Clinical features
-
**Constitutional symptoms:
- fatigue, headache**
-
Optic neuritis
- Most often the earliest manifestation
- Typically unilateral
- Can be painful
- Impaired vision and color blindness
Imaging
MRI (with and without gadolinium) is the imaging study of choice for the diagnosis and monitoring of MS.
Typical findings on MRI
- Multiple sclerotic plaques (most commonly found in the periventricular white matter) with finger-like radial extensions (Dawson fingers) related to demyelination and reactive gliosis
- In T1: hypointense or isointense lesions
- In T2 and FLAIR: hyperintense lesions, typically round or oval in shape and found in both hemispheres
- Contrast-enhancement of active lesions
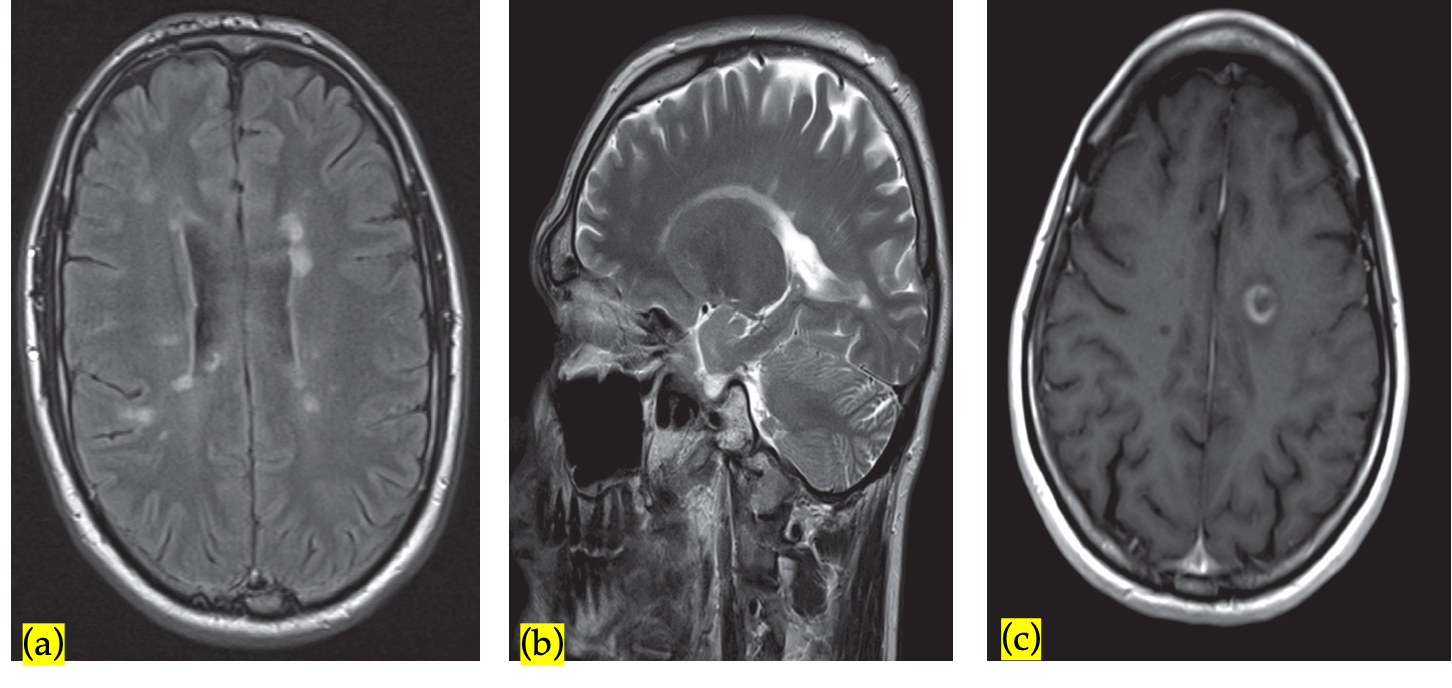 (a)Axial FLAIR sequence at the level of the lateral ventricles shows periventricular areas of linear and ovoid hyperintense signal orientated perpendicular to the body of the right lateral ventricle. This feature is known as Dawson fingers and is strongly associated with multiple sclerosis. It represents perivascular inflammation around the subependymal veins.
(a)Axial FLAIR sequence at the level of the lateral ventricles shows periventricular areas of linear and ovoid hyperintense signal orientated perpendicular to the body of the right lateral ventricle. This feature is known as Dawson fingers and is strongly associated with multiple sclerosis. It represents perivascular inflammation around the subependymal veins.
(b)Parasagittal T2-weighted MRI shows plaques of demyelination as high signal in the white matter, particularly along the margins of the lateral ventricles and immediately next to cortical grey matter.
(c)Post contrast T1 sequence showing a broken ring of enhancement typical of demyelination.
Spinal Vertebrae
Autoimmune disease. Most common demyelinating disease of spinal cord and brain. - Common in young adult women It is associated with optic neuritis
Spinal cord may be the earliest affected by MS plaques.
MRI spinal cord (with and without gadolinium):
-
To increase diagnostic yield (e.g., in patients with nondiagnostic brain MRI or symptoms of partial myelitis.
-
The most common finding on T2WI of one or more elongated, poorly marginated, hyperintense intramedullary lesions.
-
The foci may has mass effect and enhance at the post-contrast study.
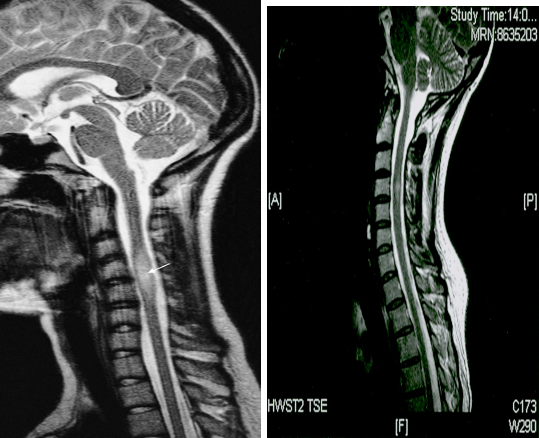
A) T2-weighted MRI showing a plaque of demyelination (arrow) in a patient with multiple sclerosis
B) Multiple sclerosis - T2-weighted sagittal MRI of the spinal cord paramedian level: evidence of a hyperintensity of the spinal cord at the level of C4.