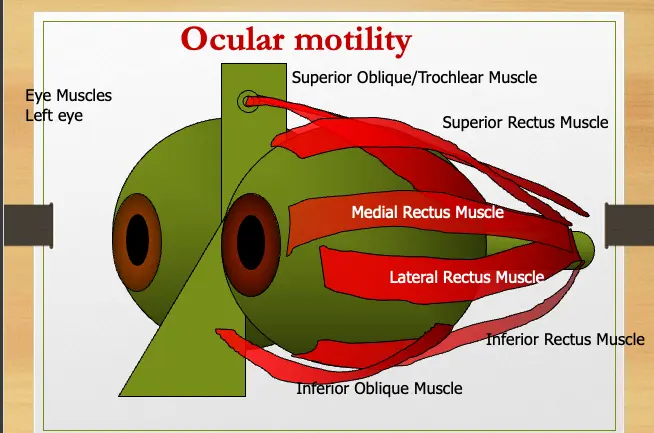
Anatomy Of The EOM’s
What are the actions of EOM surround each eye:

Anatomy Of The EOM’s
Origin A common tendinous ring (annulus of Zinn)

Blood supply Each muscle is supplied by two Anterior Ciliary Arteries except the Lateral Rectus which is only supplied by one.

Nerve supply
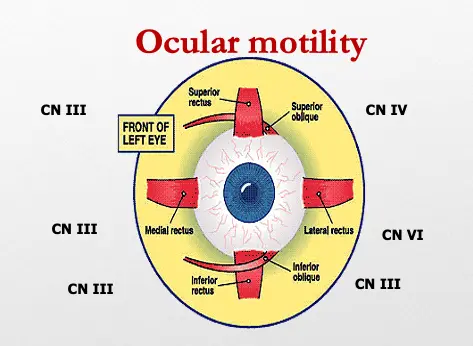
- Third: LPS, MR, IR, SR, IO
- Fourth: SO
- Sixth: LR

Ocular motility
- Normal movement of the eye ( 6 extraocular muscles )
- Binocular eye movements are called Versions
- Monocular eye movements with the other eye covered are called Ductions
Eye movement
Three directions of eye movement
- Vertically
- Upward ⇒ SR & IO
- Downward ⇒ IR & SO
- Horizontally
- Abduction ⇒ LR
- Adduction ⇒ MR
- Torsionally
- Intorsion (rotate nasally) ⇒ SO
- Extorsion (rotate temporally) ⇒ IO
Ocular motility Z
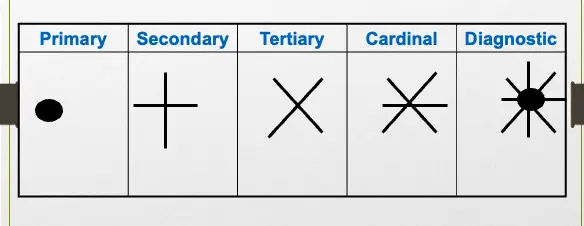
These six positions of gaze are called the cardinal positions of gaze. In addition to these, there are another 3 position of gaze :
- the primary position – looking straight ahead
- Looking up & Looking down Therefore the total number of the positions of gaze is 9
Eye position for examination
- Primary position: With condition in which head being put vertically and straightforward and two eyes looking straightforward.
- Secondary position: The two eyes being in adduction or abduction or elevation or depression position.
- Tertiary position: Two eyes gazing in oblique directions (up or downward).
Positions of gaze Z
-
Agonist Muscles: Receive equal innervation to ensure coordinated eye movements
-
Agonist/Antagonist Pairs (within each eye) Receive reciprocal innervation
Anatomy Of The EOM’s Z
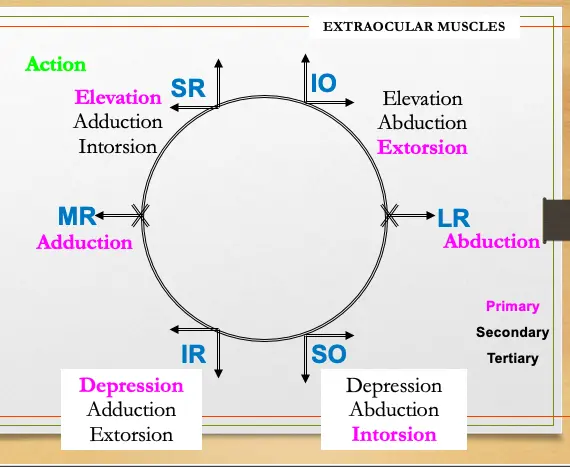
- The two Oblique are Abductors
- The two Recti are Adductors
- The (two) Superiors are Intorters
- The two Inferiors are Extorters

Medial Rectus
Adduction


Lateral Rectus
Abduction


Superior Rectus
Elevation, Adduction, Intorsion


Inferior Rectus
Depression, Adduction, Extorsion


Superior Oblique
Intorsion, Depression, Abduction



Inferior Oblique
Extorsion Elevation Abduction


Anatomy & Physiology
| Muscle | Nerve | Function | Testing |
|---|---|---|---|
| MR | 3 rd | Nasal | Look to nose |
| LR | 6th | Temporal | Look away |
| SR | 3rd | Elevate, intorts, adducts | Up & Out |
| IR | 3 rd | Depress, extrorts, adduct | Down & Out |
Anatomy & Physiology
| Muscle | Nerve | Function | Testing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Superior Oblique | 4th | Intorts, depress, abducts | Look Down & In |
| Inferior Oblique | 3rd | Extrorts, elevates, abducts | Look Up & In |
EXTRAOCULAR MUSCLES
Ocular movement
3rd nerve palsy ospe
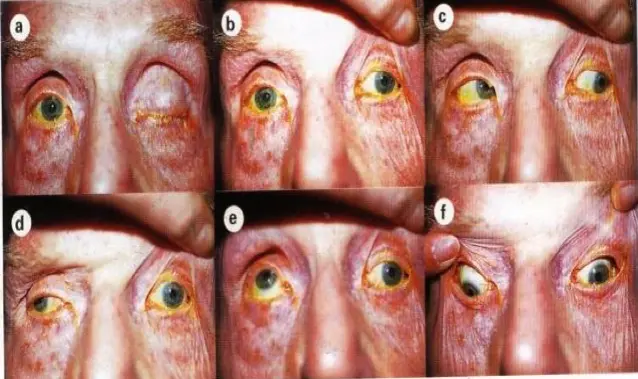
6th nerve palsy ospe
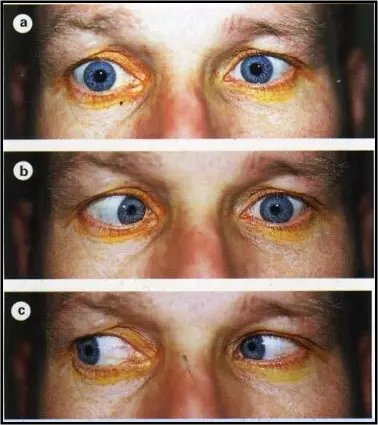 1- eso
2-
3- normal
1- eso
2-
3- normal
left lateral rectus 6th cnv
4th nerve palsy
- -Asymptomatic
- -Diplopia (vertical)
- -Head tilt position opposite to the side of the lesion.
- -Hypertropia (the eye is higher )on the affected side.
- -Limitation of depression, most marked in adduction ( SO ms)
Recovery can be achieved within 3-6 months. Neuroimaging if no improvement is noticed within 3-6 months. Z
