Necrotizing Enterocolitis
GI medical/surgical emergency. An acute inflammatory disease characterized by variable damage to the intestinal tract ranging from mucosal injury to full-thickness necrosis and perforation. The main cause of NEC is still unclear.
Symptoms
- Feeding intolerance
- Hematochezia
- Abdominal distention
- Decreased bowel sounds and motion
- Abdominal wall erythema (advanced stages)
- Apnea and lethargy
- Decreased peripheral perfusion
- Shock (in advanced stages) delayed treatment
Diagnosis
Laboratory:
- Hyponatremia
- Metabolic acidosis
- Thrombocytopenia
- Leukopenia or leukocytosis
- Prolonged PT and aPTT
- Decreasing fibrinogen
Radiography: Abdominal X-ray:
- Dilated loops,
- thickened bowel walls,
- pneumatosis intestinalis (air in intestinal walls),
- pneumoperitoneum; indicate perforation (emergency requiring surgical intervention),
- portal gas (present in the portal venous system,
- considered to be a poor prognostic sign).
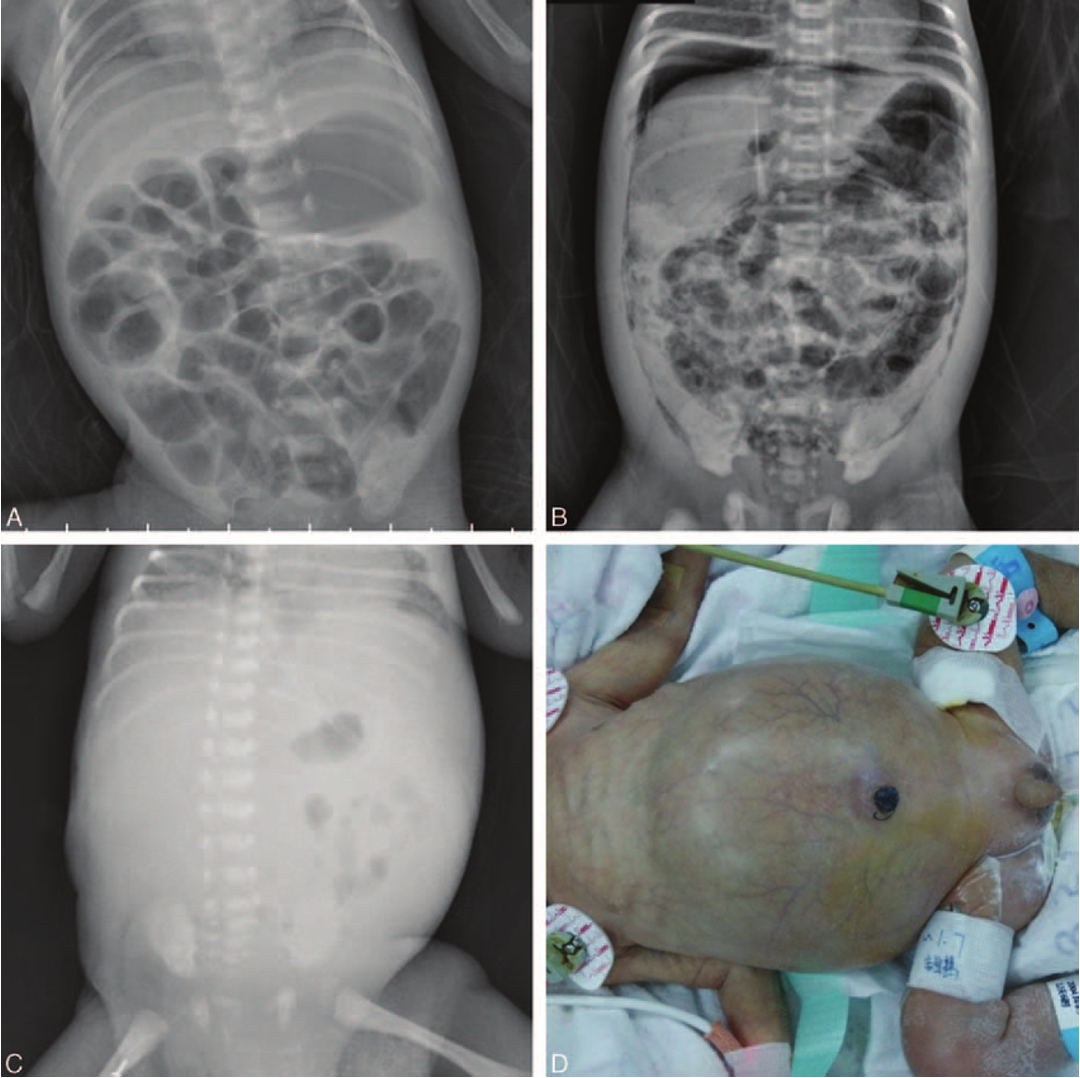 3rd abnormal gas patterns
4th cellulitis/perforation
3rd abnormal gas patterns
4th cellulitis/perforation
Management
- Nothing by mouth and IV fluids (NBO) moooooost important
- Rapid nasogastric decompression
- Start IV antibiotics after cultures for 3 weeks
- Total parenteral nutrition (TPN)
- Pediatric surgery consultation immediately
Indications for Surgery
- Intestinal perforation with free air in the peritoneal space
- Cellulitis of the abdominal wall
- If the infant keeps deteriorating despite medical treatment