Cerebellum
Common causes
- Trauma; RTA ⇒ Post. Cranial Fossa fracture
- Demyelination (Multiple sclerosis) - Myelin sheath gives whitish color, if destruction, neuron conduction would be slow (T2 enhancement MRI) “((tachycardia, ataxia, Lower motor neuron lesion, cardiomyopathy”
- Tumor (Very rare, except meningioma) paraneuroblastic tumor, PCE, or Cerebellum itself + SOL- Irreversible damage
- SOL manifestation - due abscess, tumor, etc..
- Ischemia PICA Occlusion
- Degeneration (Multiple system Atrophy)
- Paraneoplastic syndrome if there is no manifestation to cerebellum due to metastasis
- Drug Induced; (Alcoholism, Phenytoin)
- Celiac disease
Examination Process Upper Limb
-
Hypotonia; flex, extension, rotation, etc… - TONE while holding brachioradialis
-
Intentional Tremor; - Fingers nose test; fingers to nose/ (best on chest, to avoid plucking of eye) - move fingers to other three positions
-
Pass pointing - overshooting fingers touch
-
Dysdiadochokinesia - Quick Alternative moving hand
-
Rebound Phenomena; not hitting forearm after rebound is normal
-
Speech; scanning speech, repulsive speech, loud, interruptions
-
Nystagmus; be at level of the patient - follow finger in horizontal to check for any tremors when reaching to ends of the eye -
Lower Limb
- Gait
- babiniski signs,
- clonus
Upper motor neuron lesion - scissor legs - Hyperflexia muscles adductors, proximal, extensors
Power RR Reduced with pyramidal pattern of weakness (Flexors weaker than extensors in legs, and vice versa in arms)
Plantar Reflex Upgoing/extensor (Babinski positive)
Lower motor neuron lesion (Extensors are abnormal, Flexors are normal)
Power Reduced in distribution of affected motor root/nerve
Plantar Reflex Normal (downgoing/flexor) or no movement
Things to know
-
Heel shin test; if done with eyes open, cerebellum has no issue,
-
Romberg sign - close eyes, guard patient from fall its positive (not related to cerebellum, mainly patient is awake when fallen)
-
Ataxic Gait;
-
Finding Anti-Yo antibodies in a patient with ovarian cancer, but where an MRI does not show metastasis, suggests the presence of a paraneoplastic syndrome rather than direct brain metastasis of the cancer. This indicates that the immune response induced by the cancer is affecting the brain, rather than cancer cells themselves invading brain tissue.
-
Hot water, manifestation appear
Parkinson
Common Causes
- Parkinson’s disease
- Medications;
- Typical Antipsychotics: Drugs such as haloperidol and chlorpromazine, which block dopamine receptors.
- Anti-emetics: Medications like metoclopramide and prochlorperazine that are used to treat nausea and vomiting but can affect dopamine pathways.
- Other medications: This could include drugs like reserpine, tetrabenazine, and some calcium channel blockers that deplete dopamine levels or affect its recept
- Vascular Parkinsons
- Multiple Trauma
- Multiple System Atrophy
- Supranuclear Opthalmoplegia; vertical gaze downward
- Genetic + Environmental increased risk
Examination Process
- Tremors - Pill rolling tremor - parkinsonism is mostly one sided mostly idiopathic
- Synkinesia - fast movement on one side will increase tremor on the other affected side when tested
- Bradykinesia; slowness of movement and speed
- Rigidity; tone testing, - when extention there is resistance, then sudden drop. - rigidity interrupted by tremor
- Reading; monotonous speech,
- R Writing; micrographia
- Postural instability; shuffling gait, minimal swinging of arm
Idiopathic Parkinson:
-
L-dopa Treatment: L-dopa is effective in alleviating symptoms may confirm the idiopathic parkinsons with alleviation of symptoms by use - works by enhancing dopamine levels within the brain. This adjustment helps in managing symptoms more effectively, although chronic use may lead to diminishing benefits and can necessitate adjustments in therapy.
-
Unilaterality of Symptoms: Symptoms of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease often begin on one side of the body (unilateral) and can remain more pronounced on that side even as the disease progresses. This asymmetry is a key characteristic in early diagnosis.
