Vitiligo CS-OSPE
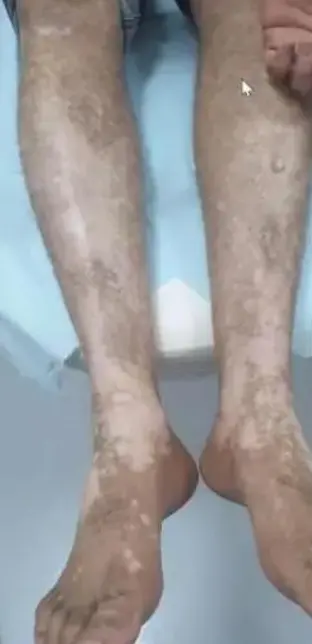
 generalized Z
generalized Z
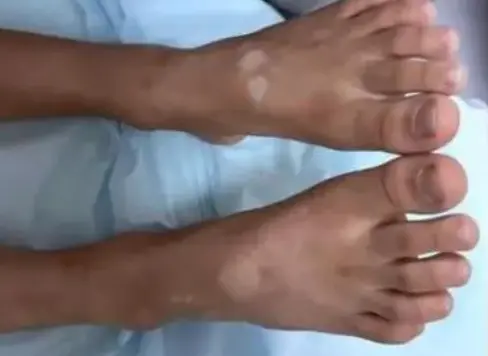

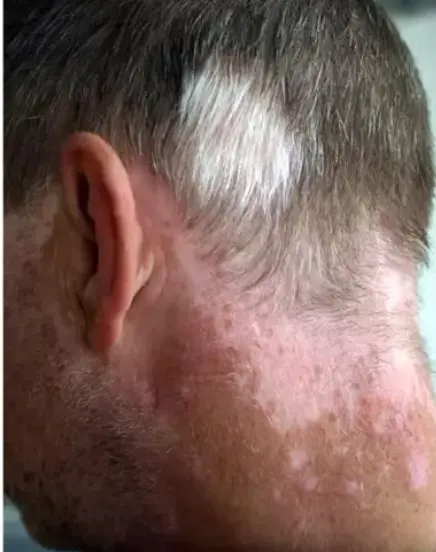
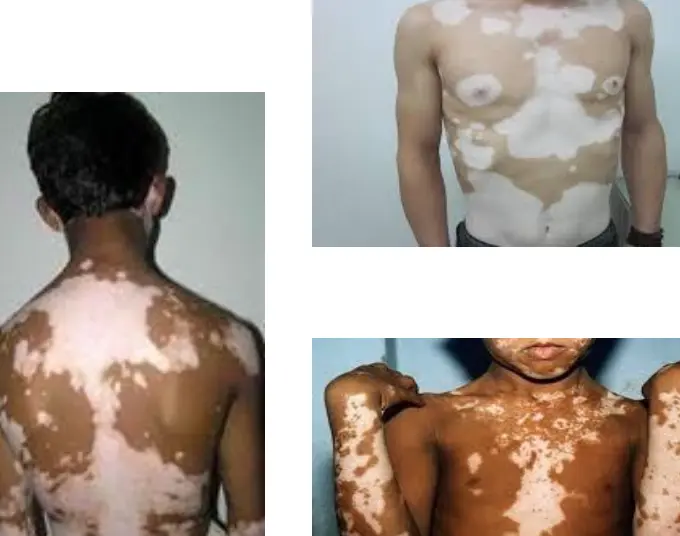
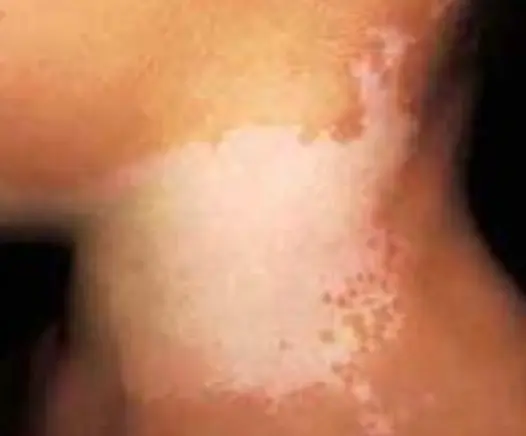 focal
focal
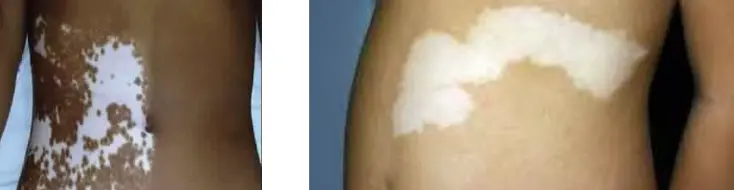
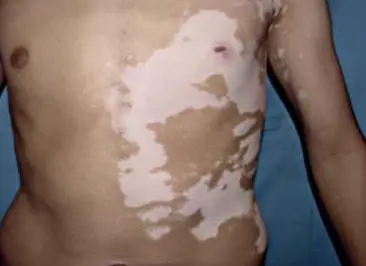 segmental
segmental
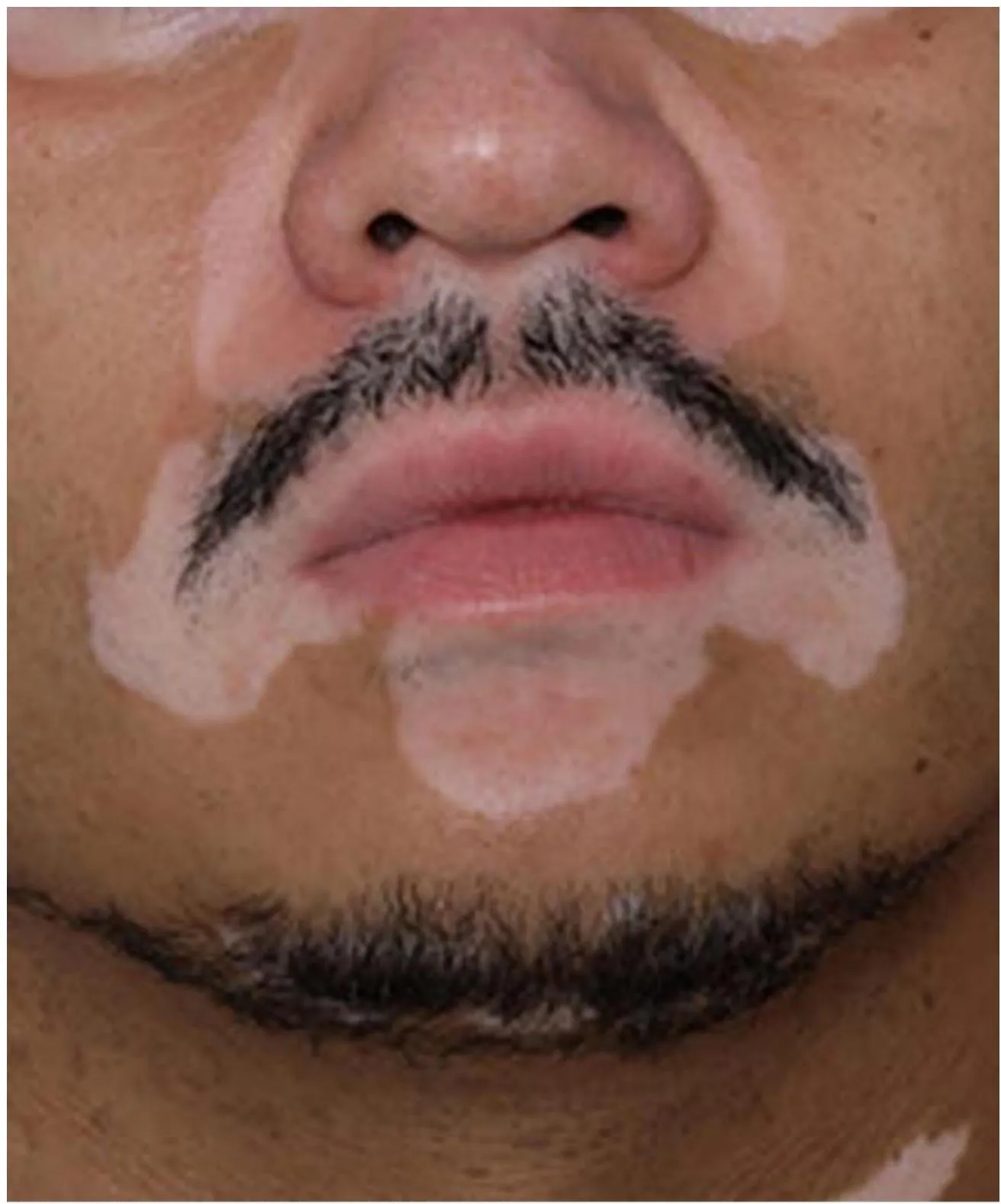
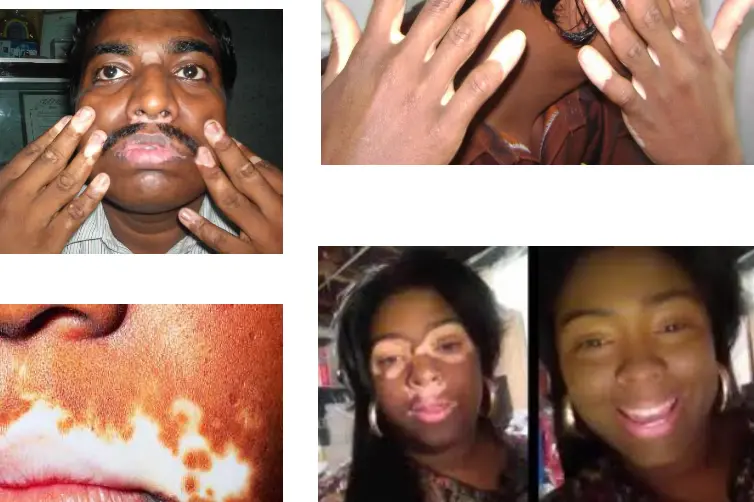 Acro-Facial
Acro-Facial
Diagnosis:
What is the diagnosis?
- VITILIGO
Description/Clinical Features:
Describe/What in this image supports your diagnosis?
- White plaques depigmentation due to loss of normal melanocytes, well demarcated, gressy hair.
Differential Diagnosis:
What is the differential diagnosis?
