Case
A 58-year-old male presented with right upper abdominal pain.
Q1: Mention 5 relevant questions you will ask this patient regarding history of present illness. Answer:
- Does the pain radiate? And to where?
- Change in stool color?
- Change in urine color?
- Decrease in appetite?
- Does the pain increase after meals, especially fatty meals?
Q2: Mention 4 possible causes for this pain. Answer:
- Acute cholecystitis
- Acute pancreatitis
- Pyogenic liver abscess
- Hepatitis
Q3: Mention 5 relevant laboratory investigations which are indicated for this patient. Answer:
- CBC (to check leukocytosis and HB)
- LFT (ALT, AST, direct Bilirubin, total bilirubin, ALP)
- Urea and creatinine
- Amylase and lipase
- ESR and CRP
Q4: Mention 3 imaging or special investigations you would request for this patient. Answer:
- Ultrasound
- X-ray
- ERCP
- MRCP
Associated Symptoms:
- Vomiting
- Relieving
CBC: wbc LFT:
- Amylase/lipase
- Renal function test
Case
A 21-year-old male complained of anal pain.
Q1: Mention 4 relevant questions you will ask regarding history of present illness. Answer:
- Is there any relation of the pain with defecation?
- Is there any change of bowel habit?
- Is there any discharge or blood?
- Since when did it start?
Q2: Give 4 differential diagnosis? Answer:
- Anal fissure
- Anal fistula
- Hemorrhoids
- Perianal abscess
Q3: Mention 2 relevant laboratory investigations which are indicated for this patient. Answer:
- CBC
- Stool culture
Q4: Mention 2 imaging or special investigations you would request for this patient. Answer:
- Colonoscopy
- Pelvic CT/MRI
Onset fever
Case
(Picture of jaundiced patient). Abdominal pain.
a. 5 points in Hx. Answer:
- Color of stool + urine?
- Itching?
- Nausea and vomiting?
- Association to fatty food?
- Who noticed it, and when?
b. 5 abdominal examinations. Answer:
- Murphy’s sign
- Corvoisier’s sign
- Tenderness
- Hepato + splenomegaly on inspection
- Percuss for hepatic and splenic sizes
c. Initial 2 investigations. Answer:
- U/S
- LFT
Since when? Any change in urine color or stool? Any itching? Does the pain radiate to anywhere else?
Case
Patient presented with epigastric pain, hematemesis, and melena for 3 days vs. Hx of abdominal pain for 3 months.
a. 5 examination findings. Answer:
- Epigastric tenderness
- Rebound tenderness
- Guarding
- Pallor (indication of anemia)
- PREX show bloody or not
b. initial 3 investigations. Answer:
- CBC
- U/S
- UGI Endoscopy
Epigastric pain Vomit blood Dark stool
Case
Obstructive jaundice
1-finding on physical examination: Answer: pale? Yellow discoloration in skin, eyes. Distended abdomen. Tender abdomen.
2-investigation: Answer: CBC, LFT, US, CT
3-history (5 Q you would ask the patient) Answer:
- When you noticed the pain?
- Any changes in urine or stool?
- Any associated symptoms? (Vomiting, Constipation)
- Does the pain radiate to anywhere else?
- Any itching?
Case
A 41-year old female presented with a left inguinal swelling.
Q1: Mention 5 relevant questions you will ask this patient regarding history of present illness. onset? reducible or not? painful or not? any associated symtom? any chronic disease? BPH, Asthma any other swelling in body?
- When did you notice it?
- Did it get bigger or smaller?
- How did it start? Was it during lifting something heavy or something else?
- Is it painful?
- Are you having nausea or vomiting?
Q2: Mention TWO radiological investigations initially required for the diagnosis in this case? X-ray, US by ultrasound. Answer: US, abdominal and pelvic x-ray, abdominal and pelvic CT scan
Q3: How to clinically confirm an uncomplicated inguinal hernia swelling? Answer: By inspection there will be no redness or any skin changes, and by palpation there will be no tenderness, reducibility- as if it is complication it will be not reducible, and +ve cough impulse
Q4: Mention the definitive treatment for inguinal hernia in adults. (Laparoscopic repir w mesh) hertinany w mesh. Answer: Surgical repair for the hernia and mesh.
Case
A 34 year old male complaining of RUQ abdominal pain radiating to right shoulder. biling duct
Q1: Write 5 questions you will ask the patient regarding history of presenting illness
-
onset?