-
Eye Movement and Tremors: While eye movements generally remain normal in Idiopathic Parkinson’s patients, there can be occasional eye movement abnormalities such as reduced blinking and difficulties with upward or downward gaze. Regarding tremors, they are typically present and consist of a pill-rolling tremor of the hands at rest. Although deemed a common symptom, tremor patterns do not deviate significantly from the usual presentation without compounding factors.
Treatment
L-dopa Treatment: L-dopa alleviates symptoms by increasing its uptake and conversion to dopamine in the brain. This enhancement helps compensate for the diminished production of dopamine characteristic of the condition.
Carbidopa (often combined with L-dopa): Primarily acts in the peripheral system to prevent the premature conversion of L-dopa to dopamine outside the brain, optimizing its effects. After approximately 15 years of medication use, patients might experience dyskinesia due to changes in dopamine receptors.
Bromocriptine: Bromocriptine, an ergot alkaloid, functions as a dopamine agonist. However, it may lead to complications like retroperitoneal peritonitis. Clarifying safety and long-term effects is recommended for this medication.
Amantadine: The mechanism by which Amantadine enhances Parkinsonian symptoms is not well-understood, but it is considered safe and initially developed as an antiviral drug.
Selegiline (Deprenyl - an MAO-B inhibitor): Selegiline prevents the breakdown of dopamine, thereby increasing its availability and duration of action in the brain. This action helps to mitigate symptoms related to dopamine deficiency.
Benztropine: As a cholinergic antagonist, Benztropine is particularly effective if the primary complaint is tremor, helping to reduce its severity by countering excessive acetylcholine activity.
COMT Inhibitors: While effective in extending the effect of L-dopa, COMT inhibitors can lead to side effects such as delusions and hallucinations. There is also a concern about hepatotoxicity, particularly with agents like tolcapone; monitoring liver function is essential.
Pallidotomy: This surgical procedure targets the globus pallidus to reduce dyskinesia and improve motor functions in Parkinson’s disease patients. best to direct brain stimulation treatments rather than Pallidotomy.
Other Notes
Vascular Parkinsonism:
- Characterized by parkinsonian hyperreflexia.
- Test reflexes using a tendon hammer, focusing on bicep reflexes at C5-C6 and tricep reflexes at C5, C6, C7. Ensure proper tendon location is palpated before testing to observe accurate reactions.
- Other associated signs might include hyperreflexia, indicators of a stroke, and cardiovascular diseases.
Multiple System Atrophy (MSA):
- Presents with parkinsonian and cerebellar features.
- Testing for nystagmus can help indicate autonomic nervous system issues accompanying postural hypotension, a hallmark of MSA.
- Typically, MSA features more generalized parkinsonian manifestations, with the exception of nystagmus pertaining specifically to eye movements.
Supranuclear Ophthalmoplegic Lesions:
- These lesions typically affect the brain areas that control eye movements, specifically the regions above the nuclei of cranial nerves that control gaze.
- As a result, people with supranuclear lesions often experience difficulties with vertical gaze, meaning they have trouble moving their eyes up or down.
- in contrast to multiple system atrophy - Horizontal gaze nystagmus
MTB substance abuse:…
Carbon Monoxide Poisoning:
- May mimic parkinsonian manifestations such as movement disorders.
- Patients often present an environmentally induced red appearance in the skin.
Other Symptoms of Parkinsonian Syndromes:
- Check for cervical dermatitis which may provide an indication of associated skin issues.
- An expressionless face is a common symptom that might be observed.
