Pediatrics
Chickenpox
DR MANSOUR.M. ALQURASHI
INTRODUCTION Z
- Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) is one of eight herpesviruses. It is a double-stranded, linear DNA virus.
- VZV infection causes two clinically distinct forms of disease: varicella (chickenpox) and herpes zoster (shingles).
- Primary VZV infection results in the diffuse vesicular rash of varicella/ chickenpox. Endogenous reactivation of latent VZV typically results in a localized skin infection known as herpes zoster/ shingles.
- Primary varicella infection in children is generally a mild disease compared with more severe presentations in adults or immunocompromised patients of any age.
- Immunization is recommended in all children before the age of five years and in nonimmune adults.
- For most people, getting chickenpox once provides immunity for life. A person can get chickenpox more than once, but it is uncommon.
TRANSMISSION AND VIROLOGY
It is a highly contagious disease, with secondary household attack rates of >90% in susceptible individuals.
Transmission occurs in susceptible hosts via:
- Contact with aerosolized droplets from nasopharyngeal secretions of an infected individual.
- By direct cutaneous contact with vesicle fluid from skin lesions.
- Airborne transmission of VZV to susceptible nursing staff has also been reported in a hospital unit.
- The average incubation period for varicella infection is 14 to 16 days, although this interval can range from 10 to 21 days.
- The period of infectivity is generally considered to last from 48 hours prior to the onset of rash until skin lesions have fully crusted.
CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
- Primary infection with VZV occurs during childhood and is usually a benign self-limited illness in immunocompetent children.
- Secondary cases in household contacts appear to be more severe than primary cases.
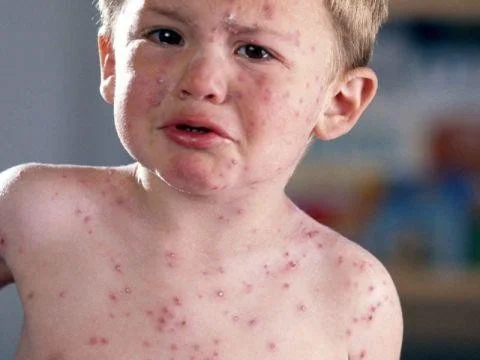
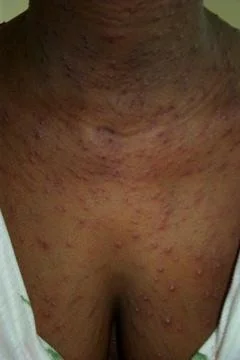
- A prodrome of fever, malaise, or pharyngitis, loss of appetite is followed by generalized vesicular rash, usually within 24 hours.
- The vesicular rash of varicella, which is usually pruritic, appears in successive crops over several days.
- The lesions begin as macules that rapidly become papules followed by characteristic vesicles; these lesions can then develop a pustular component followed by the formation of crusted papules.
- The patient with varicella typically has lesions in different stages of development on the face, trunk and extremities.
- New vesicle formation generally stops within four days, and most lesions have fully crusted by day six in normal hosts. Children usually miss 5 to 6 days of school.
- Crusts tend to fall off within approximately one to two weeks and leave a temporary area of hypopigmentation in the skin.
