PUERPERIUM
DR. RAYAN ALBARAKATI
INTRODUCTION
- Definition : The puerperium consists of the period following delivery of the baby and placenta to about 6 weeks postpartum.
- In this period, the reproductive organs and maternal physiology return toward the pre-pregnancy state, and colostrum is replaced by mature milk.
ANATOMIC AND PHYSIOLOGIC CHANGES
1. Uterus:
Involution through tissue catabolism, the uterus rapidly decreases in weight from about 1000 g at delivery to 100 to 200 g at about 3 weeks postpartum, and at a rate of 1cm/day.
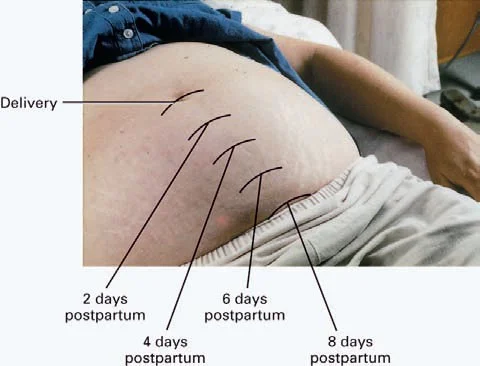
2. Cervix :
Similarly loses its elasticity and regains its pre-pregnancy firmness.
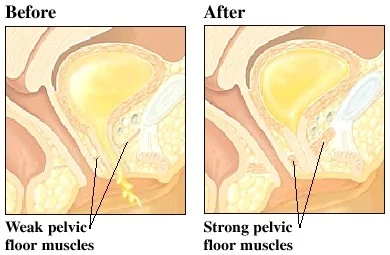
3. Vagina :
Although the vagina may never return to its pre-pregnancy state, the supportive tissues of the pelvic floor gradually regain their former tone & strength. This can be encouraged by doing Kegel exercises (intermittent tightening of the perineal muscles) to maintain & improve the supportive tissues of the pelvic floor.
Pelvic floor muscles
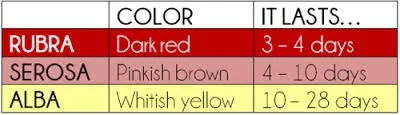
LOCHIA (THE UTERINE DISCHARGE)
Postpartum uterine discharge (lochia) appears red (lochia rubra). After 3 to 4 days, the lochia becomes paler (lochia serosa), by the 10th day, it assumes a white or yellow-white color (lochia alba).
- Note : Foul-smelling lochia suggests endometritis.
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
- Immediately after delivery, there is a marked increase in peripheral vascular resistance due to the removal of the low-pressure uteroplacental circulatory shunt.
- The cardiac output and plasma volume gradually return to normal during the first 2 weeks of the puerperium.
- As a result of the loss of plasma volume and the diuresis of extracellular fluid, a marked weight loss occurs in the first week.
Introduction
The puerperium consists of the period following delivery of the baby and placenta to about 6 weeks postpartum.
In this period the reproductive organs and maternal physiology return toward the pre-pregnancy state, and colostrum is replaced by mature milk.
PSYCHOSOCIAL CHANGES
- It is fairly common for women to exhibit a mild degree of depression a few days after delivery.
- The “postpartum blues” are probably due to both emotional and hormonal factors.
- With understanding, this usually resolves without consequence.
- Any prolonged episodes of depression should receive urgent attention.
RETURN OF MENSTRUATION & OVULATION
- In women who do not nurse, menstrual flow usually returns by 6 to 8 weeks.
- Contraceptive counseling and use should be emphasized during the puerperium to avoid an undesired pregnancy.
FOLLOW UP FOR EPISIOTOMY OR C/S WOUND
1. Episiotomy:
It is sutured with absorbable material for stitching and it gets absorbed or just falls off with time; however, you have to ensure before discharge that there is no gapping of wound and educate about the signs of infection.
