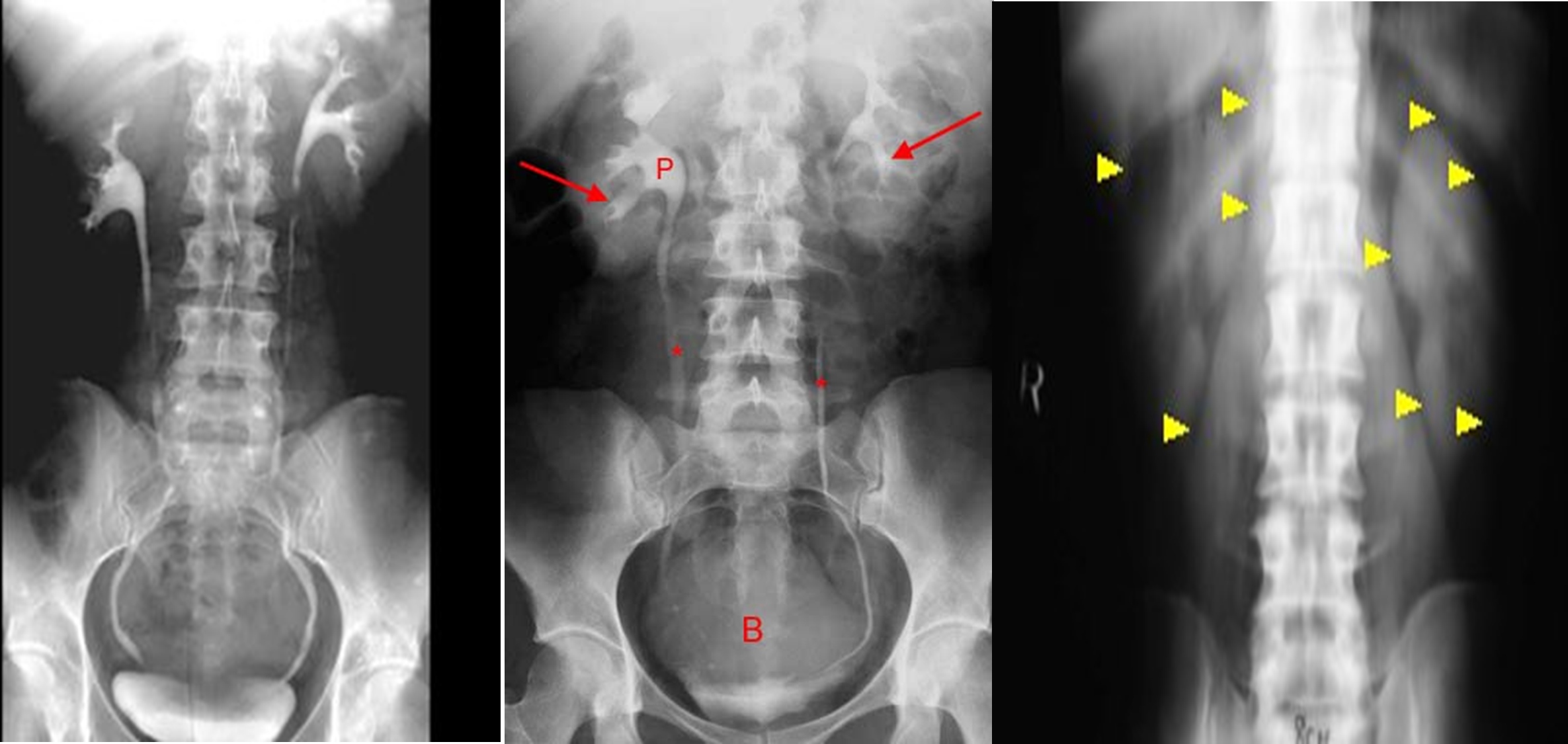
Intravenous urography
is an x-ray examination of the urinary tract consisting of kidneys, ureters and bladder following an injection of contrast into a vein in the arm.
- Shows anatomy and functions of the kidneys.
- Note that calcification can be obscured by contrast medium and stones are missed if no plain film is taken
Low osmolar non ionic contrast is used which has fewer complications.
Scout film ( abd. ) , Scout film is also called KUB
- Preparation/stone
Series of radiograph are taken
- Inject bolus of contrast
- Supine ,oblique , prone upright and post void film are taken
- Prone films to see distal ureters
The major causes of urinary tract calcification include:
- -Calculi.
- -Diffuse nephrocalcinosis.
- -Localized nephrocalcinosis (e.g. tuberculosis or tumours).
- -Prostatic calcification.
Rarely indicated given the broad availability of CT - Immediate film of the renal areas: AP film of the renal area. Aim to show the nephrogram opacified by contrast in the renal tubules.