ARF
Dr. Waqar
Normal Functions of the Kidneys
- Excretion of wastes: (Urea, creatinine)
- Acid-base balance: (excretion of acids produced in the body)
- Electrolyte balance: (Na, K, P etc)
- Erythropoietin production: (for RBC synthesis). It is a hormone.
- Salt & water balance: Maintain BP
- Activate Vit D: Thus managing Ca & Phosph.
Effects of Renal Failure
- High urea & creatinine: (uremia)
- Acidosis
- High K & Phosphorus
- Decreased erythropoietin: Anemia
- Poor water excretion: HTN, CHF
- No Vit D activation: Vit D deficiency, which causes: bone disease (details in chronic renal failure lecture)
Types of Renal Failure
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Acute (ARF) | Duration of renal failure less than 3 months. |
| Chronic (CRF) | Persistent renal failure for more than 3 months. It is progressive. CRF finally leads to end-stage renal disease (ESRD) |
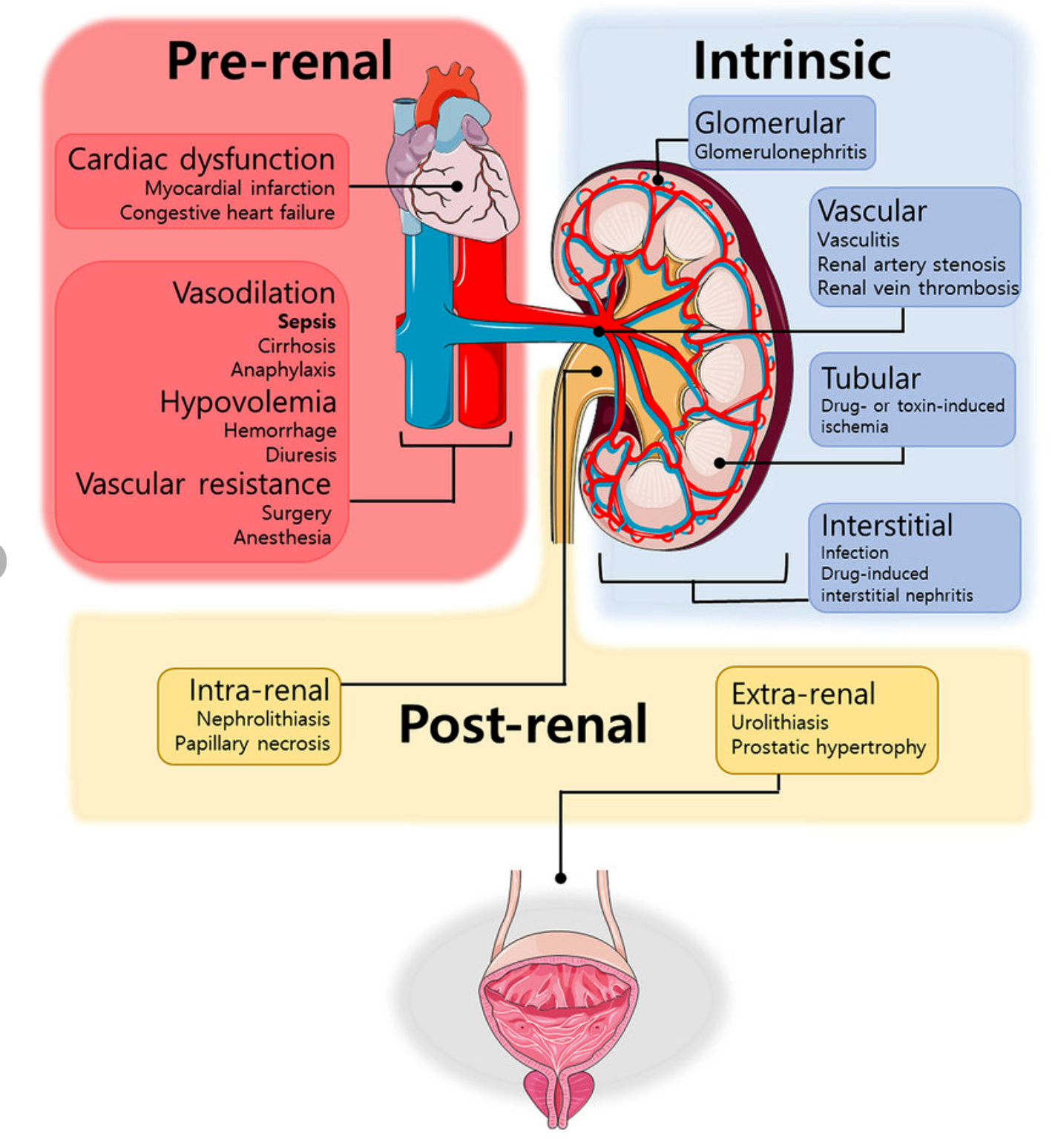
Types of ARF (Based on the site of the problem)
-
Pre-renal ARF:
Decreased blood flow to the kidneys; renal artery stenosis, HTN -
Renal ARF: Diseases “in” the kidney
Renal type specific renal diseases -
Post-renal ARF: Obstruction “beyond” the kidney
Obstructive, renal stones, bladder carcinomas