2. C/S scar:
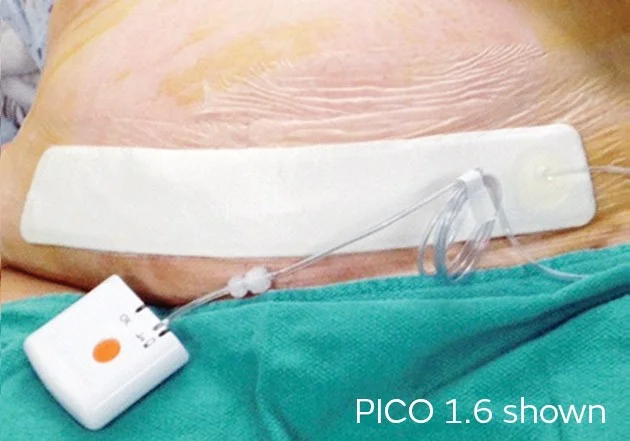
Sutured and cared for with waterproof dressing, then it is exposed to air after 48 hours or in some cases of high risk for infection, negative pressure dressings can be used instead and kept for longer periods.
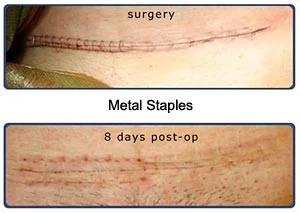
3. It could be sutured by stitches or clips
- A. Stitching: either subcutaneous (no visible stitches) or interrupted (falls within 3 weeks).
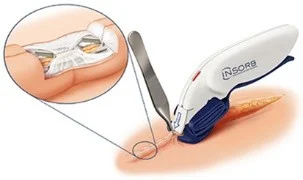
- B. Clips: either non-absorbable removed on day 5 to 7 OR absorbable, placed in subcuticular layer and dissolves by its own (INSORB).
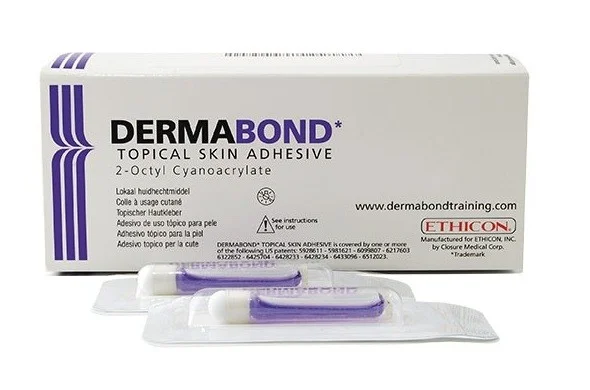
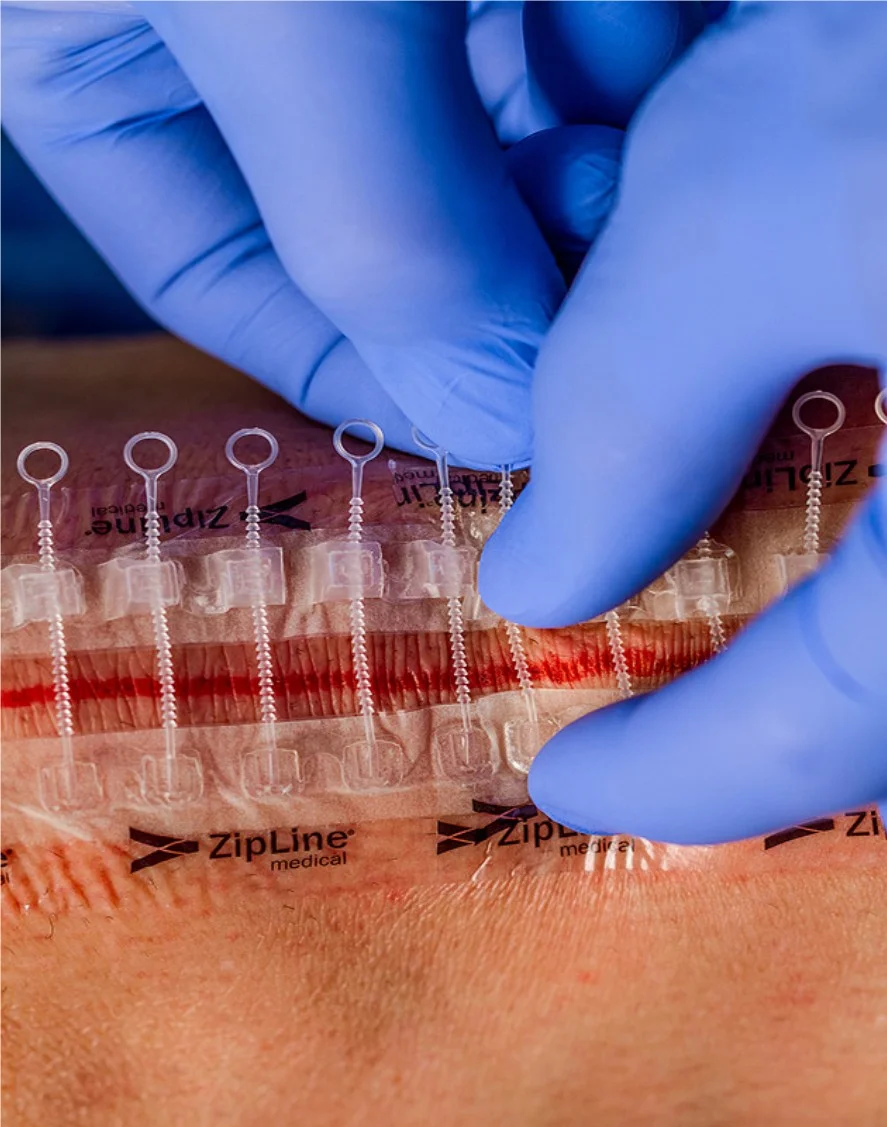
Others:
Glue (Dermabond), non-invasive skin closure zipper (Zipline medical).
EPISIOTOMY CARE