- pityriasis alba
- pityriasis versicolor
Pathogenesis/Hypothesis:
What is the pathogenesis & what are the different hypothesis?
- Destruction of melanocytes.
- Autoimmune hypothesis
- Autocytotoxic hypothesis
- Neural hypothesis (involving neurotoxin secretions)
Types/Patterns:
What are the (pattern) Types of the disease?
- Focal
- Unilateral/Segmented
- Generalized/Vulgaris
- Acrofacial
- Universal
Associated/Co-occurring Diseases:
What are the common diseases to co-occur/associated with vitiligo?
- Myasthenia gravis
- Alopecia areata
- Addison disease
- Autoimmune diseases like DM type 1
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
Prognosis Factors:
What are the bad prognosis factors?
- Widely separated (difficult to treat).
- If the tips are affected (acral) (difficult to treat).
Tests/Investigations:
Tests that can be done?
- Woods lamp (bright white/ivory whitish)
- Biopsy.
- Thyroid function test
- ANA/Ro/La
Management/Treatment:
How to manage this patient? / What are the treatment options?
- General Management: Full history, Examination, Education, Sunscreen, Skin camouflage.
- Topical Therapies:
- Corticosteroids (e.g., Hydrocortisone is the drug of choice for disease limited to small areas, effective for Repigmentation).
- Immunomodulators.
- Outdoor topical psoralen.
- Phototherapy:
- PUVA therapy (Repigmentation, used in extensive vitiligo, avoided in children under 12).
- Narrowband UVB.
- Excimer laser (308 nm).
- UVA (320-400 nm), UVA1 (340-400 nm), UVA2 (320-340 nm).