-
is there any assoit. symtom (Fever)?
-
Duration?
-
the character of the pain?
-
Does the pain come after fatty food?
- Changes in skin color
- Dark urine
- Pale stool
- Association to fatty food
- Fever
Q2: investigation Answer:
- CBC
- LFT
- Coagulation profile
Q3: what is your management?
Answer:
- Ultrasound
- MRCP
- ERCP
- cholecystectomy
Case
A 45-year old male presented with a left groin swelling which was noticed 4 weeks ago. The swelling usually becomes invisible when he is resting. + Cough impulse size surface cystic or not. onset? Does he have any chronic constipation Asthma BPH? any skin discoloration?
Q1: What 3 relevant questions you will ask regarding the chief complain? Answer:
- Pain
- Aggravating factors
- Become bigger or smaller
- Hx of cough, constipation
Q2: What 3 relevant physical signs you will elicit on palpation of the swelling? Answer:
- Cough impulse
- Relation to pubic tubercle
- Deep ring occlusion test
Q3: Mention 3 differential diagnoses (the most likely first). Answer:
- hernia, Lymphadenopathy, lipoma
- Indirect inguinal hernia
- Direct inguinal hernia
- Femoral hernia
Q4: What advice you will give if your first mentioned diagnosis is established? Answer: Avoid weight lifting, Treat cough and constipation, Better to do herniotomy with mesh repair
Case
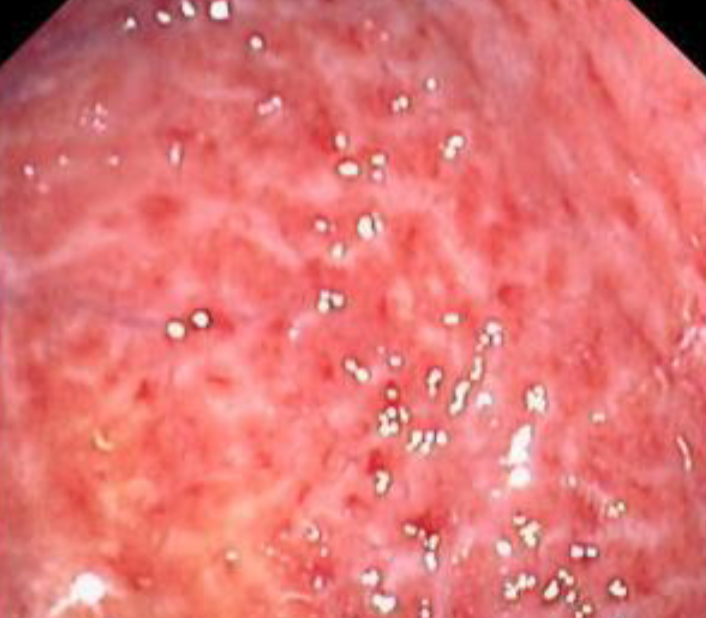 38 year old male smoker present with epigastric pain, endoscope revealed the following picture
38 year old male smoker present with epigastric pain, endoscope revealed the following picture
Q1- what is your diagnosis? Gastritis
Q2- what is your management?
- Stop smoking,
- Give PPI and analgesic other than NSAID
Case
Q1: Name the (A) imaging study and (B) mention the main abnormality. (A) Erect chest X-ray. (B) Air under the diaphragm (pneumoperitoneum).
Q2: Name TWO clinical conditions where you can get this finding:
- Perforated bowel,
- post operative,
- injury as knife injury
Q3: Mention 4 important steps in the management including the most important if the patient is unstable clinically.
- FAST
- Keep NPO -NGT
- ABC
- Analgesia and antibiotics
- Surgery (most important if unstable)
1-x-ray showing air fluid level
Finding: Air fluid level
DDx: Post operative, perforated viscus, penetrating trauma
Laboratory investigation: CBC, LFT
Management: NPO, NG tube, IV fluids
2-gall stone
Type of stone: Cholesterol, black, brown
Imaging investigation: Ultrasound
Complication: Cholecystitis, cholangitis, sepsis, peritonitis
3-lab result showing high level of amylase, ALP, bilirubin
Diagnosis = most likely pancreatitis Causes: Gall stone, alcohol, neoplasm, idiopathic
Complication: Necrosis, pseudocyst, progressive jaundice, bleeding
4-naso gastric tubes
Indications: Gastric decompression, feeding in pt w malnutrition, post op ileus
Complications: Electrolyte imbalance, infection, vomiting, injury nasopharynx
5- Ascites special tests
- shifting dullness
- fluid thrill
- PREx
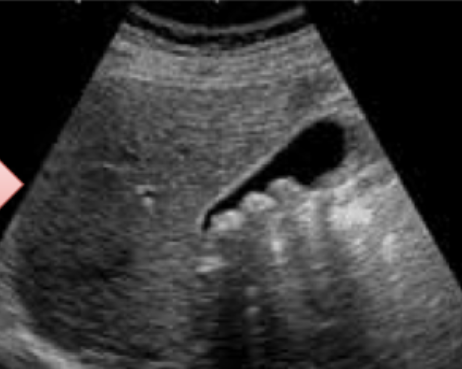 1- What is your diagnosis?