Scores
1. Grading of Power (Muscle Strength)
| Grade | Description |
|---|---|
| 0 | No muscle contraction detected - Complete Paralysis |
| 1 | Flicker Visible muscle contraction with no movement |
| 2 | Movement possible, but not against gravity |
| 3 | Movement possible against gravity but not against resistance |
| 4 | Movement possible against some resistance but weaker than normal |
| 5 | Normal strength |
2. Grading of Reflexes
| Grade | Description |
|---|---|
| 0 | No response (areflexia); absent |
| 1+ | Diminished, low normal, or occurs only with reinforcement (LMN Lesion) |
| 2+ | Normal |
| 3+ | Brisker than average; possibly but not necessarily indicative of disease (UMN LESION) |
| 4+ & Above | Very brisk, hyperactive, with clonus (involuntary, rhythmic, muscular contractions and relaxations) |
3. Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS)
Assesses patient’s neurological condition Value range 3 -15
- 3 totally comatose patient
- 9-12 Moderate altered level of conscious
- 15 fully alert patient
| Behavior | Response | Score |
|---|---|---|
| Eye opening response | Spontaneously | 4 |
| To speech | 3 | |
| To pain | 2 | |
| No response | 1 | |
| Best verbal response | Oriented to time, place, and person | 5 |
| Confused | 4 | |
| Inappropriate words | 3 | |
| Incomprehensible sounds | 2 | |
| No response | 1 | |
| Best motor response | Obeys commands | 6 |
| Moves to localized pain | 5 | |
| Flexion withdrawal from pain | 4 | |
| Abnormal flexion (decorticate) | 3 | |
| Abnormal extension (decerebrate) | 2 | |
| NO response | 1 | |
| Total Coma Scale | Best case scenario / Fully Alert | 15 |
| Altered Level of Conscious | 9-12 | |
| Comatose | 8 or less | |
| Deep coma | 3 |
Cranial Nerves
CN I - Olfactory;
Smell test, close one nostril, test the other. Disease that effect it: - COVID 19, Cold, flu - Meningioma - Truama - Surgery - Frontal Lobotomy - Congenital - Kallman’s syndrome -FSH LG = Hypogonad, anosmia
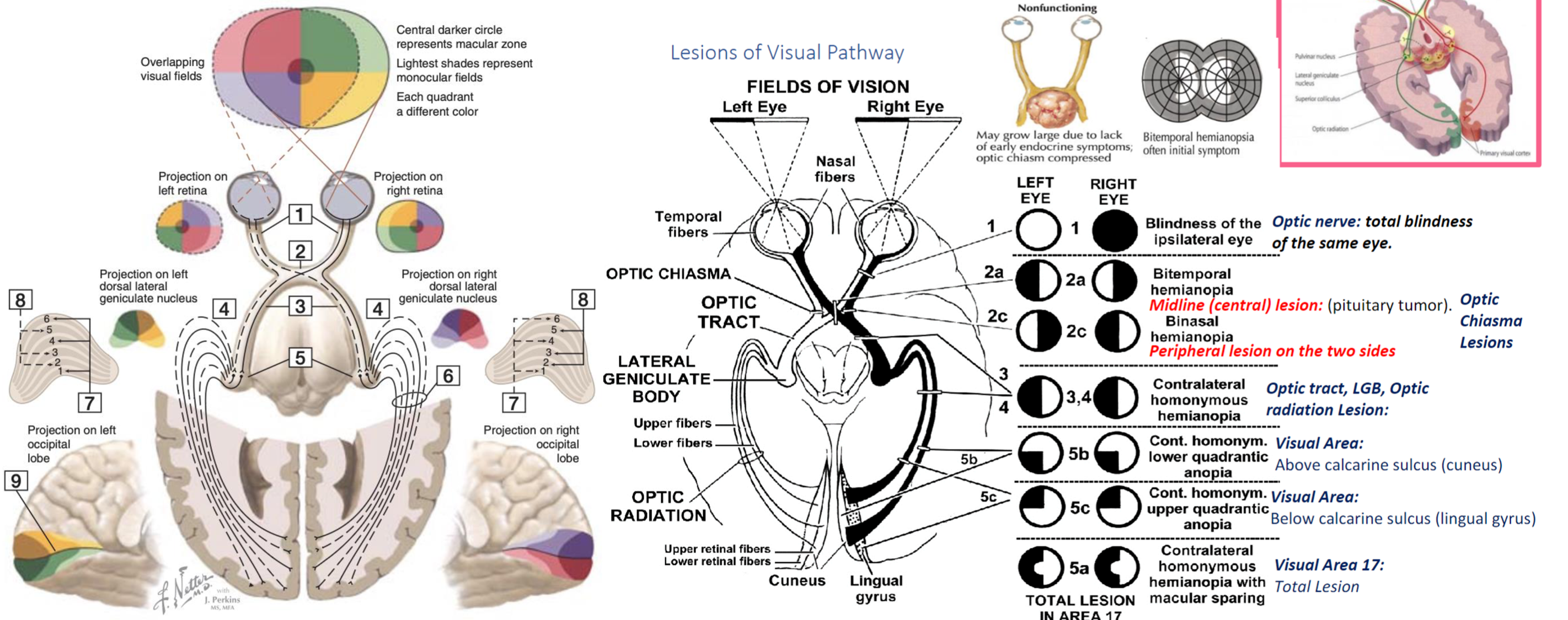
CN II - Optic Nerve
Disease that effect it: - Multiple Sclerosis - Diabetes - Pituitary Tumor
Examination - Visual acuity - (snellen chart) - 6 meters, if negative, test with numbers of fingers, then movement of hand, then light stimulation otherwise the patient is light blind. - Ischehara test - Color blindness related conditions; (X-Linked, Digoxin or anti-tuberculosis; Ethambutol) - Visual Field - Confrontation test - stay in same level to the patient, test one eye, close the other same as you - let the patient stare at your eyes without any movement. pull your finger towards center to confirm first sight with finger shaking, use your visual field as reference point. - testing temporal outer and nasal from central
Its important to know diseases related to the damaged lesion; Aforementioned in this graph
Other Tests includes
Indirect Light Reflex Testing:
- Use a dim torch as a light source rather than a phone to avoid excessive brightness.
