Case. Chest pain – central venous line – pneumoperitoneum - pneumomediastinum Diaphram not seen, continues diaphragm sign indicate air in diaphgragm
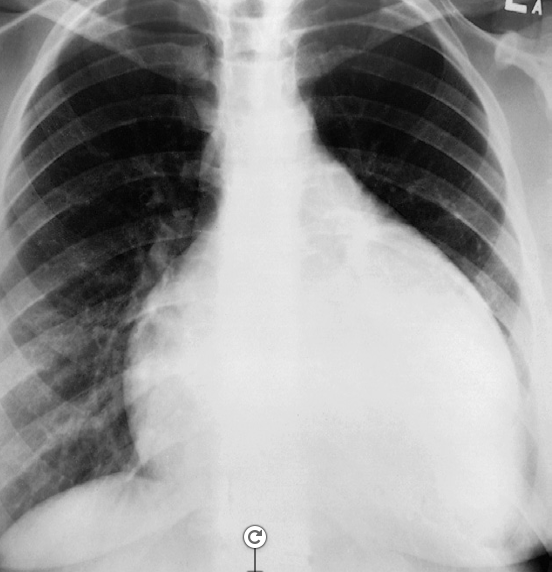
Congestive cardiac failure. There are large bilateral pleural effusions. The heart is enlarged although it is difficult to measure it precisely because the pleural fluid obscures its borders. //– Chest x-ray pleural effusion both, in right costrophrenic & left meniscus sign -
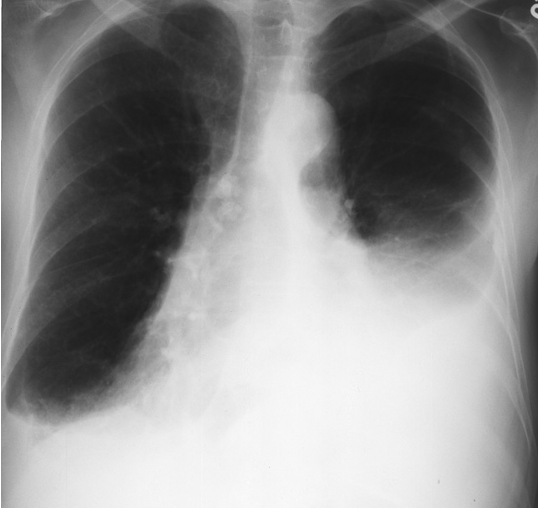
Pericardial effusion. The heart is greatly enlarged. The outline is well defined and the shape globular (Flask - bottle). The lungs are normal. The cause in this case was a viral pericarditis. // Flask shaped, pericardial effusion