Chronic calcular cholecystitis.
1- What is your diagnosis?
Chronic calcular cholecystitis.
2- Give 4 complications? -
- Pancreatitis. -
- Obstructive jaundice. -
- Gall bladder cancer. -
- Cholangitis
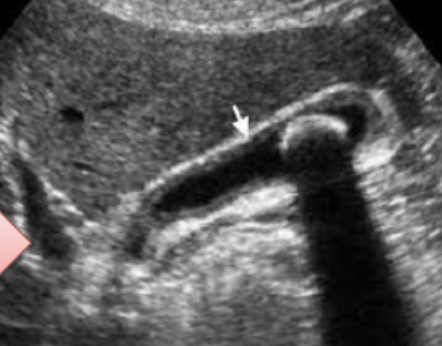
Acute Calcular Cholecystitis
U/S from patient with recurrent upper abdominal pain.
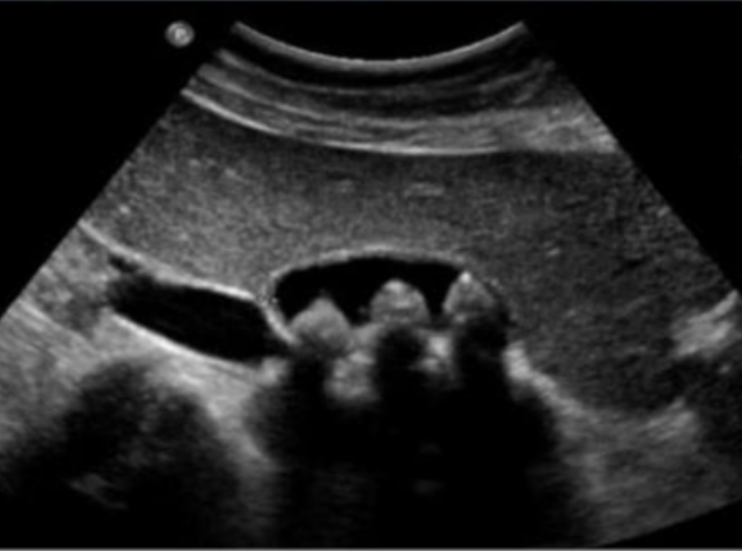 Diagnosis -
calculous cholecystitis
Diagnosis -
calculous cholecystitis
Four common complications
- cholangitis
- peritonitis
- perforation
- choledocholithiasis
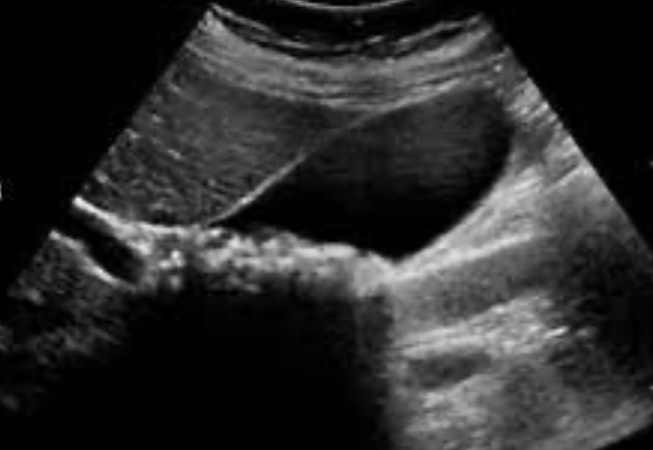
Gallbladder stone (calcular cholecystitis)
Complication:
- cholangitis,
- choledocholithiasis,
- pancreatitis,
- gallbladder perforation
Imaging technique:
- ultrasound
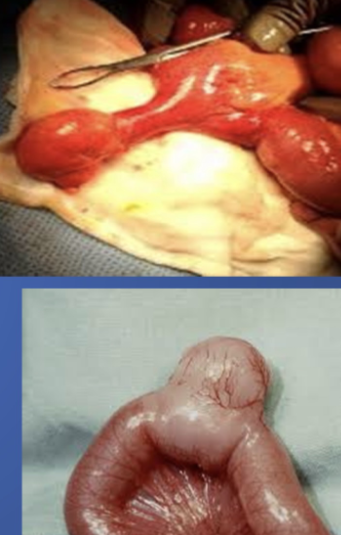
Meckles diverticulum
**Give two complications?
- rectal bleeding = anemia
- Peritonitis/infection
colonscope view of 58 year male complained rectal bleeding
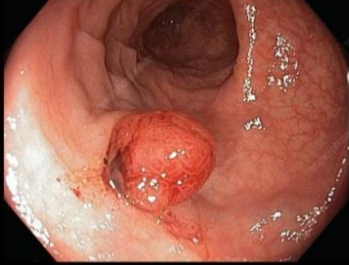 diagnosis
Colonic polyp
diagnosis
Colonic polyp
Common type lesion ademp,atpis
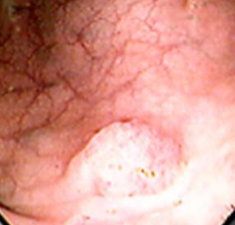 1- What is your diagnosis?
Sessile colonic polyp.
1- What is your diagnosis?
Sessile colonic polyp.
2- What is the important significant of it ? It has high potential for malignancy.
Instrument
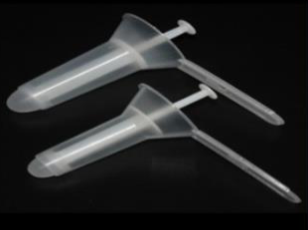 Name
Name
- Protoscope
Two uses
- examine anorectal
- banding for hemorrhoids
Sign was found during cl exam
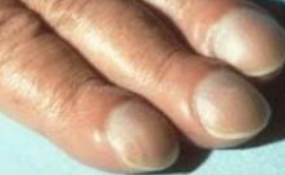 Clubbing due COPD/Ulcerative colitis
Clubbing due COPD/Ulcerative colitis
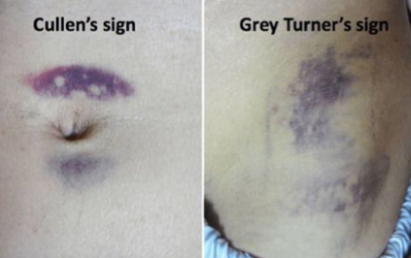
This eye sign was found in a 45-year-old female complained of right upper abdominal pain.
 Q1: What is this abnormality? Jaundice
Q1: What is this abnormality? Jaundice
Q2: Name FOUR common causes of this abnormality in this patient? Jaundice, Pyogenic liver abscess, Hepatitis, Cholangitis
An ultrasound image from a patient with recurrent upper abdominal pain.
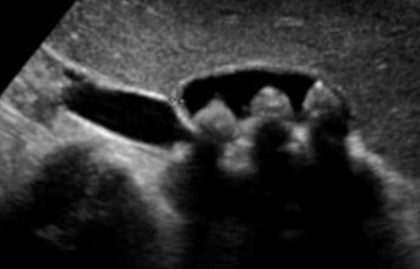
Q1: What is your diagnosis?
- Cholecystitis
Q2: Name FOUR common complications of this disease.
- Cholangitis,
- Peritonitis,
- Perforation,
- Choledocholithiasis
Severe abdominal pain elicited by doing this clinical maneuver
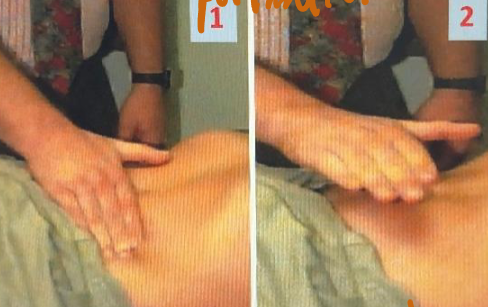
Q1: What is this sign? Rebound tenderness
Q2: Mention TWO conditions associated with this finding?
