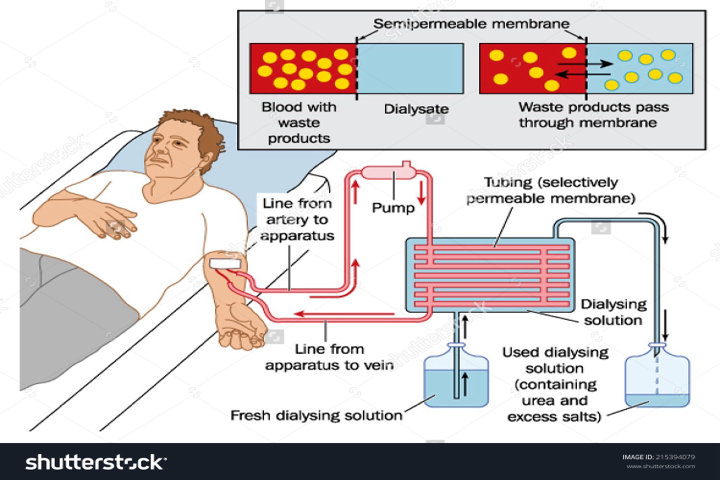
HEMODIALYSIS
- Most commonly used type of dialysis
- Blood from the patient goes into the machine
- “dirty things” removed
- clean blood returns to the body
- The dialysis solution in the machine is called “dialysate”
VASCULAR ACCESS FOR HEMODIALYSIS
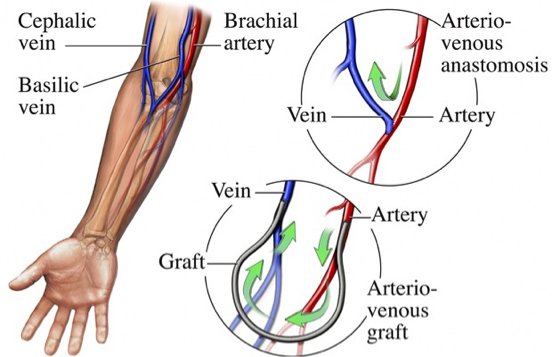
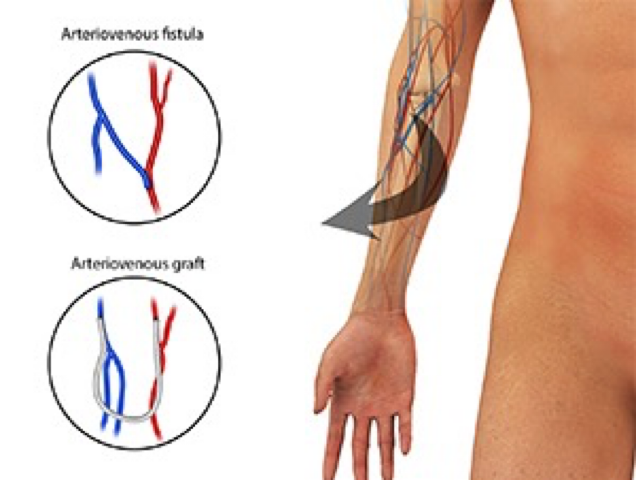
FISTULA OR GRAFT FISTULA IS PREFERRED (less chances of infection & also longer lasting). (remember: F F Fistula First)!
Fistula/Graft is always placed in the non-dominant arm.
Fistula or graft need some time to “mature” and so cannot be used immediately (Fistula takes few months & graft takes few wks)
For immediate use: central line
- Internal Jugular vein
- Subclavian vein
- Femoral vein
Note
- Hemodialysis is done in hosp. / dialysis centers
- Usually done 3 times / wk
- Each session is about 3-4 hrs.
- Heparin is used as an anticoagulant.
H.D.
ADVANTAGES
- Efficient removal of waste
DISADVANTAGES
- Needs special team and equipment
- Needs heparinization
- Can not be done if BP is low
- Not possible in people with poor veins
COMPLICATIONS of H.D.
-
Hypotension (during dialysis)
- due to too much fluid removal
- Rx: Give iv fluids, decrease the rate of dialysis
-
Blockage of the fistula/graft (thrombosis or stenosis)
-
Infection of the graft, fistula or central line
-
Dialysis Disequilibrium syndrome Occurs in the first few treatments when dialysis is started for the first time
Rapid removal of toxins and water causes osmolar shifts in the blood → cerebral edema → N/V, headache, seizures
So, in the beginning, start H.D. with shorter time duration (may be 1-2 hrs each session).
-
Dialysis steal syndrome: Decreased blood flow to the palm & fingers, causing pain, pallor and may be necrosis of hand muscles