I. UMN Facial Paralysis
- Caused by lesions in the brain above the facial nucleus.
- Lesion Site: Supra-nuclear (from cerebral cortex to the facial nucleus)
- Causes:
- Trauma
- Inflammation (e.g., encephalitis, brain abscess)
- Brain Tumors
- Cerebral Vascular Accidents (thrombosis, hemorrhage, embolism)
- Degenerative Diseases (Multiple Sclerosis)
II. LMN Facial Paralysis
- Resulting from lesions in the facial nucleus or the facial nerve itself.
A) Intracranial Causes
- Lesion in the pons affecting the facial nucleus (similar causes to UMNL)
- Lesion at the cerebello-pontine angle (e.g., Acoustic Neuroma, arachnoid cyst, congenital cholesteatoma)

B) Intra Temporal (Otogenic) Causes
(During its course in the temporal bone)
- Idiopathic: Bell’s palsy
- Traumatic:
- Accidental (e.g., birth trauma, transverse temporal bone fracture)
- Operative (e.g., during mastoidectomy)
- Inflammatory:
- Bacterial (secondary to otitis media or malignant otitis externa)
- Viral (e.g., Herpes Zoster Oticus/Ramsay Hunt Syndrome)
C. Extracranial (Infratemporal) Causes
- Malignant parotid gland tumors
- Traumatic:
- Accidental
- Surgical (e.g., during parotidectomy)
- Birth trauma due to forceps pressure over the stylomastoid foramen (usually incomplete and transient)
- Inflammatory:
- Peripheral neuritis (viral or diabetic mellitus)

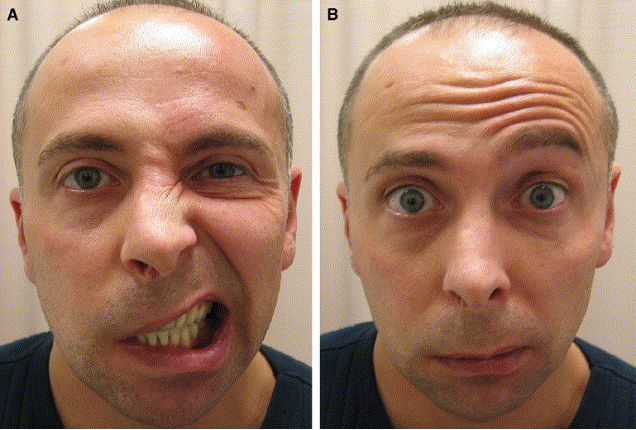
UMNL vs. LMNL
| Feature | UMNL | LMNL |
|---|---|---|
| Affected Area | Lower half only (upper half spared due to bilateral innervation) | Whole face |
| Movements | Emotional (involuntary) preserved | Both voluntary and emotional movements lost |
| Paralysis Type | Spastic paralysis with no muscle wasting or degeneration | Flaccid paralysis with muscle wasting and degeneration |
| Associated Symptoms | Usually accompanied by hemiplegia | No hemiplegia |