- optic nerve, following its pathway to the midbrain and the Edinger-Westphal nucleus, which relays information to the oculomotor nerve, resulting in pupillary constriction.
Accommodation Reflex:
- Observes pupillary constriction when focusing on an object moving from a far to a near distance, assessing the accommodation ability of the eye.
Funduscopy:
- For a direct examination of the patient’s fundus, align your eye with to the patient’s right eye - your left arm on left shoulder of patient.
- Close your own opposite eye to avoid distraction and move closer progressively until you identify the yellow optic disc area surrounded by blood vessels.
- During this examination, observe the light reflex, which can provide additional information on the reflective properties and health of the optic nerve and retina.
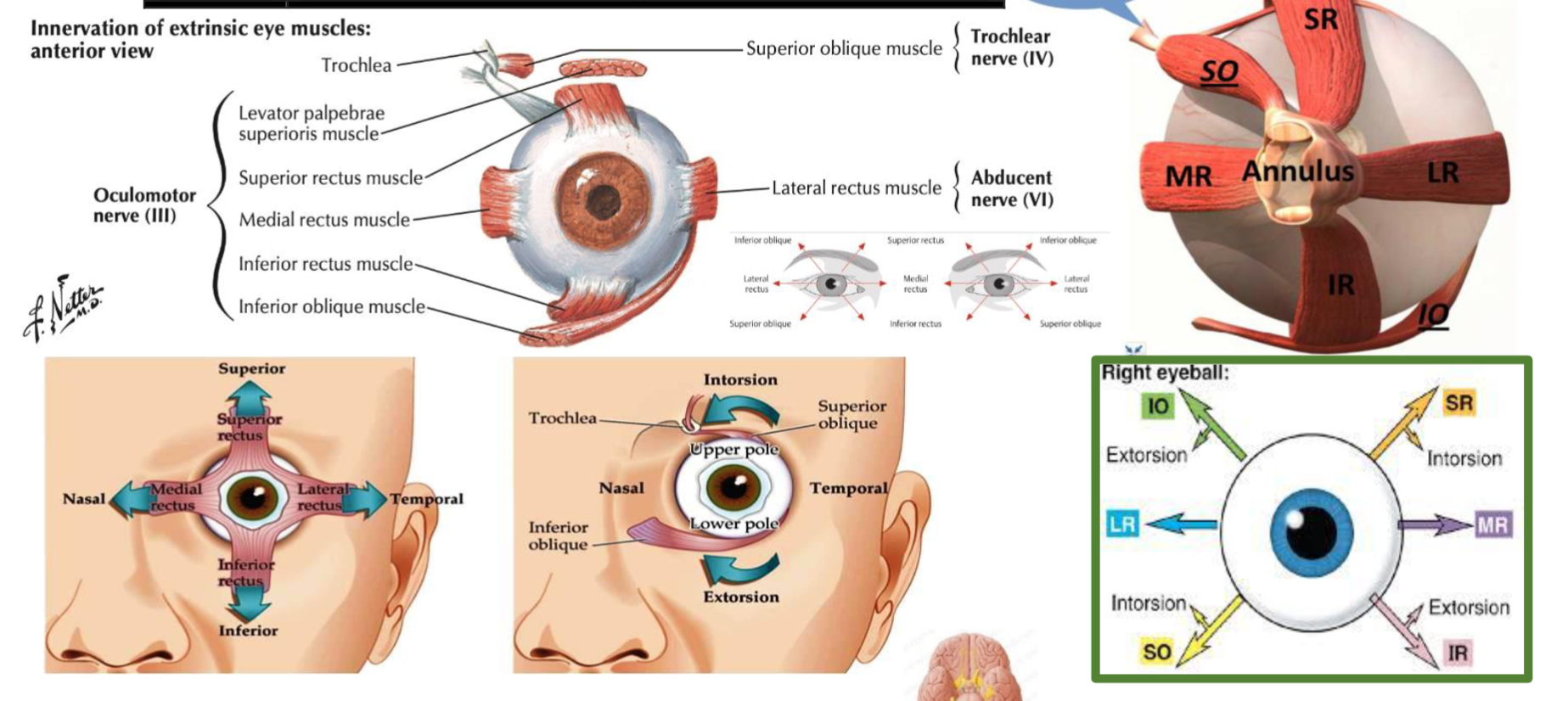
CN III, IV, VI -
Superior orbital fissure Signs: - H test switch fingers at middle - to test otherwise