- Acute appendicitis,
- acute cholecystitis
Chest X-ray image obtained from a patient
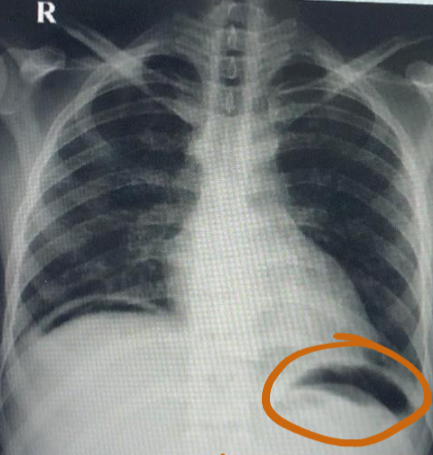
Q1: What is your finding? Free air under diaphragm
Q2: Name TWO causes of this abnormality. Perforated duodenal ulcer, Penetrating trauma
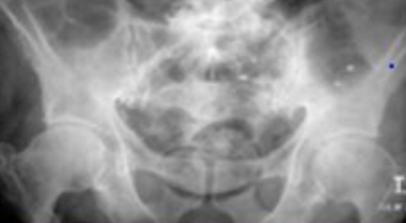
Large bowel obstruction
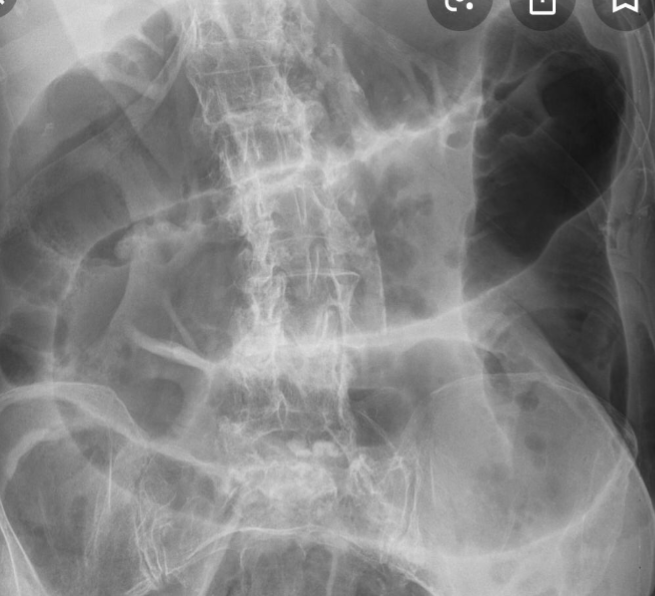
1- What is imaging technique? X-ray
2- what is your findings? Dilated + obstructive intestine
Mention 4 causes of this condition? Neoplasm, volvulus, polyp, hernia, adhesions, intussusception
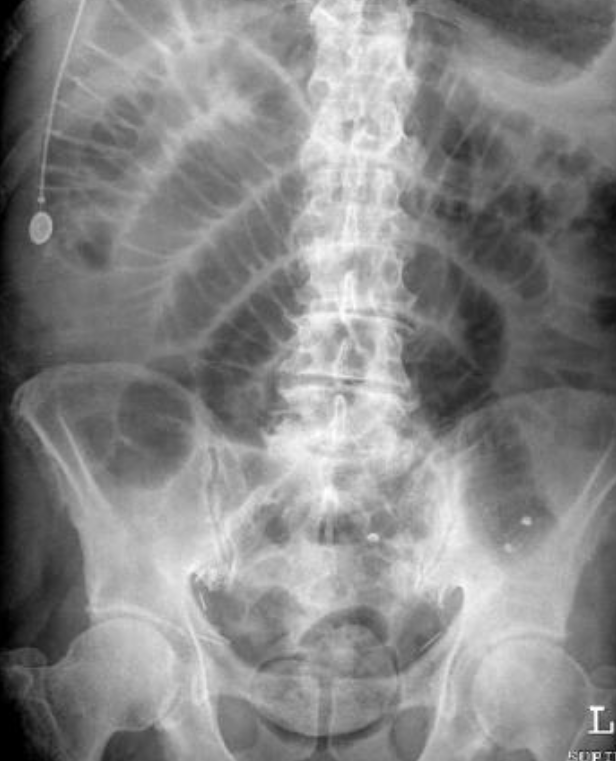
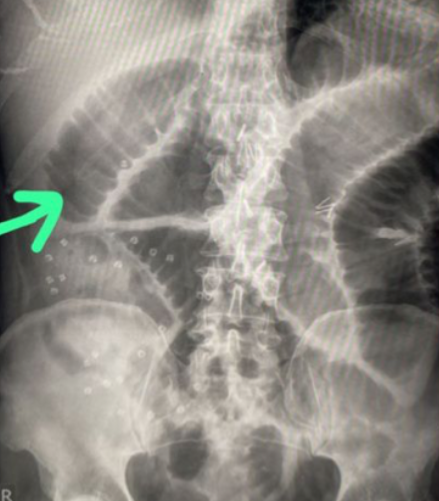
Small bowel obstruciton
Q1- Write the name of this imaging and what is your finding?
