Dr. Nada Abdelrahman
Introduction
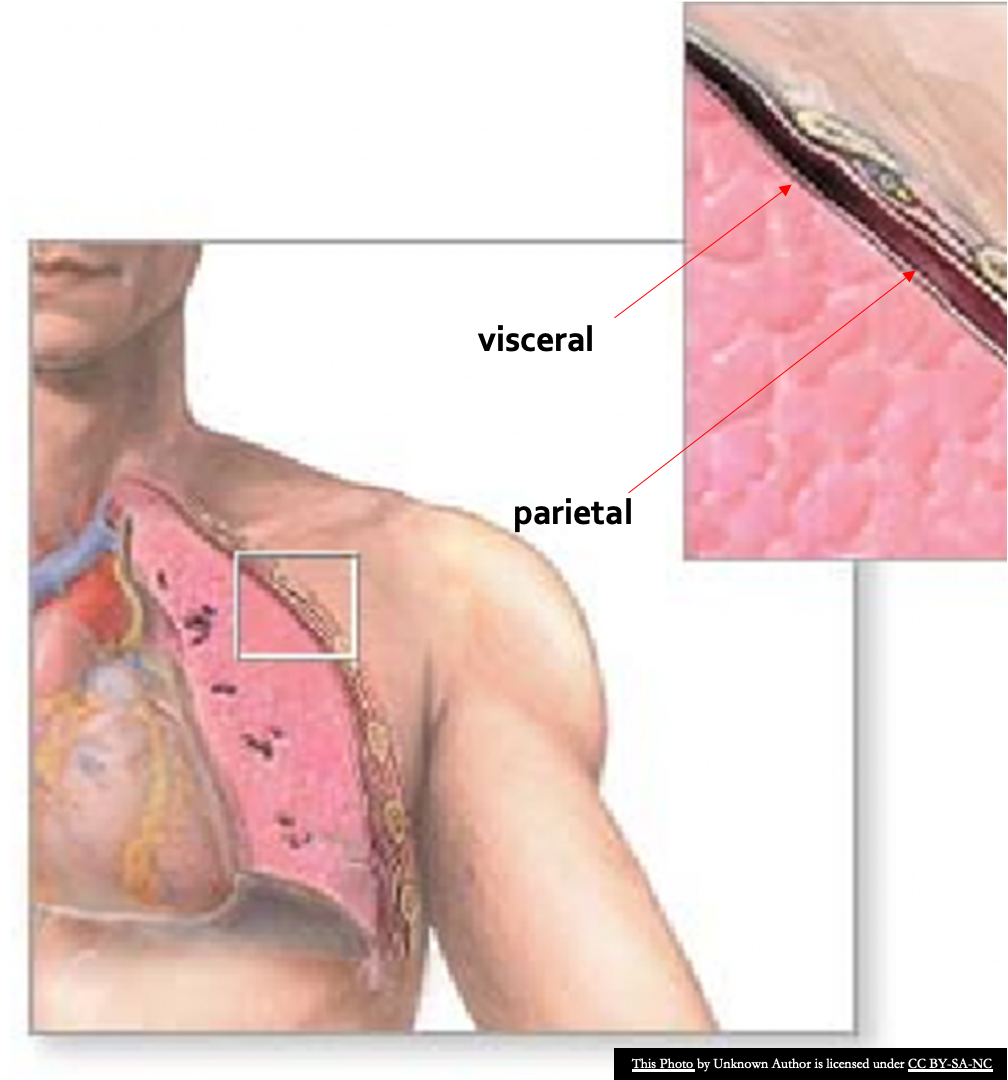
- Pleura: A layer of connective tissue covered by simple squamous epithelium.
- Two layers:
- Visceral pleura: Covers the lung surface
- Parietal pleura: Lines the thorax
- Two layers:
- Normal intrapleural pressure: Negative
- Pleural fluid: Small lubricating fluid (5-10 ml) between the visceral and parietal pleura.
- Pleurisy: Sharp localized pain worse on deep inspiration.
- Empyema: Accumulation of pus.
- Haemothorax: Accumulation of blood.
- Chylothorax: Milky accumulation of lymph in the pleural space, leakage from the thoracic duct following trauma or carcinoma.
Pleurisy: Aetiology
- Viral infections: Most common (Coxsackieviruses); abd pain, bone disease
- Bacterial infections
- Pneumonia (parapneumonic pleuritis)
- Tuberculosis (TB pleuritis)
- Inflammatory conditions:
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
- Sjogren syndrome
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Pulmonary conditions:
- Pneumothorax
- Asbestosis
- Malignancy (e.g., mesothelioma)
- Pulmonary embolism
- Cardiac conditions:
- Myocardial infarction
- Aortic dissection
- Cardiac surgery
- Drugs:
- Amiodarone, bleomycin, methotrexate; folic acid antagonist
- Isoniazid, procainamide, hydralazine for TB
- Bornholm Disease: Epidemic myalgia
- A self-limiting disorder characterized by upper respiratory tract infection due to Coxsackie B virus in young adults, followed by pleuritic chest pain, and upper abdominal pain with tender muscles.
- X-ray chest is normal.
Pleurisy: Clinical feature
Pleural Friction Rub: is heard on deep inspiration on auscultation. - sound of inflamed pleural layers rubbing together during inspiration and expiration) -
Other features include Pleuritic chest pain
Further symptoms depend on the underlying disease, e.g.:
- Constitutional symptoms
- Dry cough
- Dyspnea
Pleurisy: Diagnosis
- History and physical examination
- CXR: Signs of underlying pulmonary pathology (e.g., pneumonia, pleural effusion)
- Rule out life-threatening causes of pleuritic chest pain: ECG (MI or pericarditis).
Differential Diagnosis of Pleuritic Chest Pain
- Myocardial infarction: chest pain
- Pulmonary embolism: acute
- Pneumothorax: truama
- Pericarditis: position
- Bornholm disease
Pleurisy: Treatment
- Analgesia: NSAIDs (first line) - relief of symptoms
- Treat underlying cause accordingly.