Occulomotor nerve palsy: - SLE , - Diabetes, - Tumor from outside emergency for surgery - if no papillary reflexes - cavernous sinus thrombosis
| Muscle | Innervation | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Superior Rectus | Oculomotor nerve (CN III) | Elevates, adducts, and medially rotates the eyeball |
| Inferior Rectus | Oculomotor nerve (CN III) | Depresses, adducts, and laterally rotates the eyeball |
| Medial Rectus | Oculomotor nerve (CN III) | Adducts the eyeball |
| Lateral Rectus | Abducens nerve (CN VI) | Abducts the eyeball |
| Superior Oblique | Trochlear nerve (CN IV) | Depresses, abducts, and medially rotates the eyeball |
| Inferior Oblique | Oculomotor nerve (CN III) | Elevates, abducts, and laterally rotates the eyeball |
| Levator Palpebrae Superioris | Oculomotor nerve (CN III) | Elevates the upper eyelid |
 | ||
| ![[Note Pyramidal System-20240426004827251.webp | 292]] |
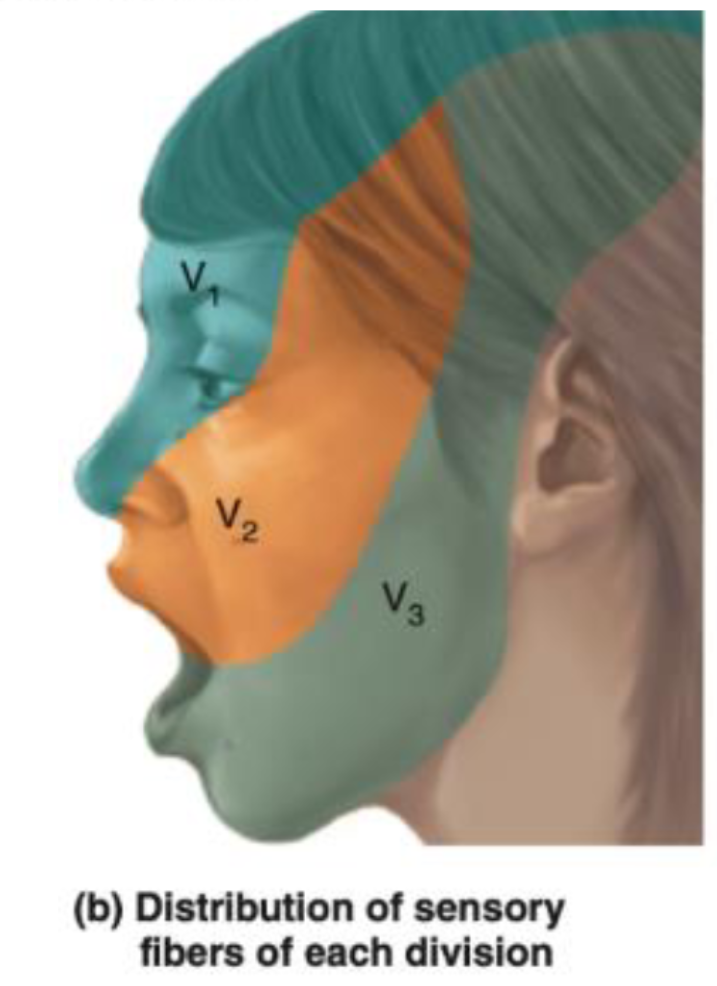
CN V – Trigeminal Nerve
-
Ophthalmic (V1) - Passes through the superior orbital fissure.
