History
- The course of pain.
- Is there evidence of a systemic disease?
- Is there evidence of neurologic problems?
- Occupational history.
- Risk factors.
- Red flags.
- Yellow flags.
- Circumstances associated with pain onset.
- Factors altering pain (stiffness at rest or at night, decrease with movement)
- Is pain present continuously or on & off?
- Effect of pain on activities.
- Effect of pain on sleep.
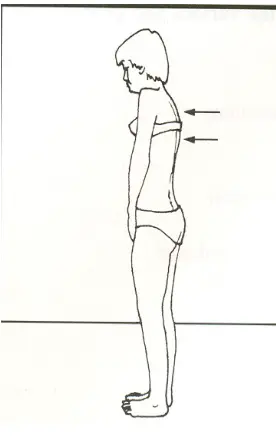
Back Pain Examination
- Inspection of back and posture
- Palpation/Percussion of spine
- Range of motion
- Neurologic examination
- Straight Leg Raising (SLR)
General Examination Principles
- Permission
- Explain
- Privacy
Vital Signs
- Patient should be standing with the whole trunk exposed.
Examination Steps
- Look ➔
- Feel ➔
- Movement ➔
- Neurologic Al tests
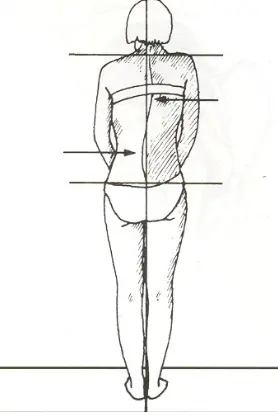
Inspection
-
Gait
-
Posture
- head/shoulders, — listing, flexion/extension, pelvic tilt
-
Muscle balance, - Habitus
-
Alignment
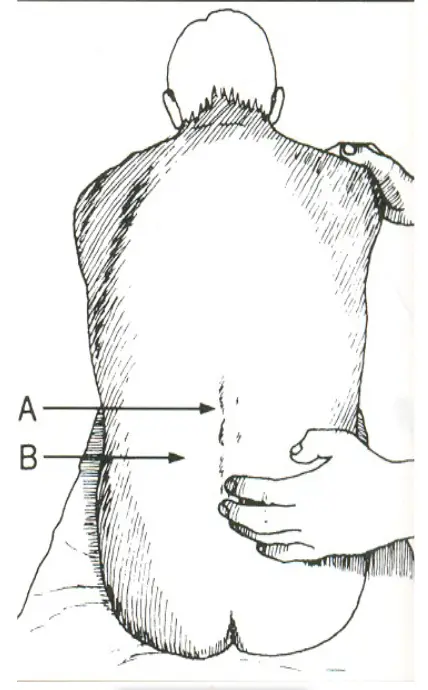
Palpation and Percussion
-
Bone
- tenderness or deformity -
- over spinous processes
