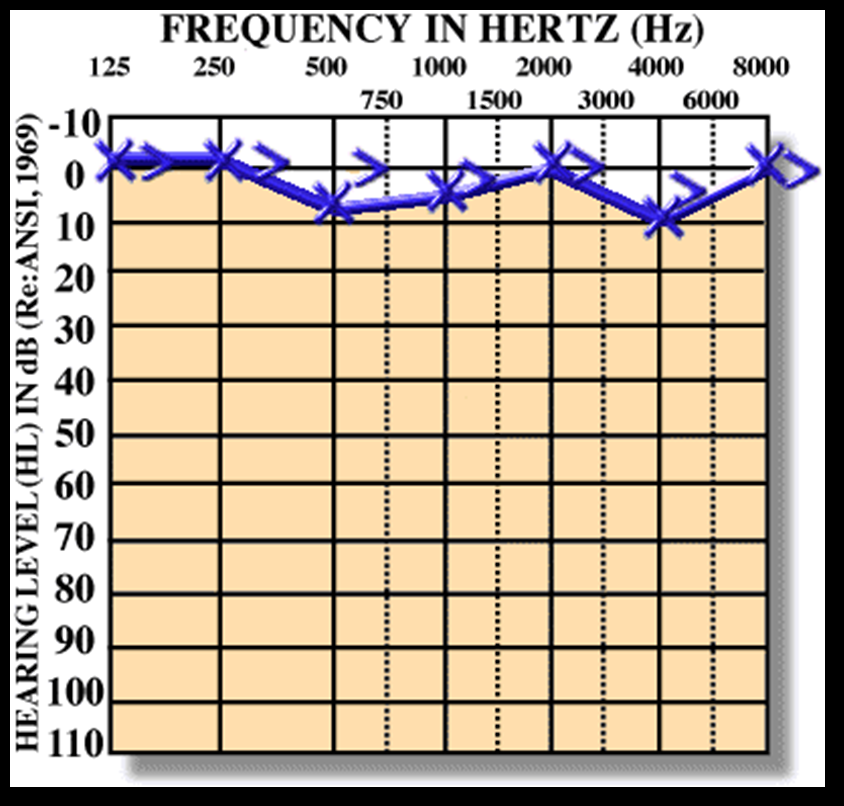 Conductive Hearing Loss
Conductive Hearing Loss - Causes in external ear, TM, or middle ear
- Air decreased, Air-Bone gap present
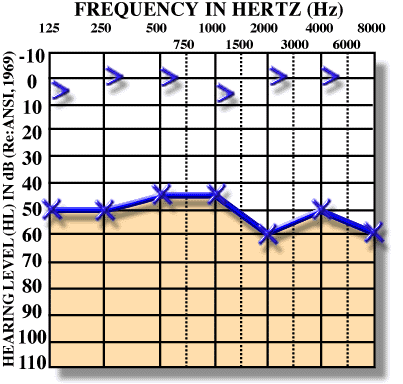 bone conduction negative renne weber (osteosclerosis, cholestestoma)
bone conduction negative renne weber (osteosclerosis, cholestestoma)
- positive renne, negative = conductive
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
- Causes in inner ear, acoustic nerve, or central
- Both Air and Bone decreased, no Air-Bone gap
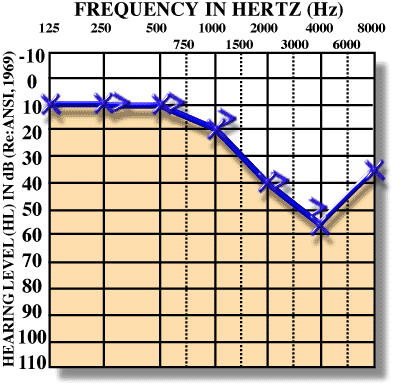
Mixed Hearing Loss
- Both Air and Bone decreased, Air-Bone gap present
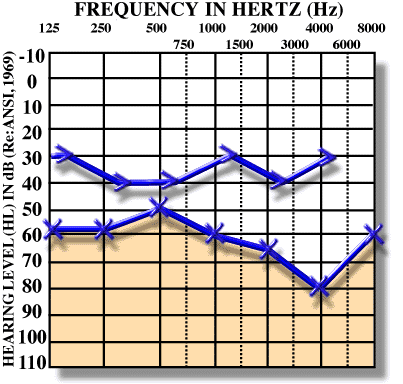 old age with perforation, meinner disease with wax.
old age with perforation, meinner disease with wax.
