Contrast agents in conventional radiography & computed tomography & MRI
Contrast radiography
Description: projectional radiography with contrast agent used to better visualize certain structures.
Urography, urethrocystography, and excretion urography
Visualization of the urinary tract after administration of radiopaque contrast medium (containing iodine).
Intravenous injection of contrast media: excretory urogram.
Retrograde administration of the contrast medium through the urethra into the bladder: Urethrocystography and voiding cystourethrography
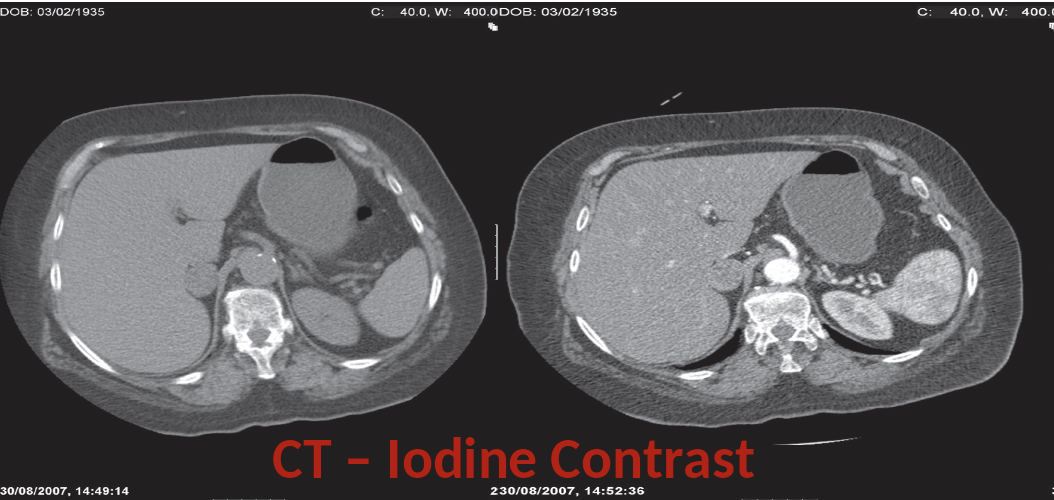
CT intravenous contrast
- Low ionic ,low osmolar solutions
- High level of iodine absorbed X-ray (appear white)
- Opacifies structures based on amount of blood flow
- Excreted by kidneys .Contraindicated in patients with renal failure >>> Acute tubular necrosis (GFR < 30 or creatine > 1.5, contraindicated)
CT oral contrast
- Helps distend and define the bowel