- tenderness or deformity -
-
Joints
- facet and sacroiliac joint -
- tenderness
- facet and sacroiliac joint -
-
Muscles
- paraspinal tension and -
- trigger points
- paraspinal tension and -
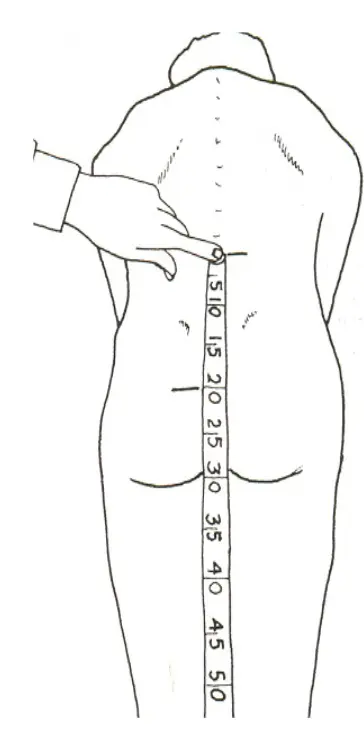
Range of Motion
- Often very limited globally -
- Secondary to pain
- Perform slowly with physical -
support
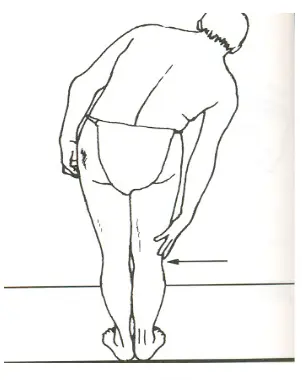
Flexion (normal = 90 degrees)
Lateral Bending
- (normal = 45 degrees, hand to knee)
Rotation
- (normal = 90 degrees, stabilize hips)
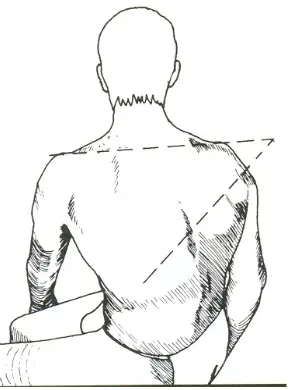
Extension
- (normal = 30 degrees)
- narrows canal, loads facet joints
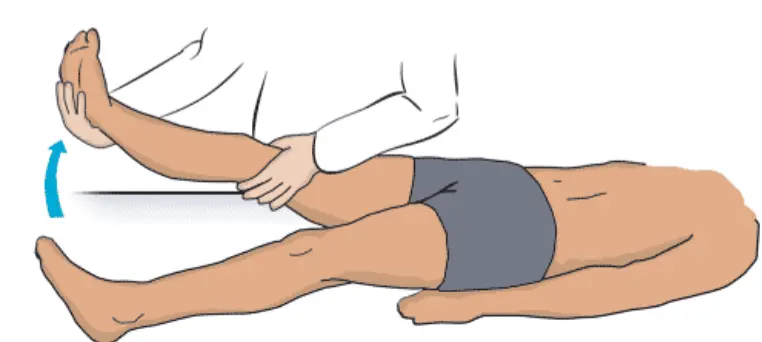
Straight Leg Raising (SLR) OSPE
-
Raise the patient’s extended leg with the ankle dorsiflexed.
-
Normally 80 – 90 degrees no pain
-
It will be limited by sciatica pain in lumbar disc prolapse. (<70 ) → (exactly from 30 to 70)
Neurologic Testing
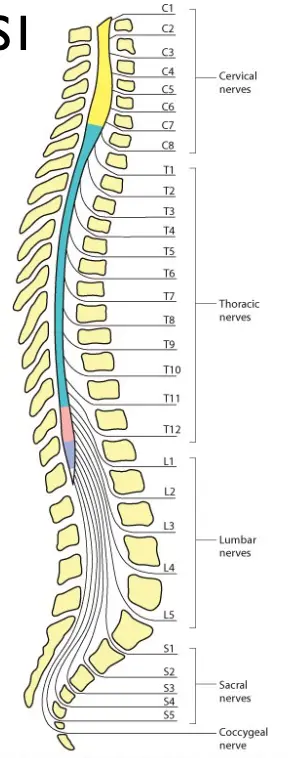
- We should focus on the L5 and S1 nerve roots
- 98% of disc herniation occurs at L4-5 and L5-S1
- Then we test the Reflexes:
- L4 – The knee reflex.
- S1 – The ankle reflex.
