Labs
| Total B | Direct | Type of hyperbilirubinemia |
|---|---|---|
| <5 mg/dl | ||
| 1.5 mg/dl | 0.6 mg/dl | Normal |
| 25.2 mg/dl | 20.5 mg/dl | Conjugated |
| 20.26 | 0.8 mg/dl | unconjugated |
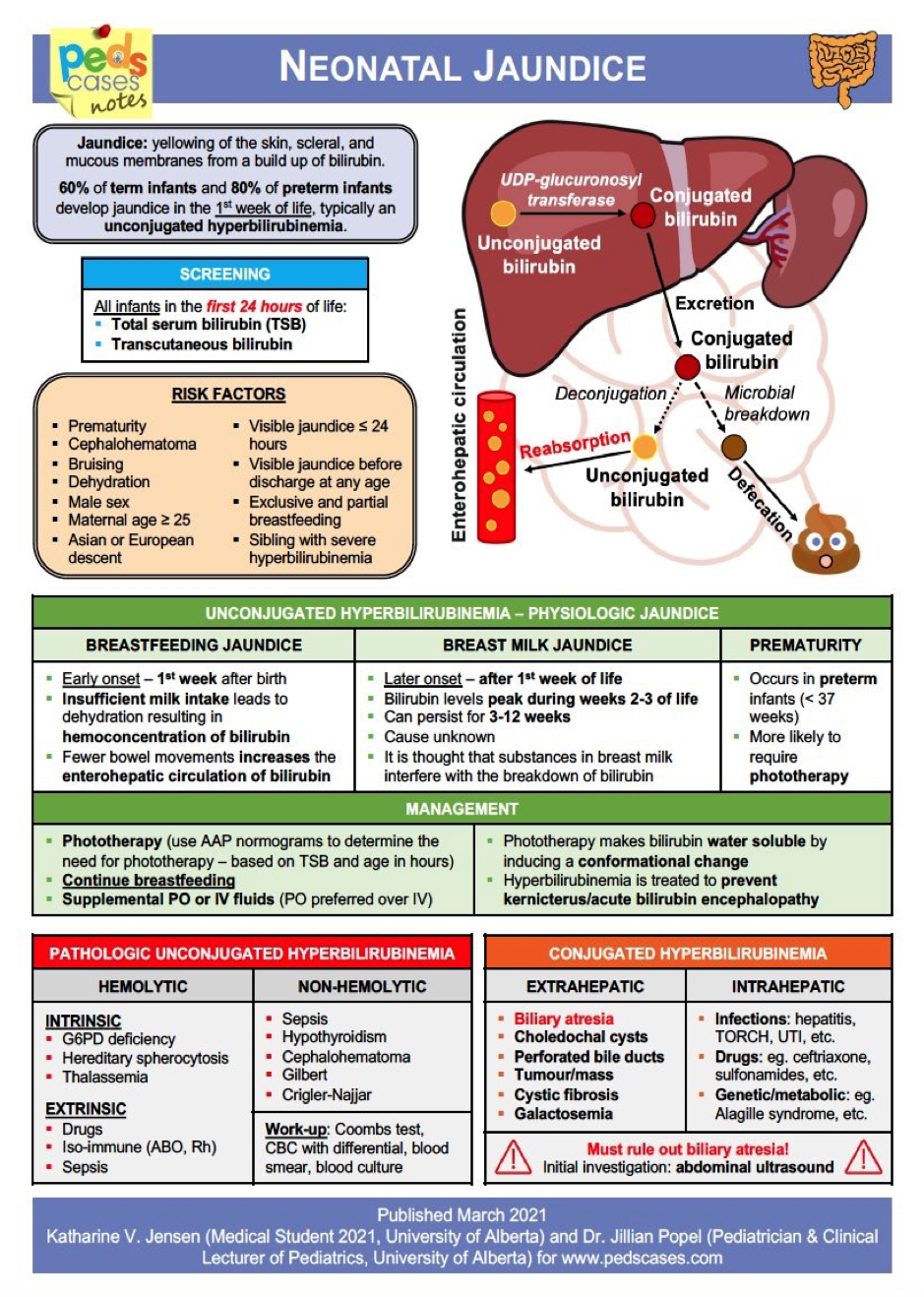
CAUSES OF HYPERBILIRUBINEMIA
Unconjugated Hyperbilirubinemia:
- ABO incompatibility
- Rh isoimmunization
- G6PD deficiency
- Cephalhematoma or extensive bruising
- Hemoglobinopathies or other RBC membrane defects
- Gilbert’s syndrome & Crigler-Najjar syndrome
- Hypothyroidism
- Breastfeeding jaundice
- Breast milk jaundice
- Ileus
- Intestinal obstruction
- UTI
Conjugated Hyperbilirubinemia:
- Biliary atresia
- Choledochal cyst
- Alagille syndrome
- Tyrosinemia
- Galactosemia
- Sepsis
- TORCH infection
- Idiopathic neonatal hepatitis
- Parenteral nutrition related cholestasis