Primary varicella lesions
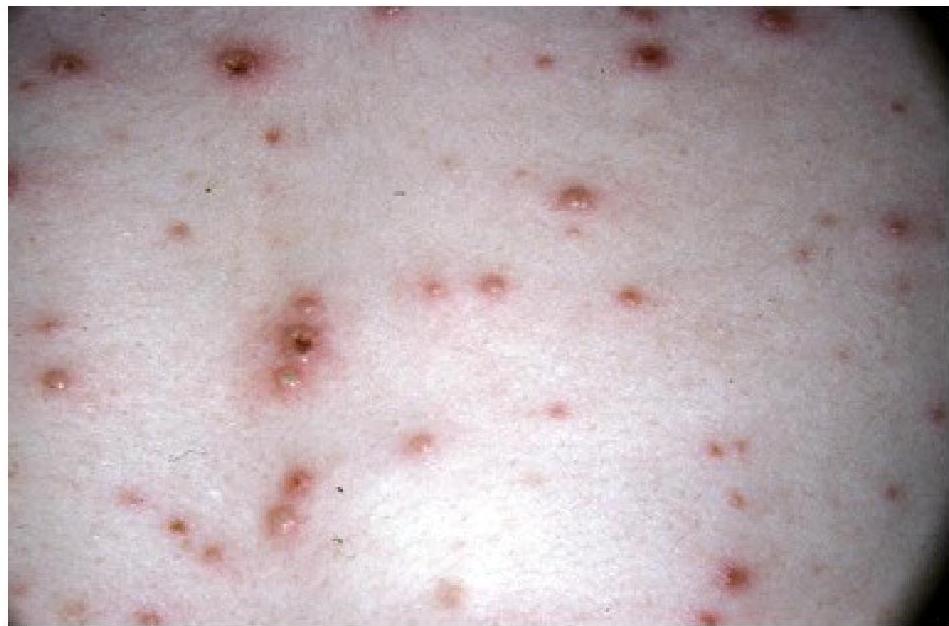
Vesicular lesions on an erythematous base are characteristic of chickenpox. The lesions occur in crops and are present in a variety of stages from maculopapular to vesicular or even pustular. Central necrosis and early crusting is also visible.
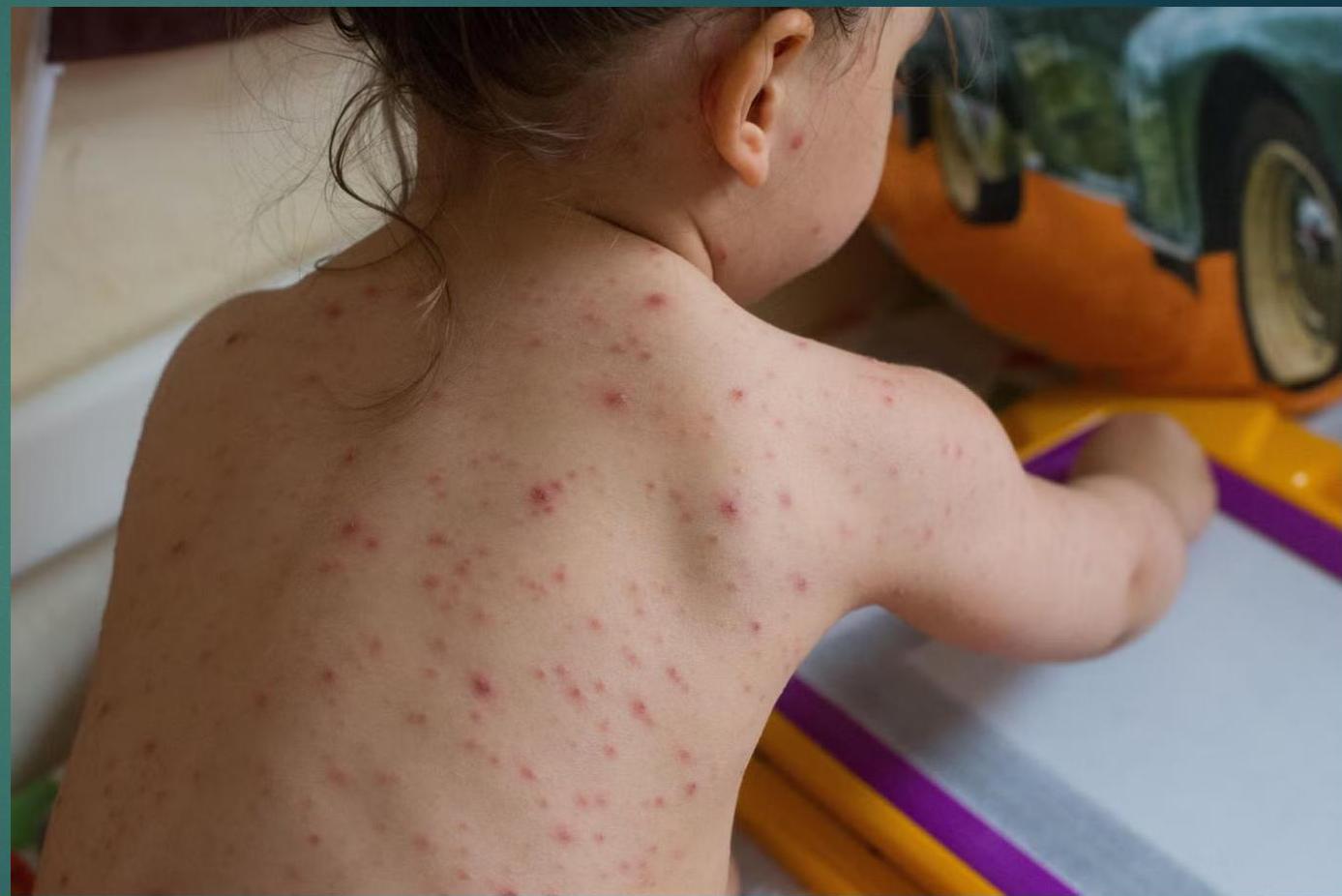
Impact of vaccine on clinical manifestations
- 20 % of children who receive one dose of varicella vaccine may develop varicella infection, known as “breakthrough disease”, if exposed to VZV.
- In vaccinated children 1 to 14 years of age, varicella was more often mild and modified than in unvaccinated children (eg, less fever and a lower number of lesions).
- The accompanying rash was significantly more likely to be atypical in nature among vaccinated children (eg, maculopapular).
- Complications were less likely to be reported among vaccinated children than unvaccinated children.
- Neurologic complications (eg, encephalitis) continue to be rare.
COMPLICATIONS OF VARICELLA
- Skin/soft tissue infections — Primary varicella infection in children is associated with an increased incidence of invasive group A streptococcal soft tissue infection, included cellulitis, myositis, necrotizing fasciitis, and toxic shock syndrome.
- Neurologic complications — Encephalitis, transient focal deficits, aseptic meningitis, transverse myelitis, vasculitis, and hemiplegia. Reye syndrome is rarely seen.
- Encephalitis: typically develop toward the end of the first week of the exanthem, but there are cases in which central nervous system involvement has preceded the rash.
- Acute cerebellar ataxia.
- Diffuse encephalitis.
- Pneumonia.
- Hepatitis.
- Other — Diarrhea, pharyngitis, and otitis media.
- Disseminated varicella: due to impaired cellular immunity, manifested by ongoing development of crops of vesicles over weeks, large and hemorrhagic skin lesions, pneumonia, or widespread disease with disseminated intravascular coagulation.
Herpes Zoster INTRODUCTION
- The incidence of HZ in adolescent is 1 per 1000 person-years.
- Herpes zoster (shingles) results from reactivation of latent VZV that gained access to sensory ganglia during varicella.
- Herpes zoster is characterized by a painful, unilateral vesicular eruption, which usually occurs in a single or two contiguous dermatomes.
