MED
Pulse
Palpate the radial pulse Heart Rate: the number of pulses occurring per minute Rhythm: the pattern or regularity of pulses Volume: the perceived degree of pulsation
- Normal volume
- Small volume – low cardiac output
- Large volume – thyrotoxicosis, anaemia
Character: an impression of the pulse waveform or shape. Radio femoral delay (Coarctation of the aorta) Vessel Wall stiffness (arteriosclerosis)
Rate - Feel the radial pulse with 2 or 3 fingers. Count the pulse rate for 15 seconds and multiply for 4 to get pulse rate per minute
Locomotor Brachialis
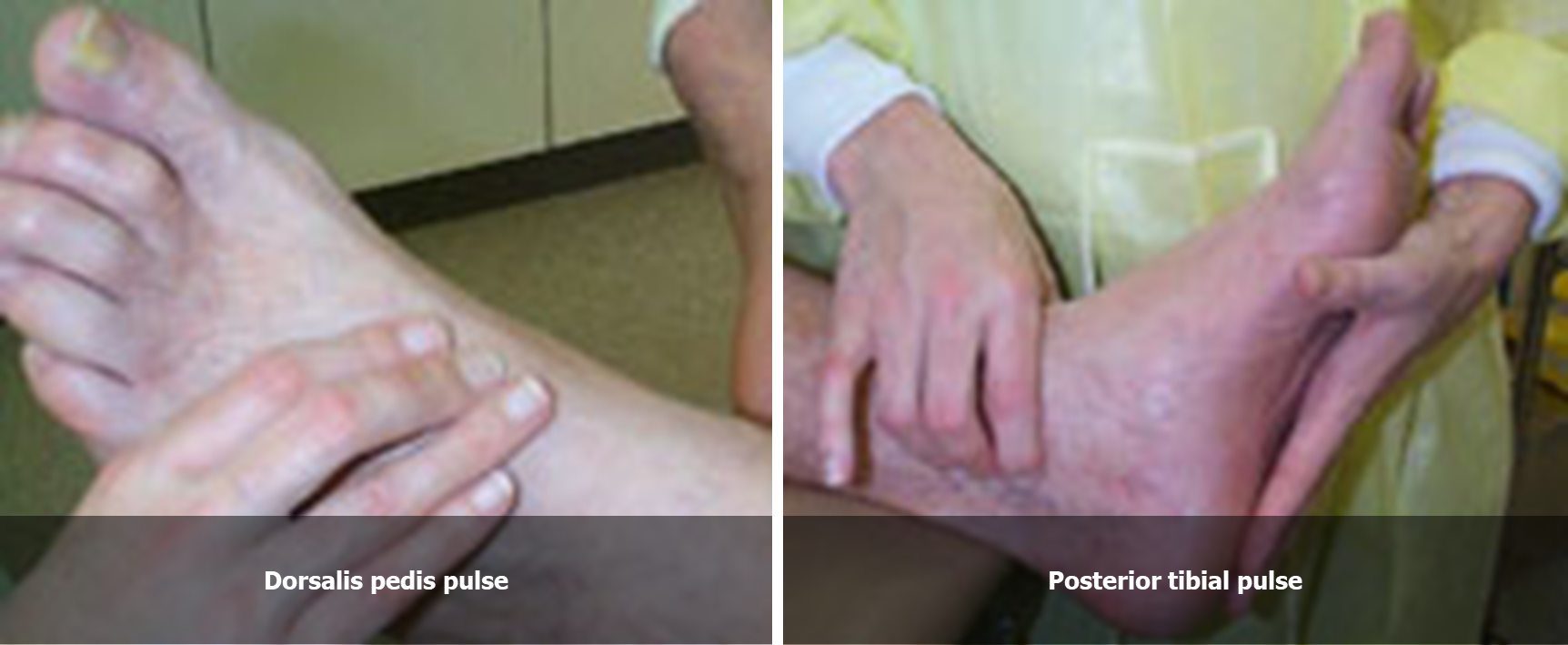
Peripheral Pulses Peripheral Pulses Examination
Skill
defined as pressure blood pushing on wall of artery, as heart beats and rests
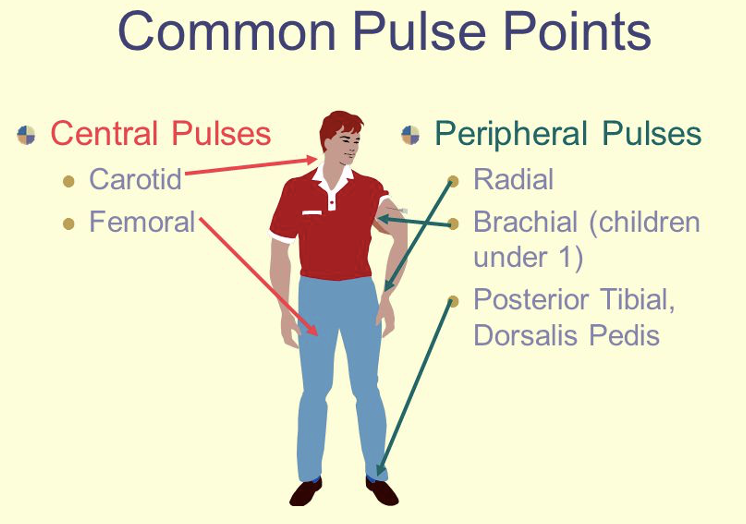
- There are two types of pulses A) Central pulse: Carotid & Femoral B) peripheral pulse: Radial, Brachial (blood pressure), Post. Tibial, Dorsalis Pedis
Blood Pressure devices
- Aneroid
- Electronic
- Mercury
Blood pressure measurement process
- Position of arm should be at level of hearts
- Measure by side of bicep tendon, medial.