- Supplies: Sensation to the forehead, upper eyelid, and cornea.
- Involved in the corneal reflex: The afferent limb (sensory input) of the corneal reflex is through the ophthalmic branch of the trigeminal nerve. The efferent limb (motor output, which closes the eye) is via the facial nerve (CN VII).
-
Maxillary (V2) - Passes through the foramen rotundum.
- Supplies: Sensation to the middle part of the face, cheek, upper lip, and upper teeth.
-
Mandibular (V3) - Passes through the foramen ovale.
- Supplies: Sensation to the lower part of the face, lower lip, and lower teeth. It also carries motor fibers to the muscles of mastication.
- The anterior two-thirds of the tongue receives general sensation (not taste) via the lingual nerve, a branch of the mandibular division.
- Taste from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue is carried by the chorda tympani nerve (a branch of the facial nerve, CN VII), not the trigeminal nerve.
Examination process
-
Sensory Testing:
- Cotton Test: Use a soft piece of cotton to lightly touch different areas of the face. This tests the sensory function of all three branches of the trigeminal nerve. The patient should have their eyes closed during the test to rely solely on their sensory perception. Specifically, test:
- The forehead, upper eyelids, and cornea (ophthalmic branch).
- The cheeks, upper jaw, and upper teeth (maxillary branch).
- The lower jaw, lower teeth, and part of the tongue for general sensation (mandibular branch).
- Cotton Test: Use a soft piece of cotton to lightly touch different areas of the face. This tests the sensory function of all three branches of the trigeminal nerve. The patient should have their eyes closed during the test to rely solely on their sensory perception. Specifically, test:
-
Motor Testing: power (Medial and Lateral pterygoid, temporalis, masseter)
- Mandibular Movements:
- Ask the patient to clench their jaw to test the muscles of mastication, assessing the motor function of the mandibular branch (V3).
- Have the patient open their mouth and then move their jaw side to side, observing for any deviations or difficulties, which might indicate an issue with trigeminal motor function or asymmetrical muscle weakness.
- Mandibular Movements:
buccinator supplied by facial
