Pheochromocytoma:
- Rare, catecholamine-secreting tumor
- 10% is malignant
Symptoms & Signs
Classically, it manifests with the classic triad: Headaches, Palpitations, Diaphoresis
Severe hypertension/ related complications:
- Cardiovascular complications such as myocardial infarction and arrhythmias
- Sudden death may occur in patients with undiagnosed tumors who undergo other surgeries or biopsy.
- Precipitate hypertensive encephalopathy & cerebral hemorrhage.
- Panic attacks
The following may also occur: Tremor, Nausea, Weakness, Anxiety, sense of doom, Epigastric pain, Constipation
Diagnosis:
- 24-hour (urine-VMA
- Plasma metanephrine metabolite of Epinephrine)
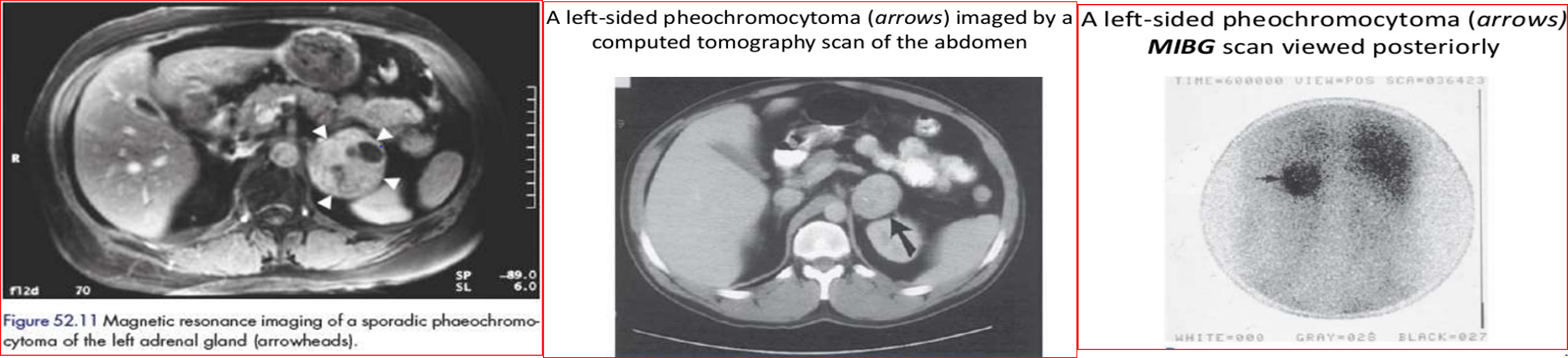
- CT/MRI to locate tumor/ (MIBG scan)
Intervention:
-
Alpha-blocking agents
- Prazosin (Minipress) to decrease BP
-
Beta-blocking agents
- Inderal to control heart rate
-
Sedatives
-
Surgical resection of the tumor is the treatment of choice and usually cures the hypertension
An MIBG scan iodine-123 meta-iodobenzylguanidine
-
is commonly used for the detection of neuroendocrine tumors, such as neuroblastoma and pheochromocytoma.
-
It can also aid in the detection of carcinoid and medullary thyroid carcinoma