The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the system that controls involuntary activity of the body.
- A) Sympathetic nervous systems (SNS).
- B) Parasympathetic nervous systems (PNS)
Every autonomic nerve is composed of two neurones: preganglionic neurone and postganglionic neurone. Both neurones are separated by ganglion.
- The suprarenal medulla is a modified sympathetic ganglion.
controls the Involuntary functions of blood vessels, Glands and internal organs (e.g.: the bladder, stomach, heart)
-
Norepinephrine - Na+ - Ca+ - MAO - Vanillyl Mandelic Acid (VMA)
-
80% Norepinephrine Re-uptake after usage - only 20% Metabolized
N.B.
Vanillyl Mandelic Acid (VMA)
is the main catecholamine metabolite in the urine. Normal Values is 4-8 mg/day. High Levels suggest the presence of a tumour in the suprarenal medulla (pheochromocytoma) that secretes excess catecholamines leading to hypertension. 2% of NE is excreted unmetabolized in the urine.
Synthesis and storage of the chemical transmitters Acetylcholine:
acetylcholine (A.Ch.) is formed in the cholinergic nerve ending by acetylation of choline by the enzyme choline acetylase in presence of Co-A.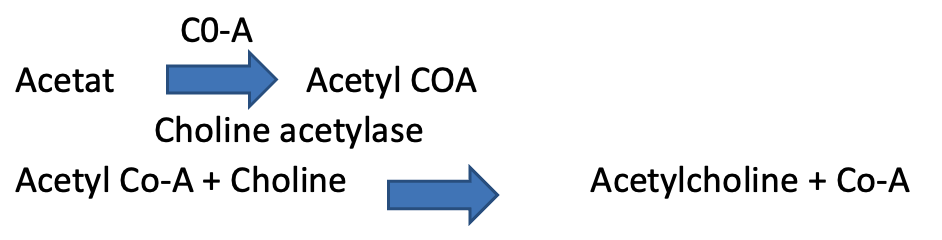 The synthesized A.Ch. is stored in granular vesicles within the axon close to the site of release into the synaptic cleft .
The synthesized A.Ch. is stored in granular vesicles within the axon close to the site of release into the synaptic cleft .