-
Reflex: Jaw Reflex (afferent efferent) - Pure reflex Gently tap the jaw with the mouth slightly open to check the reflex. A normal response would be a slight and quick involuntary clenching of the jaw. An exaggerated response might suggest abnormalities in the reflex arc, which is primarily controlled by the sensory and motor roots of the mandibular branch.
Corneal reflex (Afferent Opthalmic - efferent by facial)
CN VII - Facial Nerve
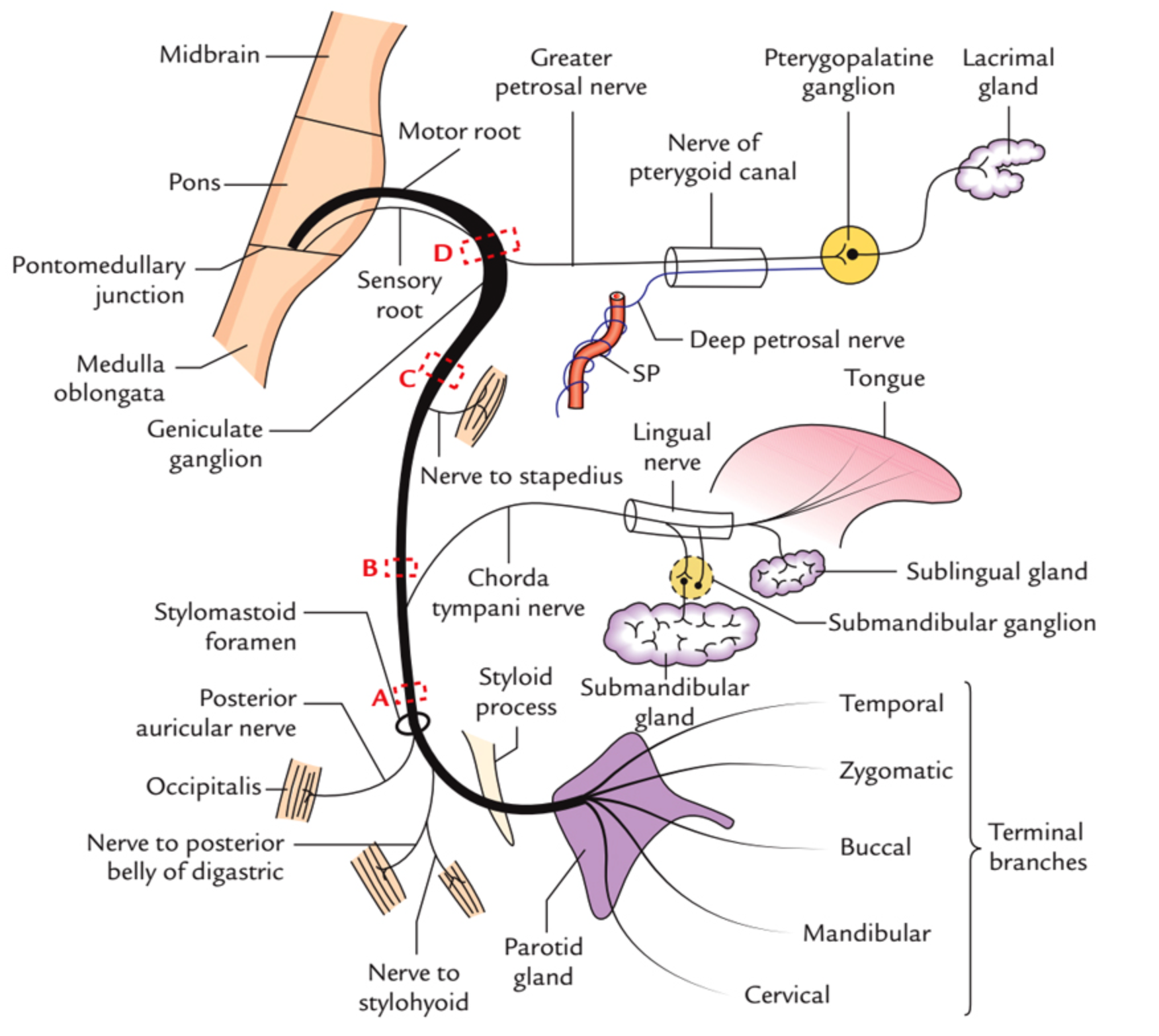 Course??
Course??
in middle ear gives two branches to chorda tympani & Stapedius (ear distrubance)
Innervations - External acoustic meatus - for sensation of ear - Motor - Movement of the face - Sternomastoid - branches nerve to stapedius - Loud sounds middle ear - & nerve to chorda tympani - Parasympathatic Submandibular & Sublingual gland
Tests
- Temporalis - raise eye brows (dont use hands )
- Orbicularis Oculi - check for resistance when eyes close
- Buccinator - Blow (palpate)
- Levator Anguli Superioris - smile
- Orbicularis Oris - whistle
- Taste anterior 2/3
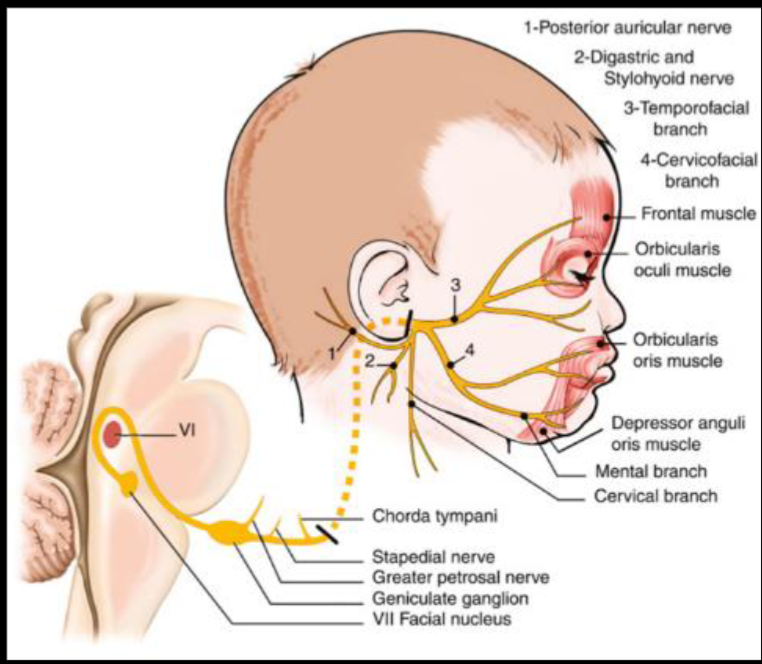 UMN Palsy - Causes Includes; (hyperreflexia)
- stroke
- MS
- trumours
- Internal capsule palsy
- Eyebrow raise is normal - if botox, contraindicated for the test
UMN Palsy - Causes Includes; (hyperreflexia)
- stroke
- MS
- trumours
- Internal capsule palsy
- Eyebrow raise is normal - if botox, contraindicated for the test
LMN Palsy - Causes includes
- Bells palsy
- Cavernous sinus thrombosis
- Fracture (truama) base of skull
- Acoustic neuroma
- Shingles
- Ramsay Hunt Syndrome with skin lesioned shingles on face and ear due to varicella ,
- Eyebrow doesn’t raise compared to contra-lateral
Bilateral facial nerve palsy - Sarcoidosis - Guillain-Barré Syndrome - Lyme disease
other notes botox mask symptoms of UMNL of facial nerve
most common causes of stroke? DVT - Stroke may transfer DVT to brain ASD - ventricular - patent foramin ovale
CN VIII - Vestibulocochlear
internal acoustic meatus enters to the skull depolization through potassium -
Cochlear division;
-
Whisper on ear while other is closed - tell him to repeat to confirm.
-
Rinne Test:
- This test compares air conduction to bone conduction. A tuning fork is used initially to assess bone conduction by placing it on the mastoid process. It is then held near the ear canal to assess air conduction.
