Antenatal & Postnatal Depression & Anxiety
Dr Mona Ahmed

Depression
Definition:
Persistent low mood or loss of interest ≥2 weeks.
Risk Factors:
- Past psychiatric illness
- Lack of social support
- Marital/family conflict
- Unplanned/unwanted pregnancy
- Medical complications
Anxiety
Definition:
Excessive worry, fear, or nervousness interfering with daily life.
Types:
GAD, panic disorder, phobias, OCD.
Risk Factors:
- Previous anxiety disorder
- Stressful life events
- Family history
- Lack of support
Screening Tools
- Depression: EPDS, PHQ-9
- Anxiety: GAD-2 → if ≥3 → GAD-7
- Screen at every antenatal & postnatal visit
Management - General Principles
Non-pharmacological:
- Psychoeducation & counseling
- CBT, interpersonal therapy
- Support groups
Pharmacological (if severe):
- Antidepressants (SSRIs)
- Anxiolytics (avoid benzodiazepines in pregnancy)
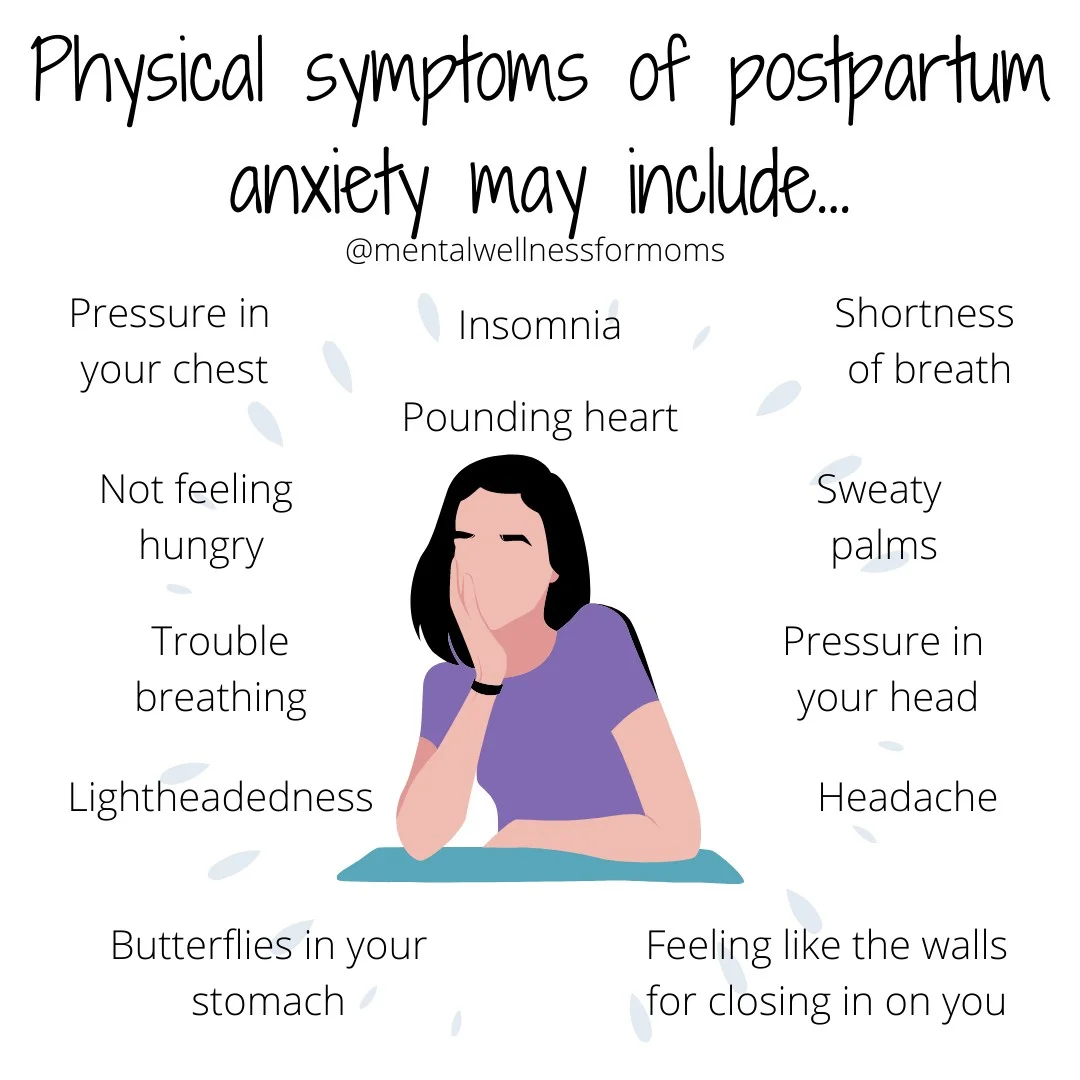
Physical Symptoms of Postpartum Anxiety
Physical symptoms of postpartum anxiety may include…
- Pressure in your chest
- Not feeling hungry
- Trouble breathing
- Lightheadedness
- Butterflies in your stomach
- Insomnia
- Pounding heart
- Shortness of breath
- Sweaty palms
- Pressure in your head
- Headache
- Feeling like the walls are closing in on you
Coping Strategies and Treatments for Postpartum Anxiety
-
MEDICATION Notably, there are potential complications that can arise from breastfeeding and taking medication at the same time.
-
COGNITIVE BEHAVIOUR THERAPY CBT is a technique used by mental health professionals to help you identify your emotions and change your thought patterns.
-
SEEKING SUPPORT Do not be afraid to lean on your support network because it really does take a village.
-
HEALTHY LIFESTYLE CHOICES Remember to take care of yourself by prioritizing eating a healthy diet and sleeping as much as you can.

Key Takeaways
- Depression & anxiety are common in perinatal period
- Early screening is essential
- Use stepwise care (mild → severe)