Jaundice starting at <24 hours of age:
- Haemolytic disorders:
- Rhesus incompatibility
- ABO incompatibility
- G6PD deficiency
- Spherocytosis, pyruvate kinase deficiency
- Congenital infection
Jaundice at 24 hours to 2 weeks of age:
- Physiological jaundice
- Breast milk jaundice
- Infection, e.g., urinary tract infection
- Haemolysis, e.g., G6PD deficiency, ABO incompatibility
- Bruising
- Polycythaemia
- Crigler–Najjar syndrome
Causes of prolonged (persistent) neonatal jaundice
Unconjugated:
- Breastmilk jaundice
- Infection (particularly urinary tract)
- Haemolytic anaemia, e.g., G6PD deficiency
- Hypothyroidism
- High gastrointestinal obstruction
- Crigler–Najjar syndrome
Conjugated (>25 µmol/L): Bile duct obstruction:
- Biliary atresia
- Choledochal cyst
Neonatal hepatitis syndrome:
- Congenital infection
- Inborn errors of metabolism
- α₁-Antitrypsin deficiency
- Galactosaemia
- Tyrosinaemia (type 1)
- Errors of bile acid synthesis
- Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis
- Cystic fibrosis
- Intestinal failure-associated liver disease (associated with long-term parenteral nutrition)
Intrahepatic biliary hypoplasia:
- Alagille syndrome
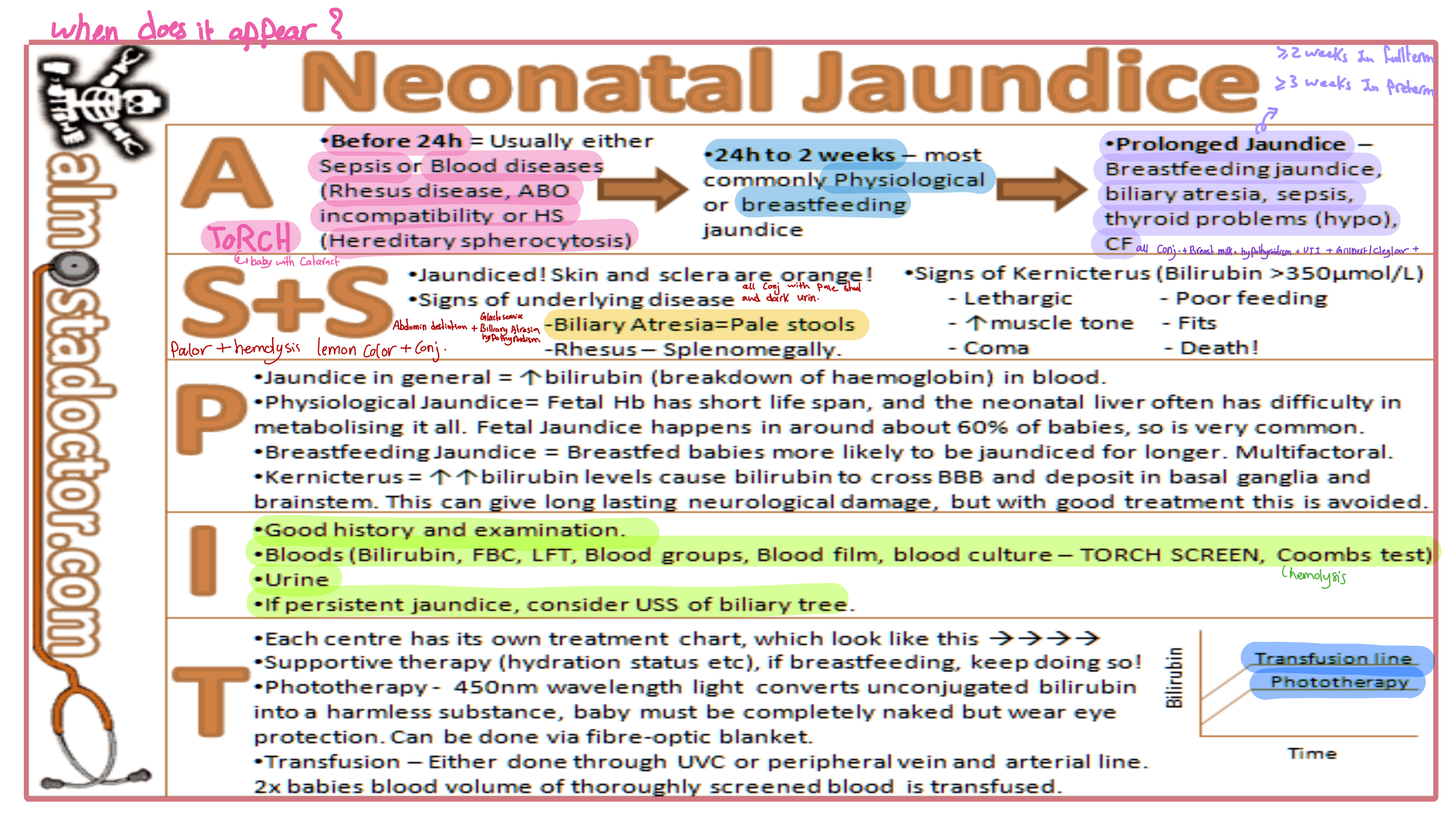
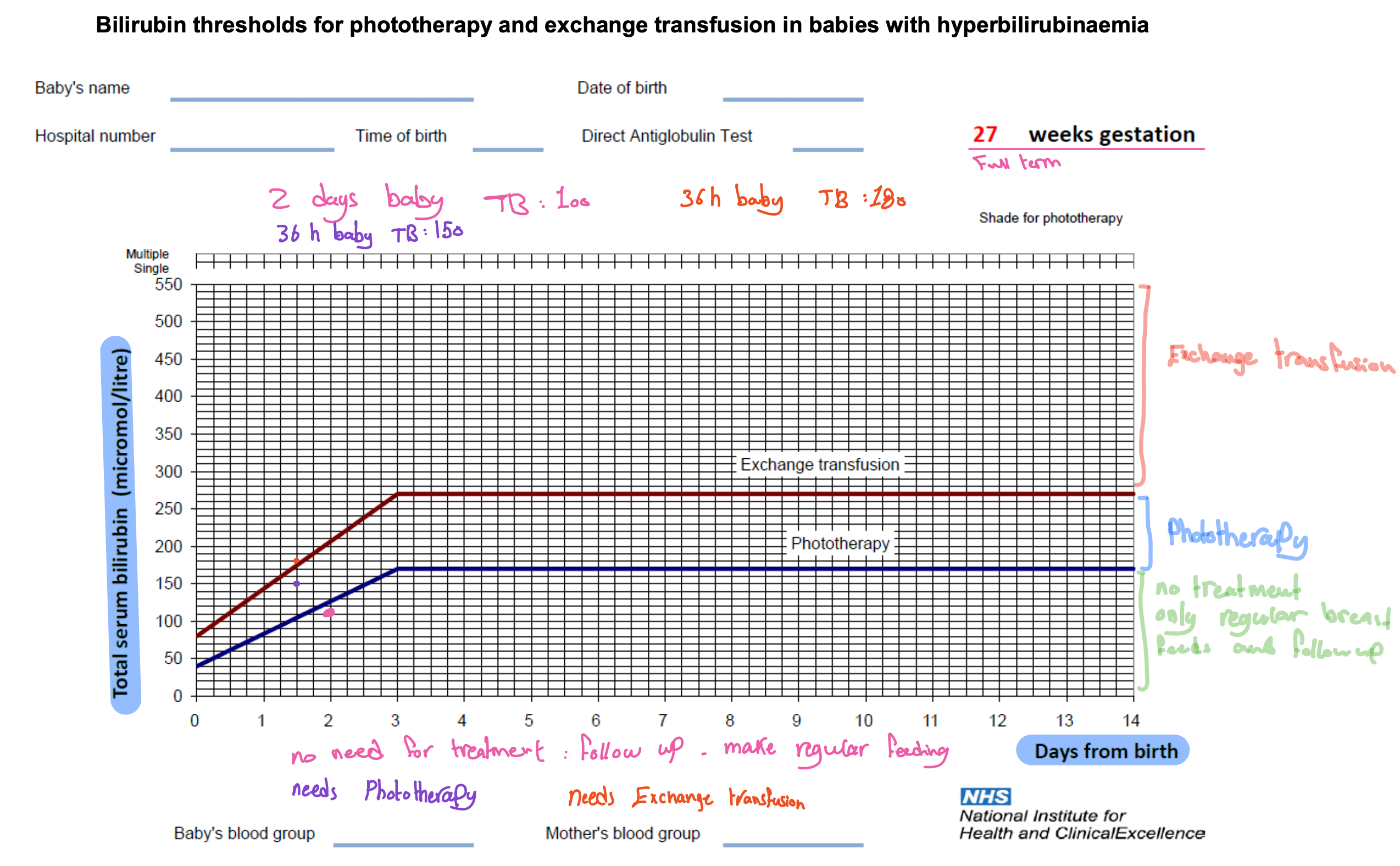
Neonatal Jaundice
When does it appear?
A
- Before 24h: Usually either Sepsis or Blood diseases (Rhesus disease, ABO incompatibility or HS [Hereditary spherocytosis])
- 24h to 2 weeks: Most commonly Physiological or Breastfeeding Jaundice
- Prolonged Jaundice: Breastfeeding jaundice, biliary atresia, sepsis, thyroid problems (hypo), CF
S+S
- Jaundiced! Skin and sclera are orange!
- Signs of underlying disease are evident:
- Pallor and Hemolysis
- Lemon color + conjugated
- Biliary Atresia = Pale stools
- Rhesus – Splenomegaly
Signs of Kernicterus (Bilirubin >350μmol/L)
- Lethargic
- Poor feeding
- ↑ Muscle tone
- Fits
- Coma
- Death!
P
- Jaundice in general = ↑bilirubin (breakdown of haemoglobin) in blood.
- Physiological Jaundice: The fetal Hb has a short life span, and the neonatal liver often has difficulty in metabolizing it all. Fetal Jaundice happens in around about 60% of babies, so is very common.
- Breastfeeding Jaundice: Breastfed babies are more likely to be jaundiced for longer. Multifactorial.
- Kernicterus = ↑↑bilirubin levels cause bilirubin to cross BBB and deposit in basal ganglia and brainstem. This can give long-lasting neurological damage, but with good treatment, this is avoided.