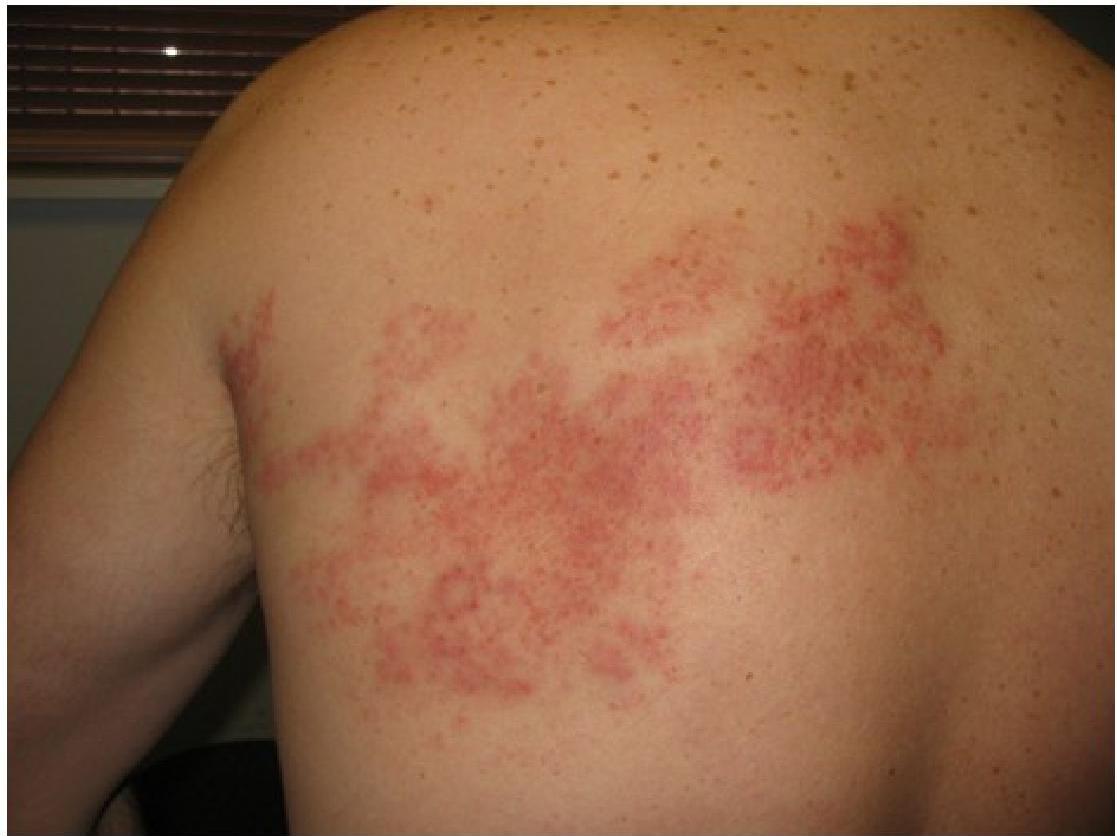 Herpes zoster
Herpes zoster
TRANSMISSION
- Immunocompromised patients are at increased risk of VZV reactivation because of reduced T cell-mediated immunity.
- Physical trauma may be a risk factor for herpes zoster, particularly cranial herpes zoster.
- Children with herpes zoster can transmit VZV, causing varicella in contacts.
- In patients with herpes zoster, VZV is spread by direct contact with active herpes zoster lesions or through inhalation of aerosolized virus from skin lesions. Lesions are considered infectious until they have fully crusted.
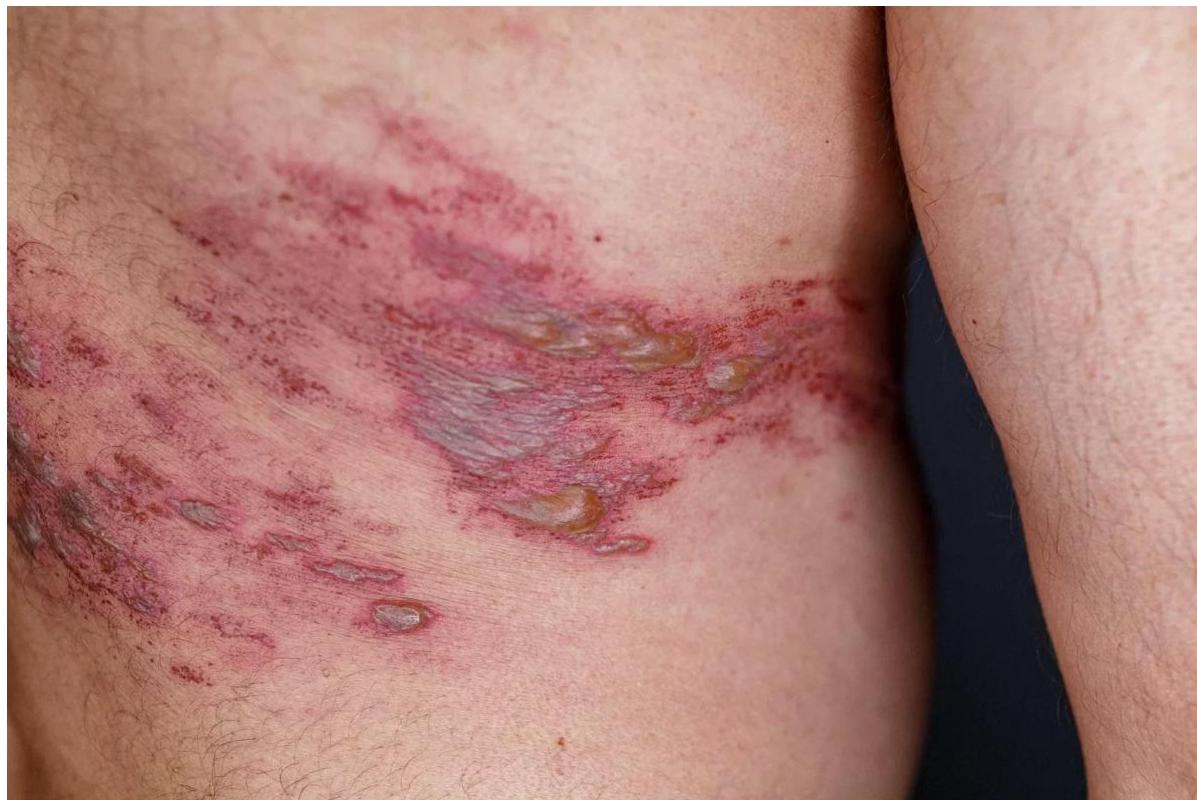
CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
-
Rash starts as erythematous papules, typically in a single dermatome or several contiguous dermatomes, corresponds to the sensory fields of the ganglion.