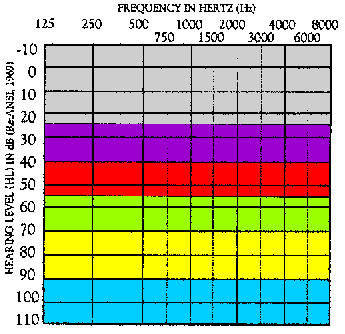
Degree of Hearing Loss
- -10 – 25 dB HL = Normal range
- 26 – 40 dB HL = Mild hearing loss
- 41 – 55 dB HL = Moderate
- 56 – 70 dB HL = Moderately Severe
- 71 – 90 dB HL = Severe
- Greater than 90 dB HL = Profound
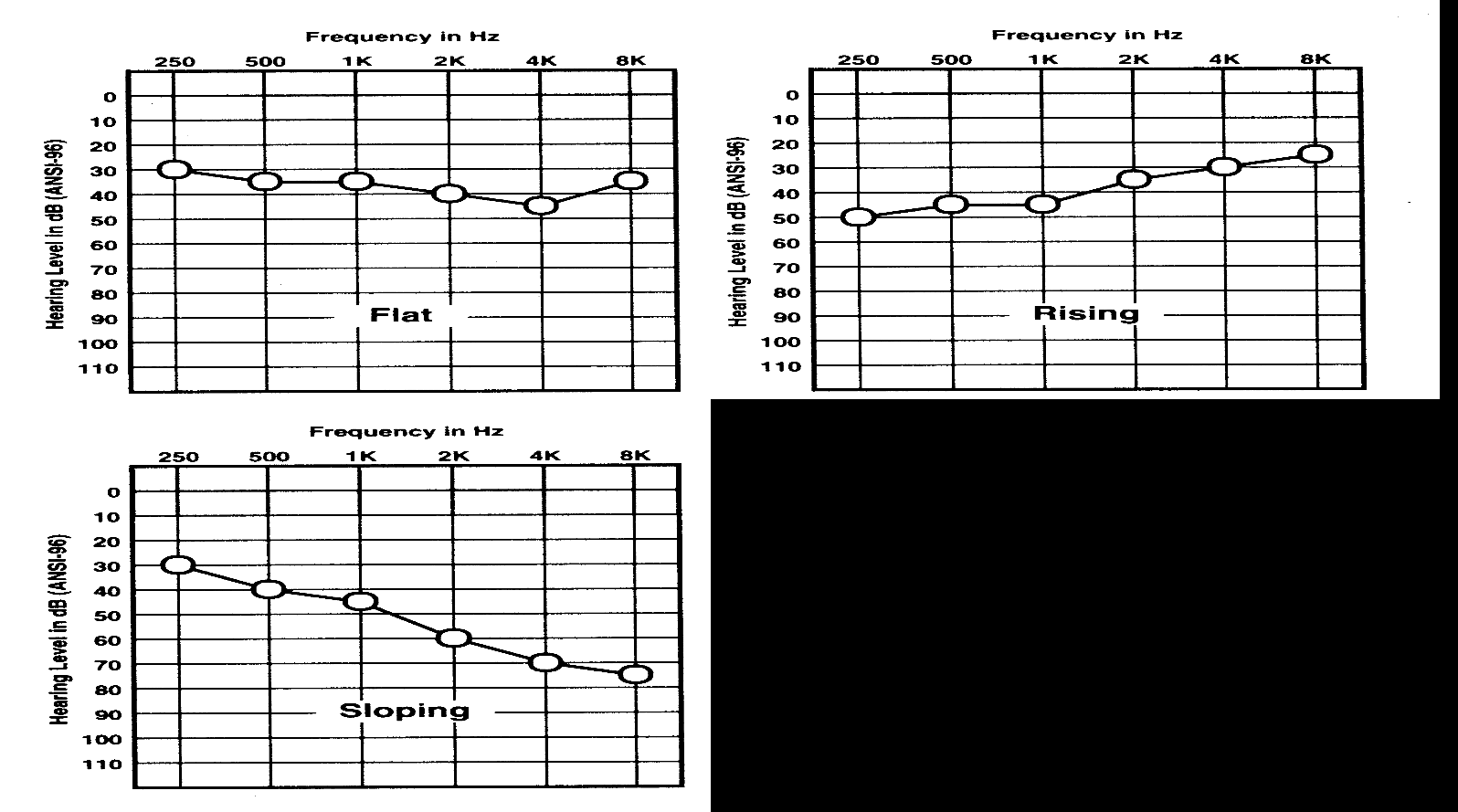
Configuration of Hearing Loss
- Rising
- Flat
- Sloping
Noise-Induced Hearing Loss
- Maximum around 4kHz (notch)
- May have tinnitus but may be subclinical
- One side may be more affected than the other