- Dilute barium sulfate most often used.
- 1000 – 1500 ml given orally about 60- 120 minutes prior to exam.
- Gastrografin(Water-soluble contrast used if there is a suspicious of bowl perforation)
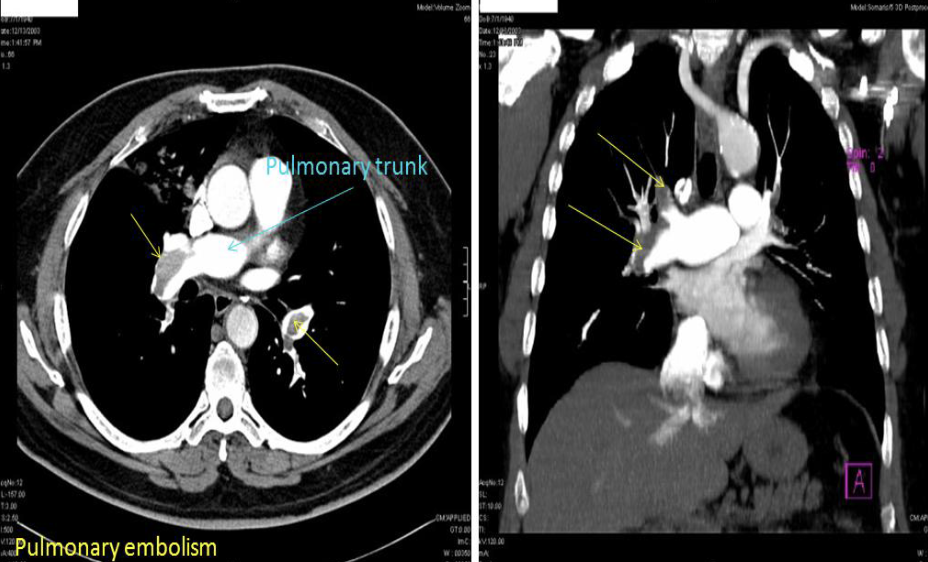
Axial and coronal CT chest with contrast. Thrombus in the pulmonary artery
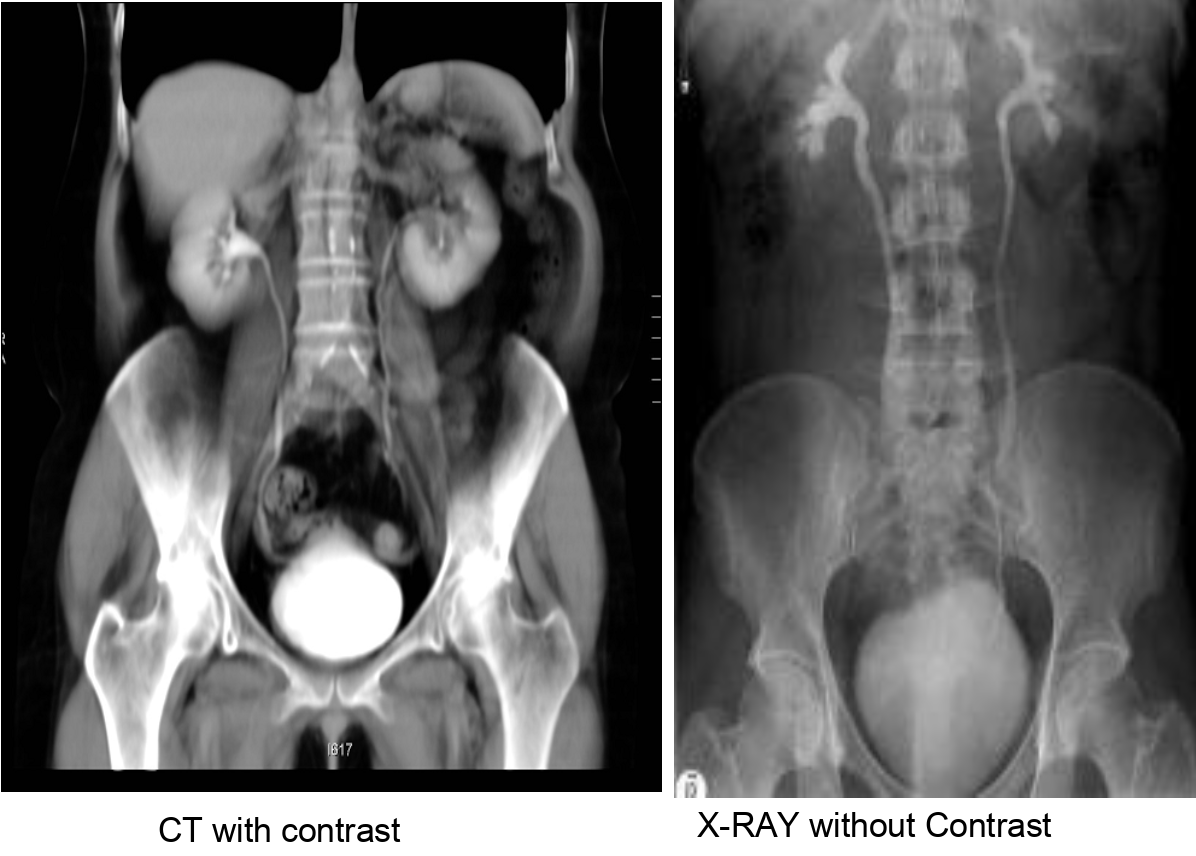
Intravenous pyelography
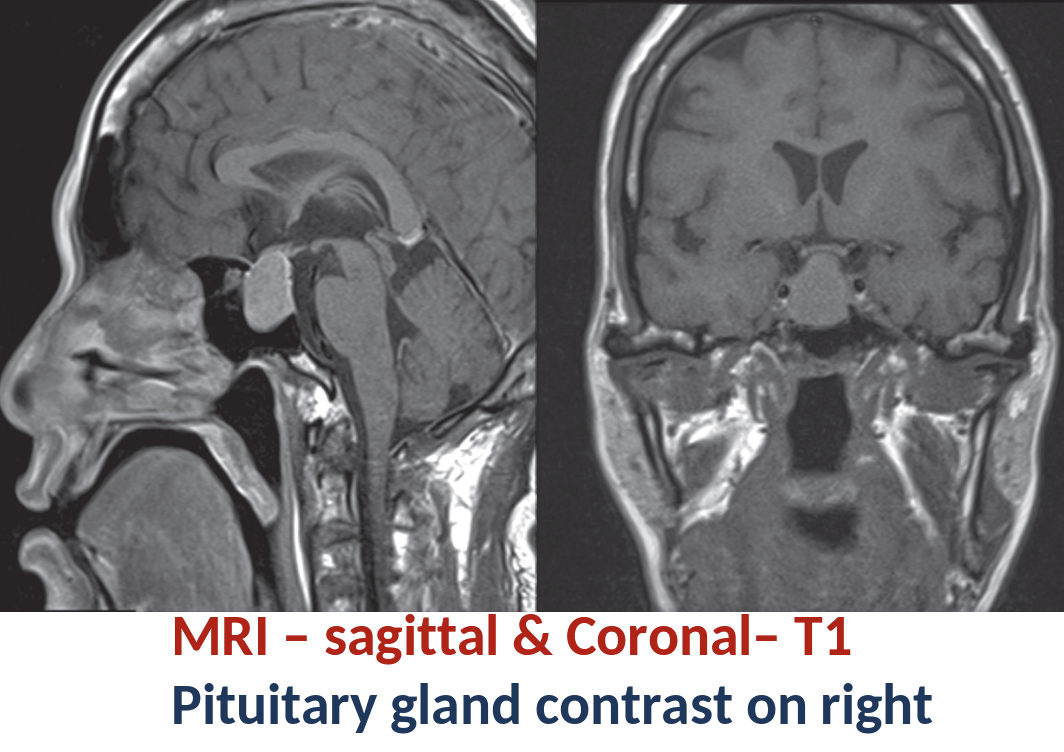
MRI with contrast:
-
Gadolinium-based contrast agents are most commonly used for MRI.
-
Application: usually intravenous
-
Tissues that concentrate the agent show very high signal intensity (i.e. they appear white) on T1- weighted images.
-
Complications: Nephrotoxicity: Gadolinium-based contrast agents should be avoided in patients with significant renal failure (GFR < 30 mL/min), particularly those receiving dialysis.
-
If gadolinium-based contrast MRI is absolutely necessary in a patient with renal insufficiency, precautions should be taken:
-
-GFR< 30 mL/min: single dose with smallest amount possible, and no further MRI examination with gadolinium-based contrast agents within the next 3 months.
-
-Dialysis patients: Gadolinium-based MRI examinations should be done on the day of dialysis before the dialysis session, followed by an additional dialysis session the day after.
Ultrasound contrast agents
-
The use of ultrasound contrast agents, which have very few side effects compared to radiocontrast agents, further expands the diagnostic applications of the modality.
-
ultrasound contrast agents have been developed. These agents contain microscopic air bubbles that enhance the echoes received by the probe.
-
The technique is used to help characterize liver and renal abnormalities and in the investigation of cardiac disease.
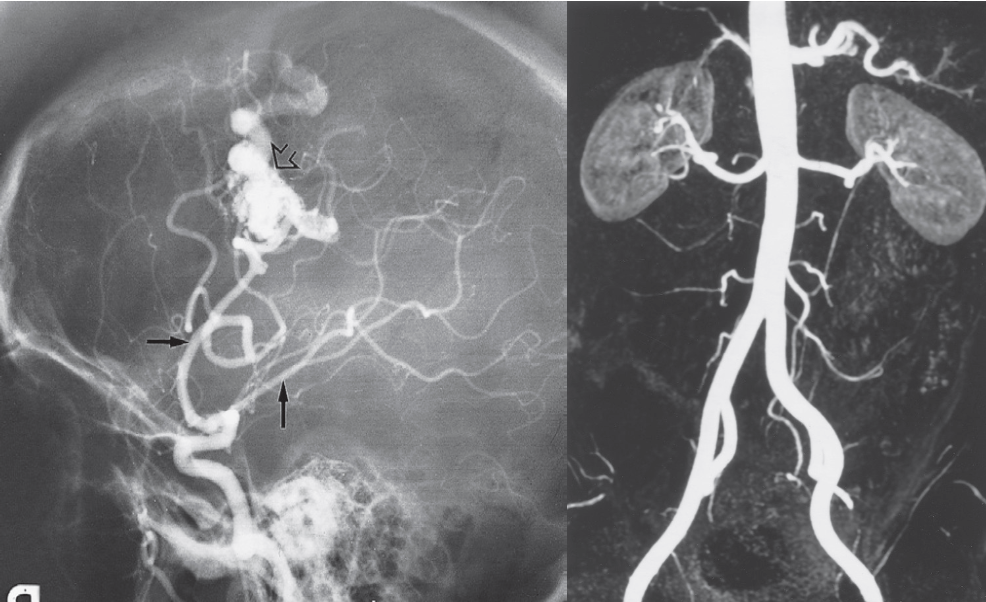
Digital subtraction Angriography & MRA; MRI Modality
contrast: Iodine base