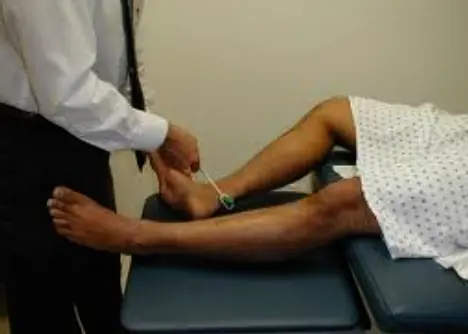
Reflexes
-
Knee (L3-4)
-
Ankle (S1-2)

Motor Testing
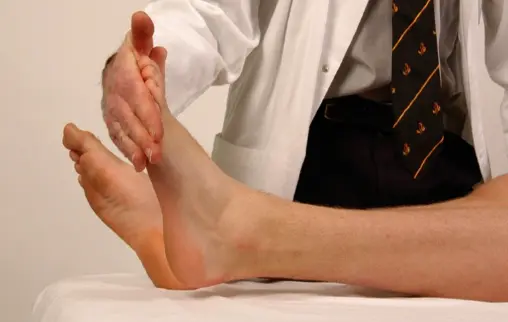
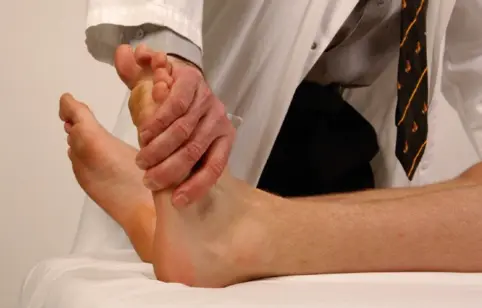
-
Ankle plantar flexion
-
Ankle dorsiflexion
-
Walking on
toes SI -
Walking on
heels L5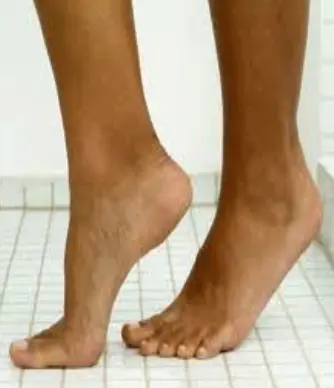
Sensory Testing
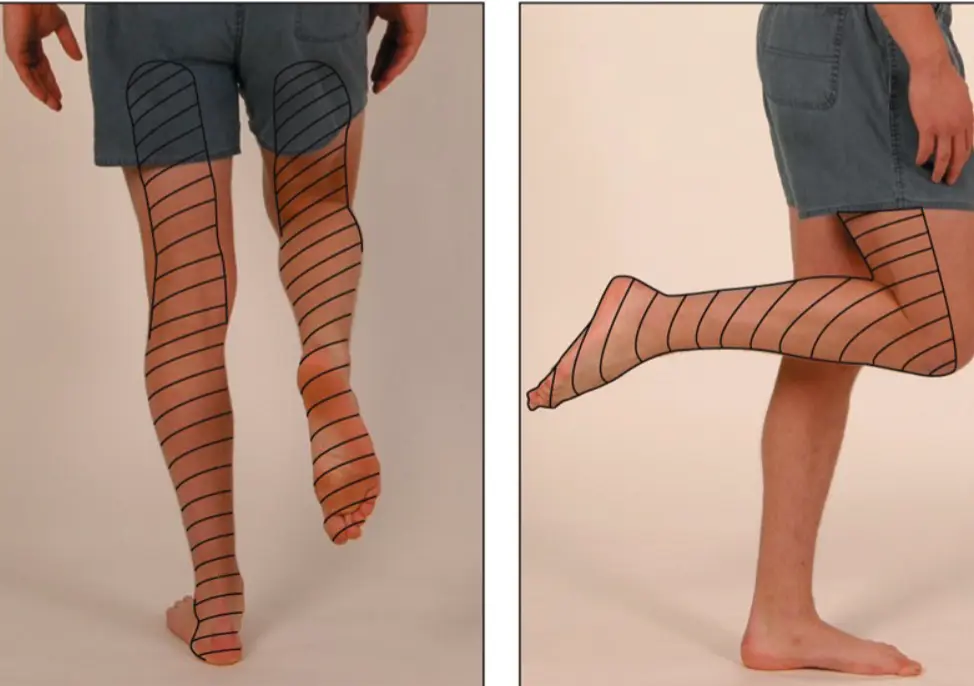
- Sciatic nerve (L4,5,S1,2)
- Sensory distribution of the sciatic nerve