- Immediately after birth and whenever swelling is present, use an ice pack for comfort.
- You may also use a portable Sitz bath or sit in a shallow amount of warm bath water.
- Repeat 3 to 4 times per day for about 10 minutes, until the swelling has gone. Alternating heat and cold may be helpful.
- Perineal pain usually improves daily.
- Take a mild pain reliever (such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen) if needed.
- Begin exercises as soon as possible.
- Keeping your stool soft and following instructions for hemorrhoids (below) will also help.
Sitz Bath

Metal Staples
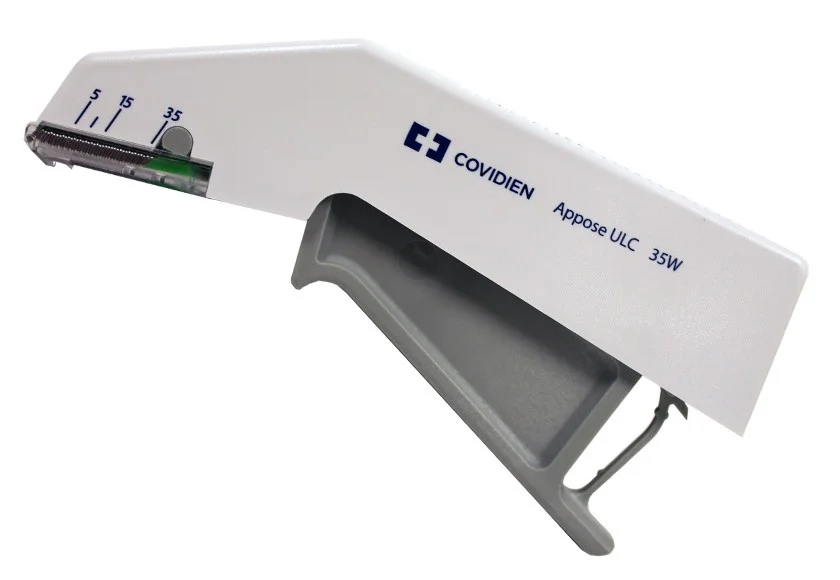

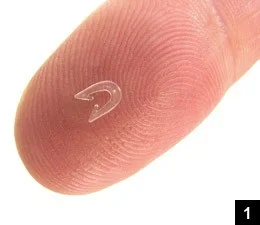
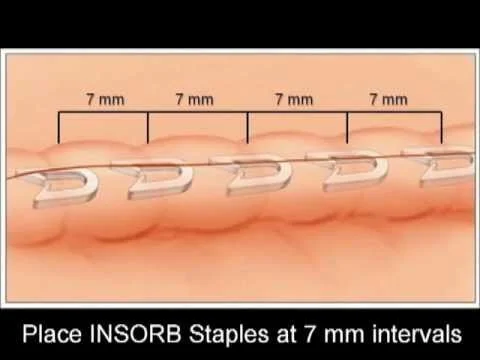
Place INSORB Staples at 7 mm intervals
- The image shows a visual guide on how to place INSORB Staples.
