https://next.amboss.com/us/article/WS0PA2?q=bilirubin+metabolism#Z924dbf25def7ca057f504e6c7a4fd13a
The lifespan of RBCs is about 120 days. After this time, macrophages in the reticuloendothelial system of the bone and the spleen phagocytose RBCs. They are then broken down and their parts recycled. heme (red) → biliverdin (green pigment) → bilirubin (yellow pigment)
-
Heme is converted to biliverdin by heme oxygenase.
-
Requires NADPH + H+
-
Carbon monoxide (CO) is released.
-
Iron is released, oxidized, and taken up by transferrin to be recycled.
-
Biliverdin is converted to bilirubin by biliverdin reductase (requires NADPH + H+)

Heme breakdown is responsible for the color changes in hematomas.
-
Unconjugated bilirubin (insoluble in water) is released into the blood by macrophages → binds to albumin and reaches the liver
-
Unconjugated bilirubin is converted into bilirubin via enzyme UDP-glucuronosyltransferase in the liver.
Bilirubin is conjugated with glucuronic acid → bilirubin diglucuronide = conjugated bilirubin (water soluble) Most conjugated bilirubin is excreted into the GI tract via bile, while some is released into the blood.
-
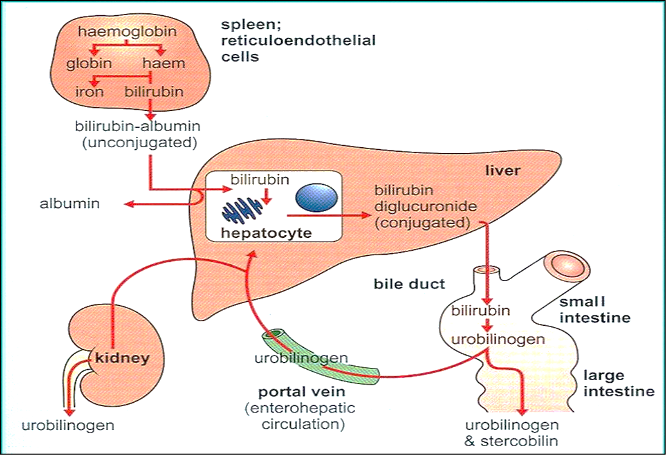
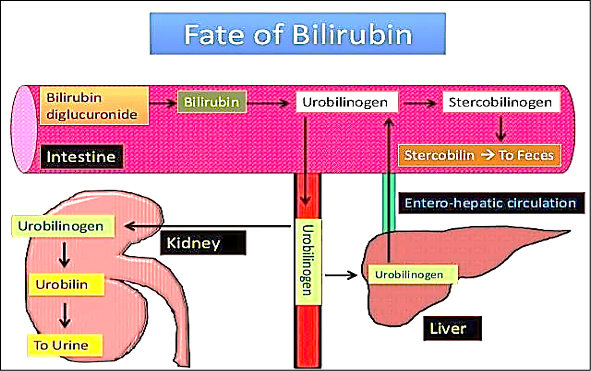
Conjugated bilirubin excreted in bile is broken down by GI bacteria into urobilinogen
Most urobilinogen is converted to stercobilin → excreted in feces (brown color). Part of urobilinogen oxidates to urobilin → excreted in the urine (yellow color)
1-Formation of Bilirubin from Heme in RES
Heme is degraded in RE system (esp. liver & spleen)
85% from RBCs
15% from turnover of immature RBCs & cytochromes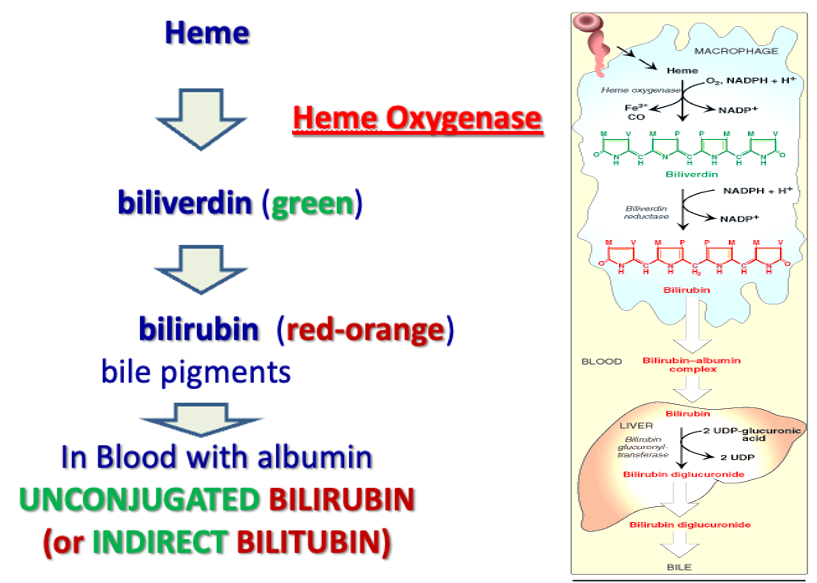
2- Bilirubin Metabolism in the Liver
1.Uptake of Bilirubin by hepatocytes: Bili dissociates from albumin & enters hepatocytes
2.Conjugation of Bilirubin: bilirubin is conjugated with two molecules of glucuronic acid by the enzyme glucuronyl transferase to form Conjugated bilirubin
3.Excretion of bilirubin into bile: Conjugated bilirubin (bilirubin diglucuronide) is transported into bile canalculi & then into bile. Process is energy dependent & is impaired in liver diseases
 In intestines
In intestines
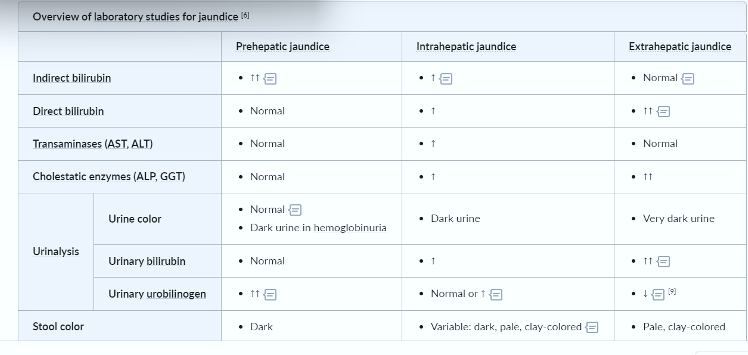
LABORATORY INVESTIGATIONS IN TYPES OF JAUNDICE