DIALYSIS
DR WAQAR
NORMAL FUNCTIONS OF THE KIDNEY
- To excrete toxic metabolites (urea, creatinine, acids produced in the body)
- To maintain serum electrolytes (Na, K, Phosphorus, Cl, Mg. etc)
- To maintain fluid balance
- To regulate RBC synthesis (erythropoietin production)
- To make Vit D (so, renal disease affects bone metabolism)
WHAT HAPPENS IN RENAL FAILURE?
- Accumulation of urea, creatinine, K+, Mg, organic acids
- Accumulation of fluid (causes HTN and edema)
- Impaired synthesis of RBC (due to low erythropoietin)
- Bone disease (non-activation of Vit.D)
First we try medical management for renal failure:
- Medicines (eg for HTN, acidosis)
- Diet control (eg low protein, low salt, low K etc)
- Fluid control (water intake)
When conservative/medical management fails, we go for: RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPY ⇒ dialysis or transplant
| DIALYSIS | TRANSPLANT |
|---|---|
| (can be for ARF or CRF) |
REMEMBER! EVERY ONE WITH RENAL FAILURE DOES NOT NEED DIALYSIS!
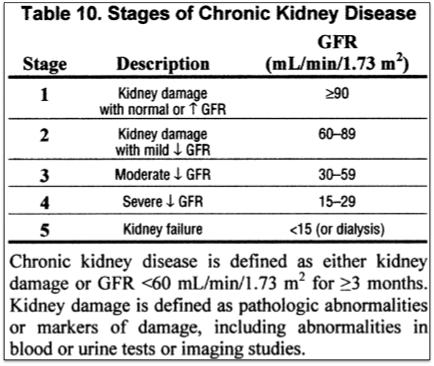
STAGES OF CRF
INDICATIONS FOR DIALYSIS
- Pulmonary edema (not responding to diuretics)
- Metabolic Acidosis (not controlled by HCO3 tab.)
- Uremic encephalopathy (seizures etc)
- Neuropathy (foot drop, wrist drop)
- Very low GFR
- less than 10 ml/min
- in DM, less than 15 ml/minZ
- Hyperkalemia (more than 7 meq). (do you remember other treatments of hyperkalemia?)
- Uremic pericarditis
- Anemia refractory to erythropoietin & Fe Rx
Some of the above may need urgent dialysis
Dialysis can be needed in, both, acute renal failure or chronic renal failure.
Dialysis is also done in many cases of drug overdose and poisonings (to remove the drug) eg aspirin, methanol
TYPES OF DIALYSIS
LONG TERM COMPLICATIONS OF BOTH TYPES OF DIALYSIS
- Cardiovascular disease (due to accelerated atherosclerosis in coronaries).
- It is the leading cause of death in these patients
- Amyloidosis (Deposition of amyloid in various tissues).
- Sepsis
RAPID FIRE QUES
- Name some indications of dialysis?
- At what GFR level you do dialysis?
- Which dialysis is better and why?
- Name the 2 types of vascular access for H.D.?
- Which is better and why?
- How to do dialysis urgently if no vascular access?
- 2 disadvantages of H.D.?
- Name 5 complications of HD?
- In the initial days of HD, which complication can occur?
- How to avoid it?
- Name 3 indications of peritoneal dialysis?
- 4 complications of PD?
- When is PD contraindicated?
- PD is contraindicated in DM patients, right or wrong?
- Long term complications of both types of dialysis?