I
- Good history and examination.
- Bloods (Bilirubin, FBC, LFT, Blood groups, Blood film, blood culture – TORCH SCREEN, Coombs test)
- Urine
- If persistent jaundice, consider USS of the biliary tree.
T
- Each center has its own treatment chart, which looks like this →
- Supportive therapy (hydration status, etc.), if breastfeeding, keep doing so!
- Phototherapy – 450nm wavelength light converts unconjugated bilirubin into a harmless substance. The baby must be completely naked but wear eye protection. Can be done via fibre-optic blanket.
- Transfusion – Either done through UVC or peripheral vein and arterial line. 2x baby’s blood volume is transfused.
Scenario 1
mother of ali 1 month complaining yellowish discoloration of sclera, since was 2 weeks of age. persistant jaundice
information
- jaundice is lemon yellow extending to the mid-abdomen
- all is B+ blood group, mother is B+ (No ABO/RHO incompatibility)
- normal vaginal delivery, uneventful pregnancy and birth, no admission to NICU
- All is is exclusively breast fed, taking frequent feds, he gained baout 500 mg. during last 2 weeks (normal growth of baby) - (no suboptimal intake)
- stool become clay colored, urine is dar (Obstructive JAundice)
- abdominal distension is noticed (Biliary atresia????)
Chief of complant
what brings you today?
- theres yellowish discoloration
HOPI
When did you notice?
- 1 month ago For how long?
Tone of color?
- Yellow Progress?
- first just sclera, extending to abdomen. Associated?
- stool/urine color changes
- constipation
- hematuria
- polyuria
- fever
- weight loss
- irritations
- Blood group of mothter & baby
- Hypothyroidism - prolonged
- increased tummy size - hepatomegaly, spleenomegaly.
- constipation (hypothyroidism)
- vomitting
- diarrhea
Review systems
CNS
- Irritiability
- high pitched cry
- seizures
Respiratory
- tachypnea
- Cough
CVS
- Cyanosis
- breathing
- fatigue
Hematology
- Bruises
- hematuria
Developments
- follow up finger to mid line
- awareness to sound
Neonatal History
less in two years, related to neonatal diseases if 7+ “is there any complications during delivery?”
Parinatal
- D-Diseases during pregnancy? (diabetes)
- A- Admissions: during pregnancy, age of mother
- T- Drugs: supplementation, any drug not prescribed by doc, medications
Neonatal
- Gestational Age (Preterm)
- Mode of delivery (complicated/noncomplicatied - prolonged/nonprolonged)
- Cried immediatly?
- Apgar score
- Cut of umbilical cord (delayed; polycyt?)
Postnatal
- admission to neonatal? How long? what drugs? - if yes take full history of it.
- Screening test (hypothyroidism) - transucutantous???
T
travel, transfusion … truama, photo therapy
Family history
- consanguinity
- Siblings with similar diseases (if yes, take full details)
- Blood diseases in family (G6PD)
- Thyroid, Liver, syndromes (Gilbert- recurrent attacks of jaundice) diseases
Social History
- depends on case - not for jaundice.
Scenario 2
10 days old complaining yellow discoloration of skin and sclera since was 3 days old
Diagnosis: Physiological jaundice / (suboptimal? open diagnosis)
Chief of complaint
What is your child complaining of?
- 7 days
HOPI
Progression, Tone, Extension, Frequency urine, blood group mother and child ABO/RHO, color urine and stool, abdomen distension, tone, lethargy, vomiting, fever, Nutrition(breast fed?); weight changes, does it come and go,
Neonatal
Perinatal
- Blood transfusions
- Vaccinations
- Diabetes
- Admission to hospital (flu, rash)
- Drugs (without prescription)
Natal
- GA
- Mode delivery
- Complication
Postnatal
- admission to NICU (take details if yes)
- screening
Family history
siblings similiar conditions…