- the mercury device should be above the brachial artery.
- then check radial artery pulse.
- start pressurizing till level where you cant feel radial pulse then increase 20-30 barr. becomes systolic -
- then use stethoscope to check barchial artery, deflate; when you hear sound its systolic, when it stops it becomes diastolic when disappears.
Arterial Pulse points

Terms to remember
Radio femoral delay Femoral pulse is delayed compared to radial pulse.
Pulsus Paradoxus Pulse becomes undetectable during inspiration
Peripheral pulse (Intact or not felt)
Examination
Examine both peripheral and central pulses. Describe them by the following characteristics:
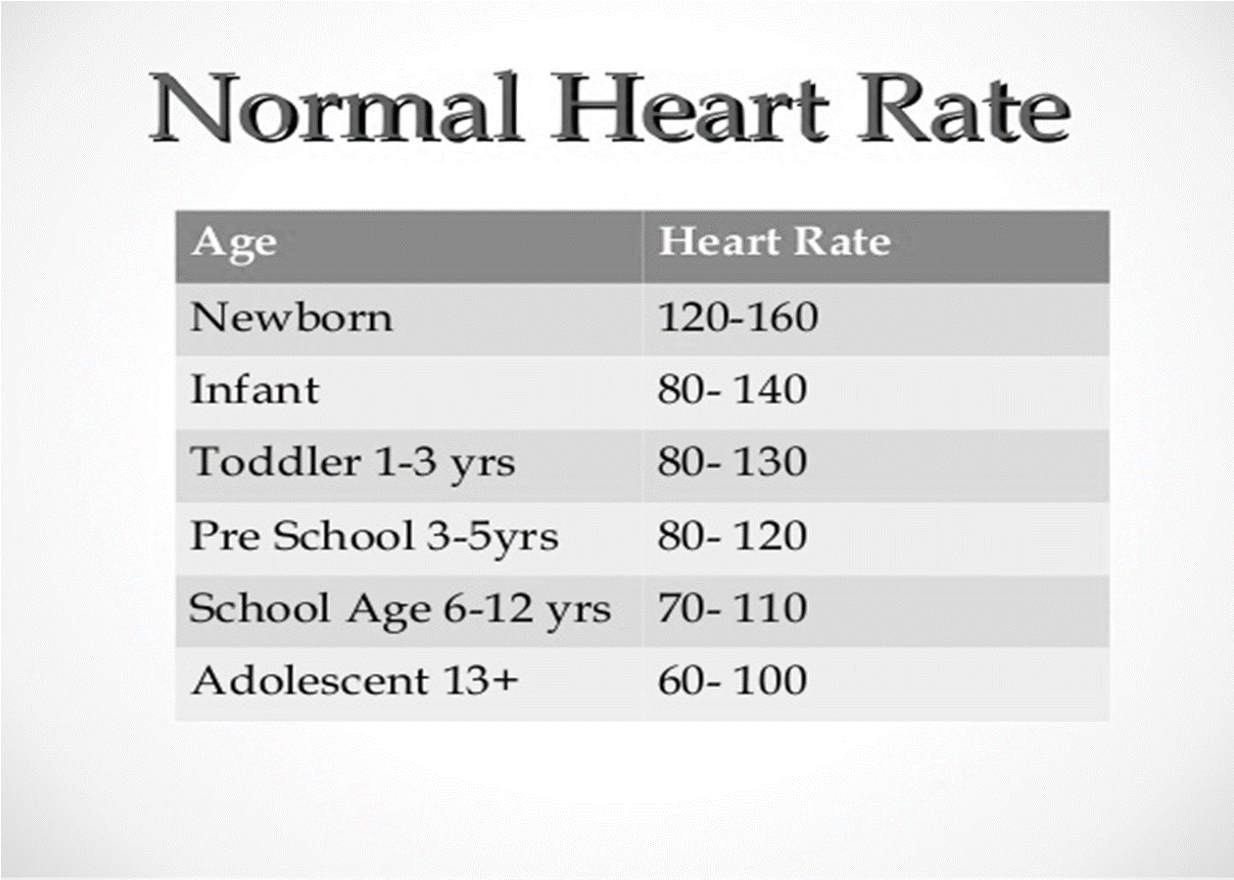
- Pulse rate: expressed in beats per minute
- Normal (60-100 bpm)
- bradycardia(<60bpm)
- tachycardia(>100bpm)
-
rhythm (regular, irregular “regular, irregular”)
-
Volume (large, weak, normal)