- A positive Rinne test (air conduction is better than bone conduction) indicates normal hearing or sensorineural hearing loss.
- A negative Rinne test (bone conduction is better than or equal to air conduction) suggests conductive hearing loss.
-
Weber Test:
- This test assesses bone conduction using a tuning fork, which is placed on the center of the forehead.
- The purpose is to determine the lateralization of sound. Sound lateralization to one ear typically indicates sensorineural hearing loss in the opposite ear or conductive hearing loss in the ear to which sound is lateralized.
sensorineural causes - Neurofibromatosis type 2 - Noise pollution - Aminoglycosiedes - Gentamycin - Test, with ringing on frontal head - check for which ear hears most = laterilzation of normal side - Pendred Syndrome = Goiter + hearing loss (thyroid manifestations are rare, but may be presentaiton)
Conductive deafness - Wax / foreign objects - Otitis Media - - Tympanic membrane rupture - Otosclerosis. - Swimmers ear - Foreign body
Note
Fracture at the base of the skull can cause sensorineural hearing loss and bleeding, with lateralization. This is a result of conductive deafness, as the vestibulocochlear nerve passes through the petrous part of the temporal bone.
CN IX - Glossopharyngeal
Tests for Gag reflex Jugular foramen - Upper motor neuron palsy - glossopharyngeal special sense, pain and temperature autonomic to the parotid
examination by gag reflex with Glossopharyngeal & Vagus open mouth check uvula for Vagus for the tongue Hypoglossal
Main Causes - Neuralgias - Compression - Surgical
CN X - VAGUS
Cough, Gag reflex -
UML pseudobulbar palsy, - hot potato speech
bulbur palsy; LML - appear as nasal speech
9,10,11,12 bulbar palsy - by speech
CN XI - Accessory
-shrug, head switch
XII - Hypoglossal
-
All intrinsic and extrinsic muscles of tongue except palatoglossus by vagus
-
UML - Pseudobulbar palsy; Hot potato; Spastic
-
LML Bulbar Palsy; Nasal speech, appear as Fasucilation; Flaccid
-
Tongue goes to the side which is damaged
-
then check power of intrisic muscles of the tongue
Focus on tone, examination process, Glasgow Coma Scale, cranial nerve, cyanosis, cerebellum, parkinsons.