- plain film air fluid level
- small bowel obstruction with coin sign (valvulae conniventes)
Q2-Write 2 of the possible causes?
- Stricture
- Complicated hernia
Q3-What is your management? concretive treatment
- iv fluid
- nasogastric tube
- observation the pt.
- CT with contras
Dx: Mesenteric ischemia (with small bowel necrosis)
Causes:
- Arterial embolus,
- Arterial thrombosis,
- Venous thrombosis,
- Polycythemia
Intra operative management:
- Embolectomy,
- Thrombectomy,
- Bowel resection,
- Vascular bypass, Endarterectomy
 Core apple apperance
Core apple apperance
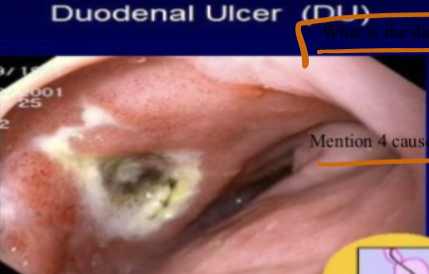 Most likely abnormality
Duodenal ulcer
Most likely abnormality
Duodenal ulcer
Criteria of abdominal pain related to condition
- Epigastric pain, night pain, hunger pain, and relieved by eating, sharp pain, may radiate to the back
Causes?
- Nsaids
- stress
- h pylori
Complications
- Perforation, bleeding, penetration, and obstruction
Q1: Mention (A) type of imaging study, and (B) Your finding. A) Abdominal x-ray/ plain film/ probably supine position
B) Dilated small bowel loops (small intestine obstruction)
Q2: What is the commonest cause of this condition? Adhesions
Q3: Mention 4 important steps in the treatment. NOP, IV fluids, NG tube, pain killers
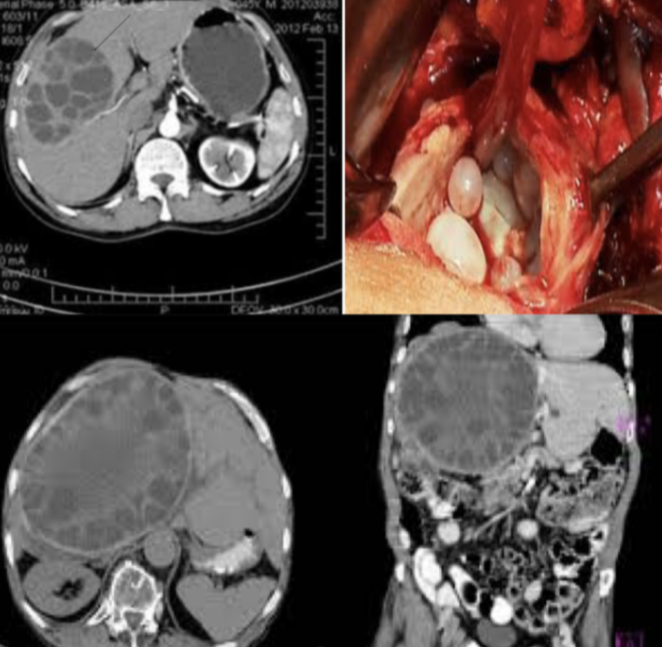 Diagnosis?
hydated cyst
Diagnosis?
hydated cyst
Causative organism? Echinococcus granulosus
Causes?
Treatment? medical
- Asymptomatic no treatment - may be treated with albendazole or mebendazole but this may be prolonged
Surgery
- Deroofing and complete excision of the endocyst
- Complete excision of the cyst (pericystectomy)
- Selected patients with central liver cyst may be suitable for puncture – aspiration-injection-re-aspiration (PAIR)