Coarctation of Aorta
-
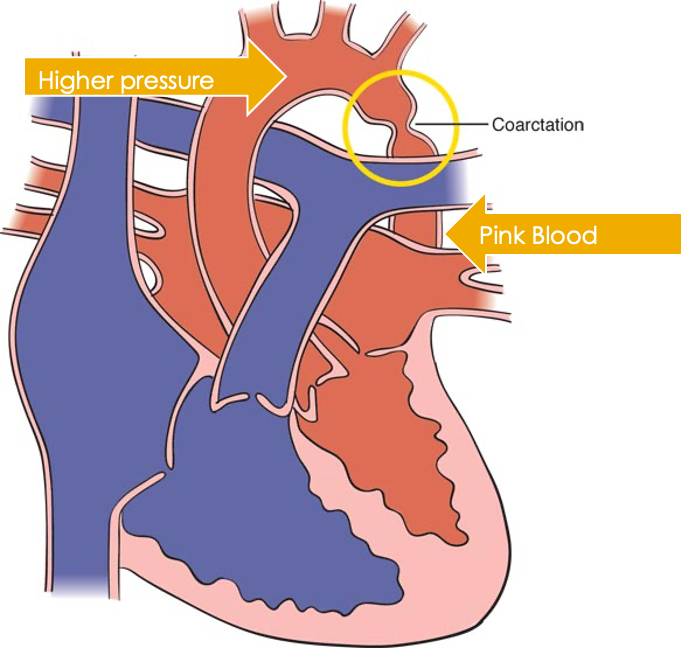
Constriction of the aorta at or near the insertion site of the ductus arteriosus
-
Reduces cardiac output
-
Aortic pressure is high proximal to the constriction and low distal to the constriction - Risk for CVA
-
Pink Blood
-
Higher pressure
Symptoms of Severe Coarctation of Aorta
- Often discovered 3-4 days after birth when the patent ductus arteriosus closes
- Symptoms of shock develop very rapidly as no oxygenated blood flows to the lower extremities
- Rapid breathing, sweating, and poor feeding often develop during the first week
Signs of Severe Coarctation of Aorta
- Most babies born at term with normal length and weight
- Systolic murmur usually heard
- Liver may be enlarged
- Left arm/leg pulses may be diminished or absent
- BP is about 20 mm/Hg higher in arms than in lower extremities
- Upper extremity hypertension
- Lower extremity cyanosis
Treatment of Severe Coarctation of Aorta
- Medical Management (Dopamine, dobutamine, Lasix)
- Oxygen
- Administration of PGE1 (prostaglandin) infusions, to maintain ductal patency and improve perfusion to lower extremities - although will cause increased pulmonary flow
- Surgical repair