-
Within several days, grouped vesicles or bullae are the predominant manifestation. Within three to four days, the rash becomes pustular. The rash can be hemorrhagic in immunosuppressed children.
-
In immunocompetent hosts, the lesions crust by 7-10 days and are no longer considered infectious. Scarring and hypo- or hyperpigmentation may persist months to years after herpes zoster has resolved. The development of new lesions more than a week after presentation suggest underlying immunodeficiency.
-
The thoracic and lumbar dermatomes are most commonly involved. Herpes zoster occurs on the face in 10% of cases.
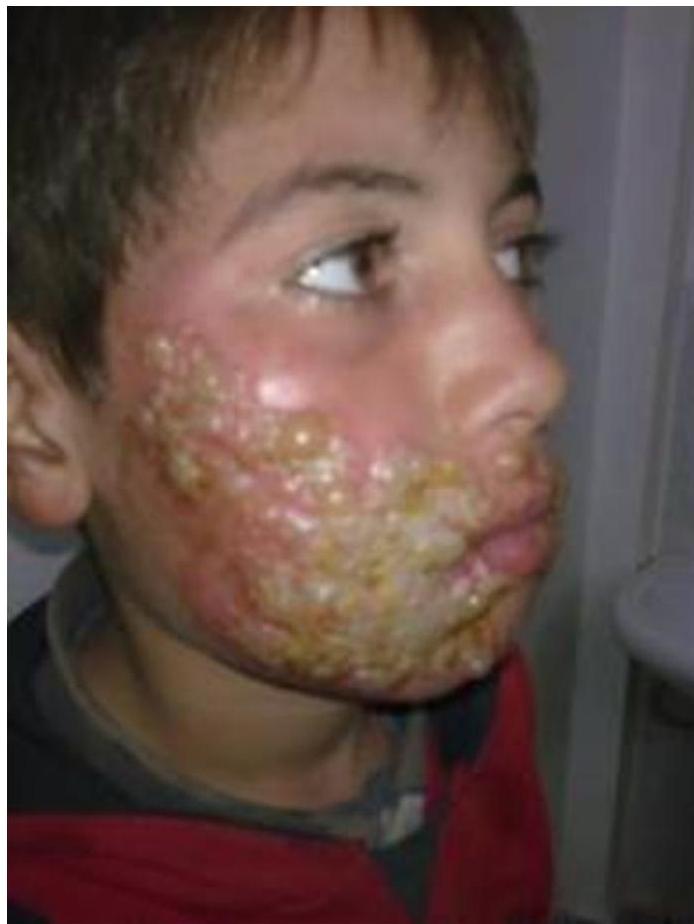
CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS..CONT
Acute neuritis :
- Pain is the most common symptom of herpes zoster.
