Large bowel obstruction
- It is an emergency condition that requires early identification and intervention.
- Acute Vs chronic
- Complete vs Partial
- Mechanical vs pseudo-obstruction
Symptoms:
- Crampy abdominal pain
- Abdominal distention
- Nausea and vomiting
Other symptoms that may be diagnostically significant include the following:
- Abrupt onset of symptoms (acute obstruction)
- Recurrent left lower quadrant abdominal pain over several years (suggestive of diverticulitis, a diverticular stricture)
- Chronic constipation, long-term cathartic use, and straining at stools (diverticulitis or carcinoma)
- Changes in stool caliber (suggestive of carcinoma)
Signs:
- Abdomen (inspection, auscultation, percussion, and palpation)
- Evaluate bowel sounds, tenderness, rigidity, guarding, and any mass or fullness
- Inguinal and femoral regions, look for a possible incarcerated hernia
- Rectum, contents of anal vault, and stool consistency; perform fecal occult blood testing as appropriate
Etiology:
- Neoplasm* (benign or malignant) 60%
- Stricture (diverticular or ischemic)
- Volvulus (colonic, sigmoid, cecal) 5%
- Fecal Impaction
Diagnosis
Labs:
- Complete blood count (CBC) : WBC, HB, Hematocrit
- Coagulation
- Electrolytes
- LFT
- Serum lactate (if bowel ischemia is a consideration)
- Urinalysis
- Stool guaiac test
Diagnosis
Radiology Imaging
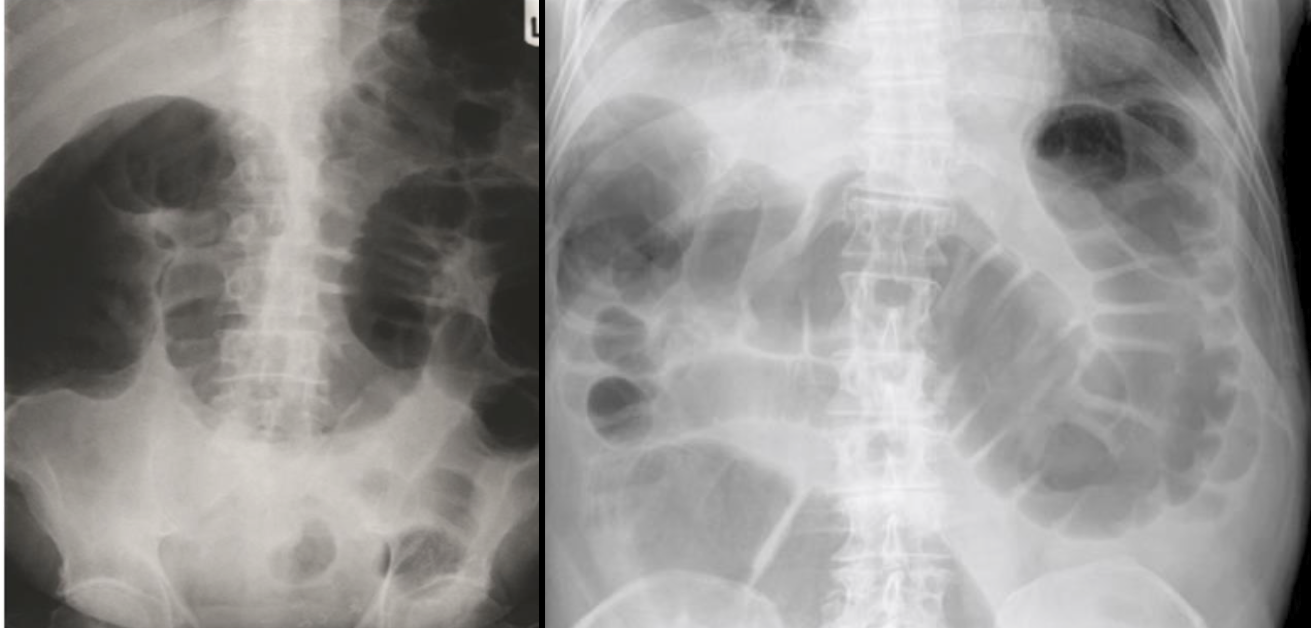
- Plain radiography (flat and upright)
- Contrast radiography with enema
Computed tomography (CT) –
- This is the imaging modality of choice
Colonoscopy/Bx
Management
Initial therapy
- Volume resuscitation
- Appropriate preoperative broad-spectrum antibiotics
- Timely surgical consultation
- Consideration of a nasogastric tube for severe colonic distention and vomiting
The following are emergencies that call for surgical intervention:
- Closed loop obstructions
- Sepsis due to complicated diverticular disease
- Bowel ischemia
- Volvulus
Supportive measures:
- Nil By Mouth
- Intake- output charts
- IV lines, and rehydration (IV crystalloid with K+)
- Foley’s catheter
- NG Tube to aspirate content for ‘decompression’
- TED stockings, DVT prophylaxis
- Antibiotics
- Antiemetics
- Analgesia
Surgery:
Closed loop obstructions, Sepsis, Bowel ischemia, Volvulus