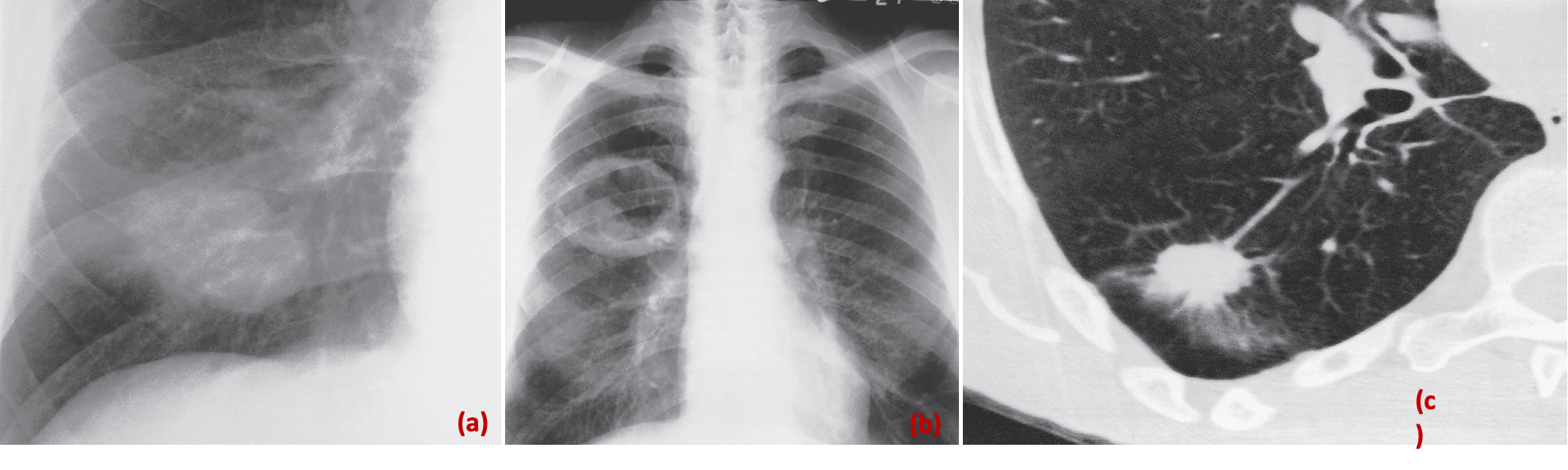
- Appearance of peripheral lung carcinoma. A lobulated mass (a) - opacity – calcified lesion
- **Cavitating mass (b) are shown on plain films.
- **A spiculated mass (c) is shown on CT
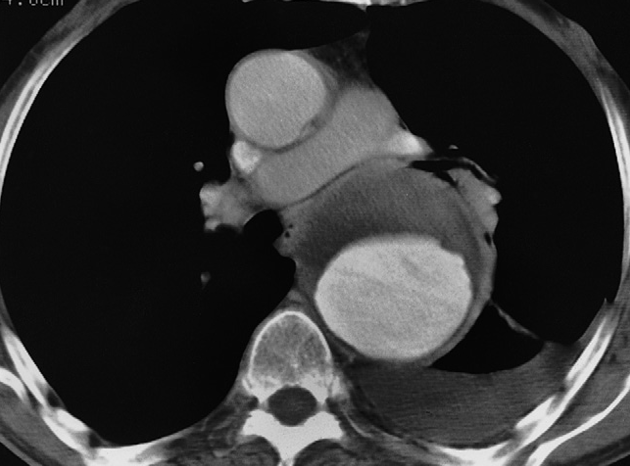
CT showing an aneurysm of the descending aorta. The lumen has been opacified by intravenous contrast enhancement. The unopacified component is clot lining the aneurysm -///
CT Chest Axial window – aortic dissection – Aneurysm diltation.
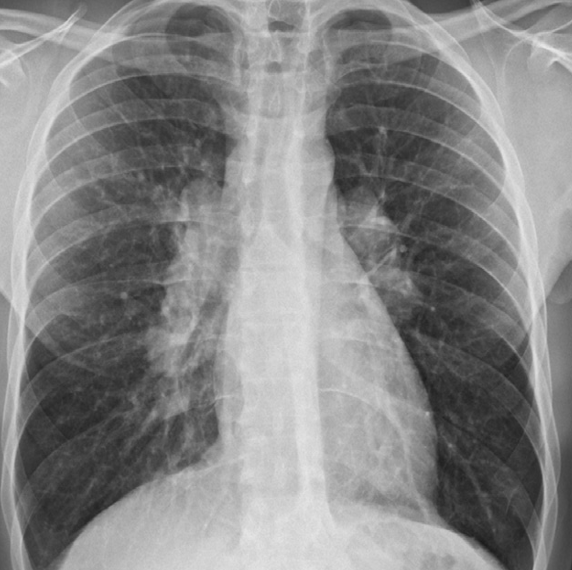
Bilateral hilar adenopathy. The enlarged hila are lobular in outline and dense. The diagnosis in this patient was sarcoidosis. –/// Hilar nodes enlargement - Diff: sarcoidosis, TB, Lymphoma -//