- The staples are to be placed at 7 mm intervals.
- A diagram illustrates the correct spacing between the staples.
- An image shows a close-up of a staple on a fingertip, demonstrating its size.
- Another image depicts the application of INSORB Staples using a specialized tool.
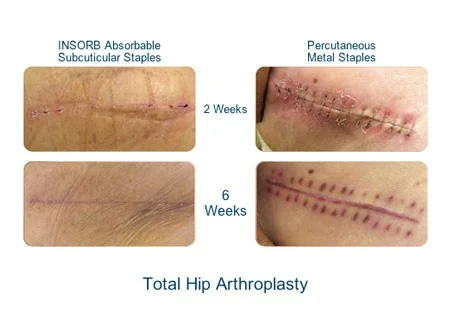
INSORB Absorbable Subcuticular Staples vs. Percutaneous Metal Staples
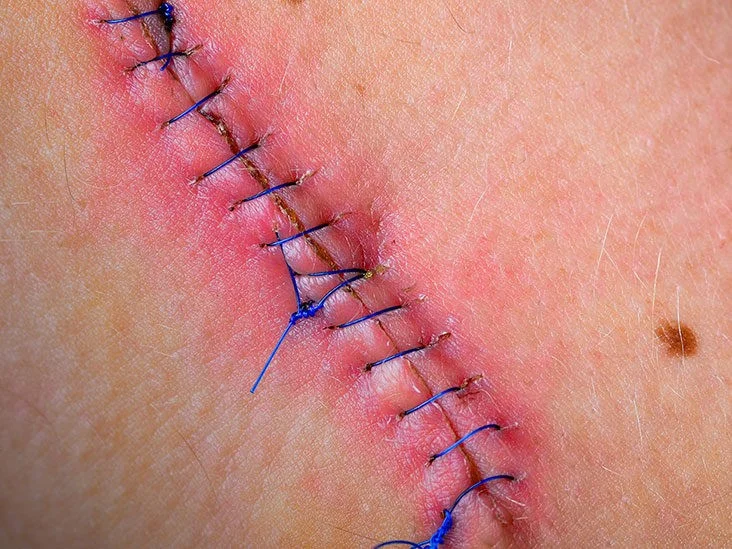
INFECTED STITCHES
PEEL DOWN
PEEL DOWN

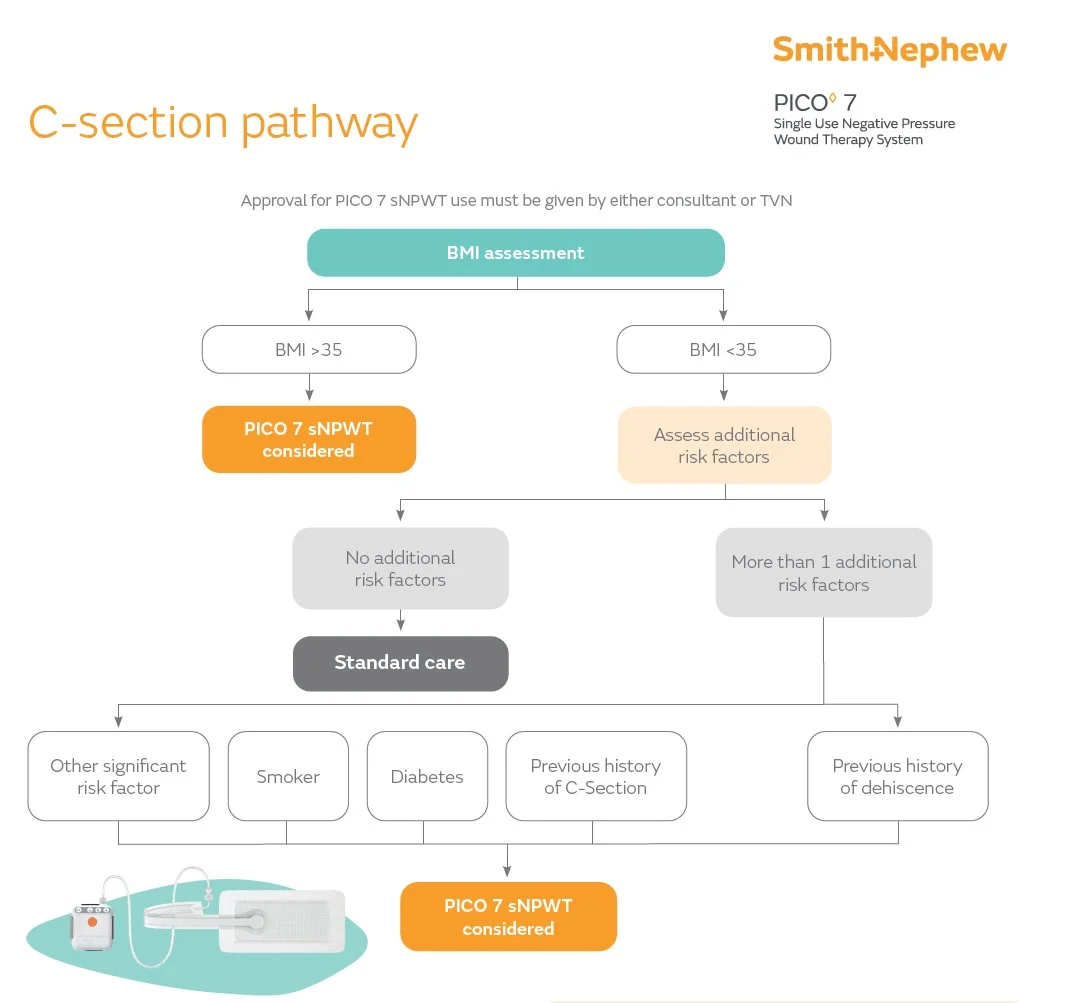
CESAREAN SECTION WOUND INFECTION PREVENTION
- BMI assessment
- BMI >35
- PICO 7 sNPWT considered
- BMI <35
- Assess additional risk factors
- No additional risk factors
- Standard care
- More than 1 additional risk factors
- Other significant risk factor
- Smoker
- Diabetes
- Previous history of C-Section
- Previous history of dehiscence
- PICO 7 sNPWT considered
- Other significant risk factor
- No additional risk factors
- Assess additional risk factors
- BMI >35
COMMON POST PARTUM COMPLICATIONS AND MANAGEMENT:
- Breast: Breast engorgement – cracked nipples – mastitis – breast abscess
- Episiotomy site: pain – infection
- Emotional disturbance: feeling overwhelmed – concerned about her physique
- Abdominal pain: uterine involution- endometritis - surgical site infection
- UTI
- Fever or Post partum pyrexia … what’s the difference?
- Vaginal infection vaginitis fungal/bacterial
- Constipation
- Hemorrhoids
POST PARTUM PYREXIA
- Definition?
- Incidence?
- Risk factors?
- Causes?
CONDUCTING A POST PARTUM ROUND
- History: review history, delivery notes, and documents including labs, baby outcome, and any previous orders or recommendations.
- Documentation: Title (post partum round, physician note), day of post partum with pt. parity, mode of delivery, and any major medical or surgical history, use the SOAP approach.
- Physical examination: V/S - general - fundal height & Abdominal distention - lochia - episiotomy site or c/s wound - Lower Limbs.
- Labs: CBC, blood group, rubella screen, U.A, blood sugar.
- Instructions: for breastfeeding – episiotomy site/cesarean section wound- life routines.
- Contraception & medications: counsel the pt. & review her medications.
- Discharge: anytime between 12 hours to 5 days depending on multiple factors.
- Follow up: routinely 6 weeks — what about other special conditions?
- Referrals?
POSTPARTUM ROUND DOCUMENTATION SAMPLE
Post-Partum Hospital Notes