- Most patients describe a deep “burning,” “throbbing,” or “stabbing” sensation.
- Pain occur in the area of rash, in may last for 1M.
- Approximately 75% of patients have prodromal pain that precedes the rash in the affected dermatome.
- Prodromal pain may be constant or intermittent and typically precedes the rash by two to three days.
Complications
- HZO begins with a prodrome of headache, malaise, and fever.
- Unilateral pain or hypesthesia in the affected eye, forehead, and top of the head may precede or follow the prodrome.
- With the onset of the rash, hyperemic conjunctivitis, uveitis, episcleritis, and keratitis may occur ptosis is rare.
- Acute keratitis typically involves the epithelial, stromal, or endothelial layers of the cornea. Patients who develop epithelial or stromal keratitis are most at risk for vision loss.
- Acute retinal necrosis.
- Postherpetic neuralgia : most common complication (5% adolescents) of HZO , defined as significant pain persisting for 90 days after the onset of rash. Sensory symptoms include numbness, pruritus, in the affected dermatome. Usually resolves within weeks.
- Encephalitis /Aseptic meningitis.
- Peripheral motor neuropathy.
- Guillain-Barré syndrome.
- Disseminated infection in immunocompromised children.
- Bacterial superinfection.
- Ramsay Hunt syndrome (herpes zoster oticus): facial paralysis, ear pain vesicles in the ear and vertigo.
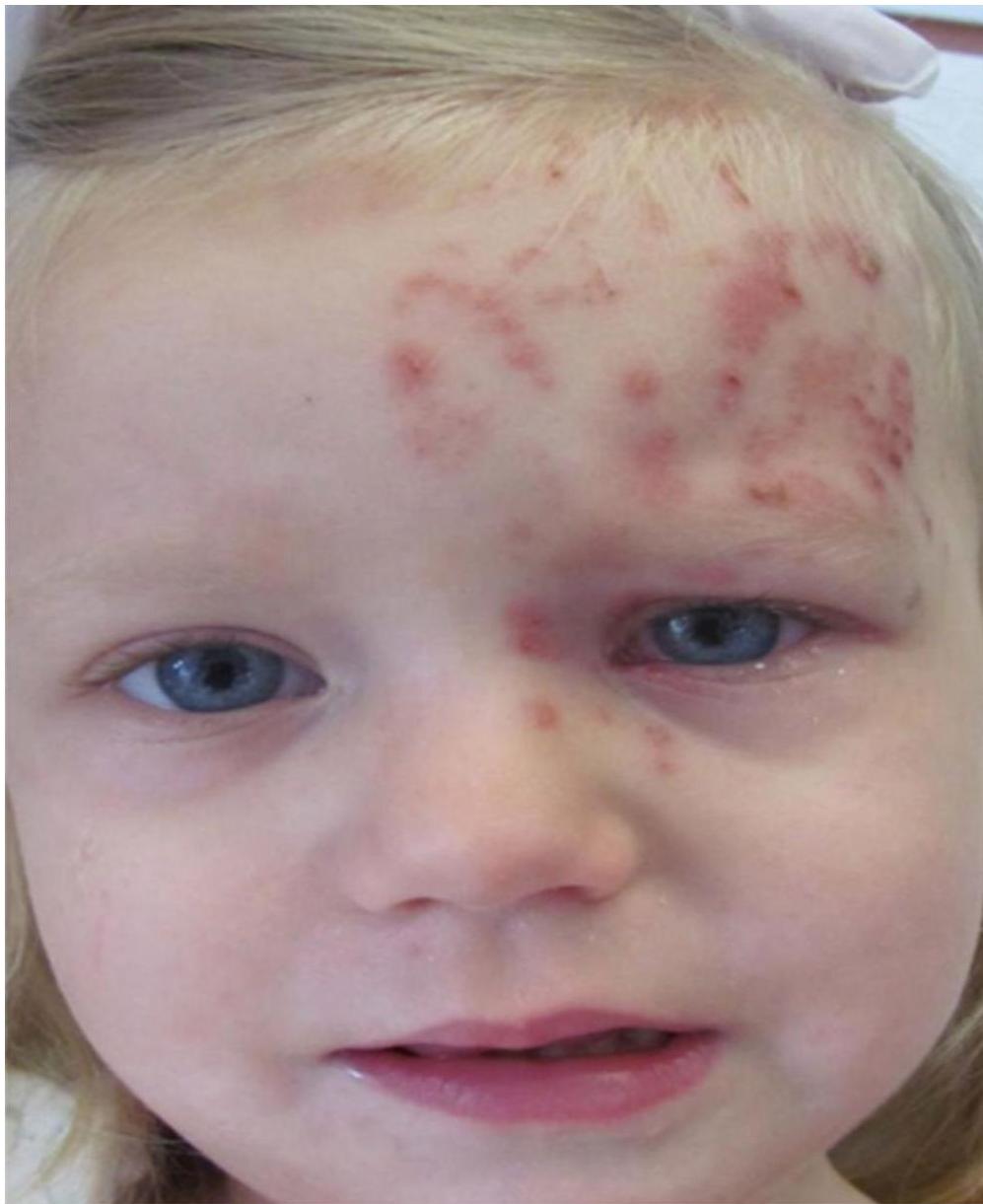
DIAGNOSIS:
☐ The diagnosis of herpes zoster is usually based solely on the clinical presentation (unilateral, usually painful vesicular eruption with a well-defined dermatomal distribution.
☐ Laboratory confirmation should be attempted when the clinical presentation is uncertain:
- PCR testing is sensitive (>95 %) and rapid (≤1 day), can be used to test lesions of all stages, CSF and blood.
- Direct fluorescent antibody (DFA) testing on scrapings from vesicular skin lesions or viral culture.
- Anti-VZV antibody testing,
- Assessing for predisposing conditions For patients with disseminated disease:
- Complete blood count, peripheral blood smear.
- Quantitative serum IgG, IgM and IgA levels.
- HIV antigen and antibodies combined testing.
- Assessment of populations of lymphocytes.
Treatment of herpes zoster
☐ Uncomplicated dermatomal zoster (excludes patients with signs and symptoms of disseminated disease or involvement of the eye, ear, or CNS):
-
Antiviral therapy within 72 H of symptom onset and uncrusted lesions, promote healing of skin lesions, lessen the severity and duration of acute neuritis. It is unclear if antiviral therapy prevents postherpetic neuralgia.
-
Antiviral therapy is also recommended for selected patients who present after 72 hours of symptom onset and have uncrusted lesions (immunocompromised, involvement of the face or neck, severe atopic dermatitis) and patients forming new crops of lesions.
-
There is no benefit of antiviral therapy once all lesions have crusted.
-
Oral valacyclovir or acyclovir for Uncomplicated dermatomal zoster.
-
Pain control: Acetaminophen/NSAIDs. Oxycodone.
-
Antibiotics.
☐ Management of complicated disease:
- Initial treatment with IV acyclovir, adjunctive glucocorticoids in selected patient eg Ramsay Hunt syndrome.
 |
|---|
Derma
Chicken Pox
- Chickenpox (varicella) and herpes zoster (shingles) are distinct diseases caused by the varicella-zoster virus
- Chickenpox is a bollus (blister disease).
- Chickenpox is a highly contagious disease that usually occurs in childhood
- It is the manifestation of a primary infection with varicella-zoster virus
Transmission
- Approximately 90% of chickenpox cases occur in children under 10 years of age
- The infection is transmitted by airborne droplets containing the virus
- Incubation period is 2 weeks after exposure
- The patient is contagious some few days before the rash appears
Clinical features
Before skin lesions (2 or 3 days) :
- Young children have a low-grade fever, and general malaise
- Adults have fever, chills, malaise, headache, and possibly, sore throat appear before the rash
Clinical features (cont.)
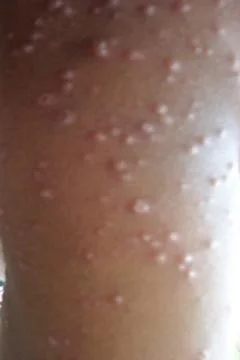
- Blisters appear first on the face and scalp, then on the trunk, and then on the arms and legs
- Itchy blisters initially appear on erythematous base
- Blisters are typically with central punctum
- They resolve in 1 to 3 weeks, usually without scarring.
- Once all the lesions are crusted over, patient is no longer contagious.
Treatment
- No specific treatment is required
- Symptomatic relief from itching an important part of treatment
- Calamine lotion can be applied, the cool sensation helps control the itching
- Systemic antibiotics is given in some cases to prevent secondary bacterial infection (but should not be a routine for all cases)
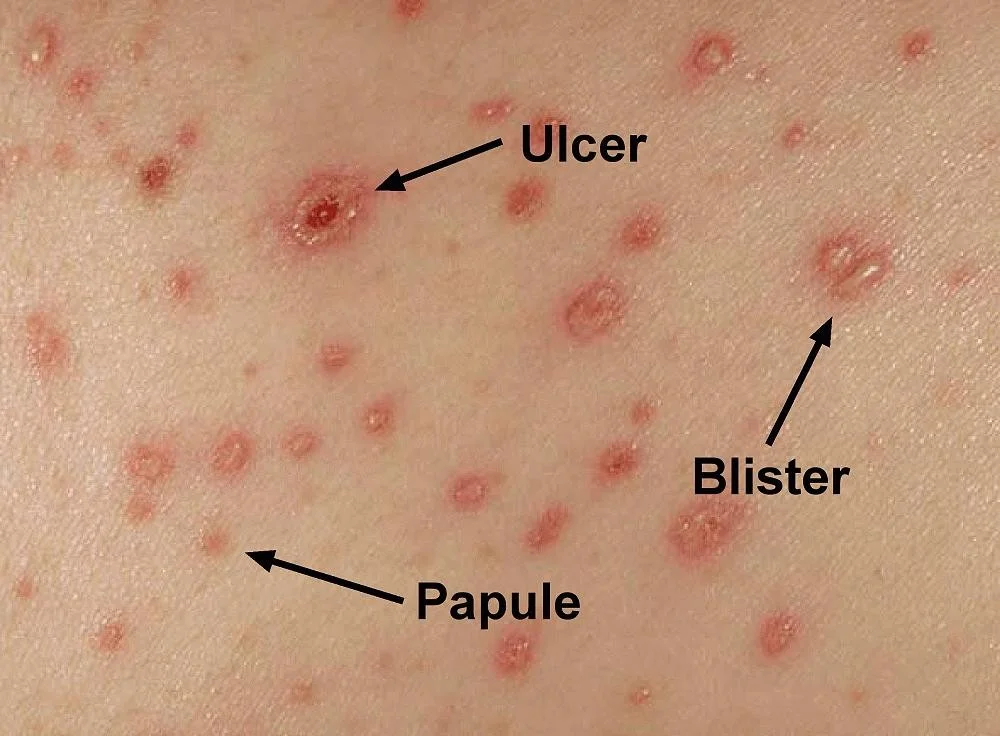
Ulcer Blister Papule