- Systemic Therapies:
- Systemic corticosteroids.
- Surgical Treatment: (Repigmentation)
- Tissue graft.
- Implantation of melanocytes.
- Depigmentation: (Depigmentation)
- Bleaching agent (for extensive cases of vitiligo).
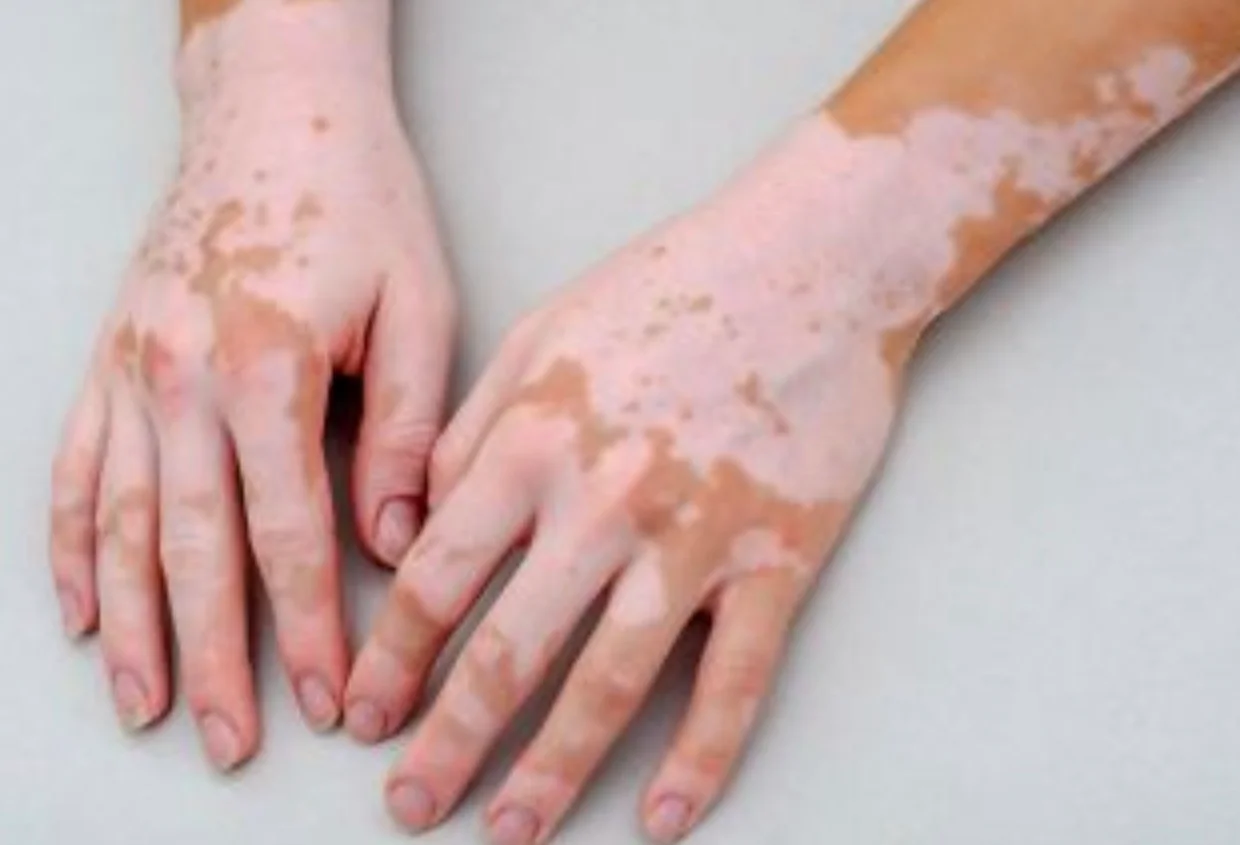

An otherwise healthy 24 Y/O women presented with 6 month history of progressive depigmentation on face, trunk, arms and legs. Around 30% body surface involvement.
Vitiligo
- What is the diagnosis?
- Vitiligo
- What is the best treatment option?
- Narrowband UVB
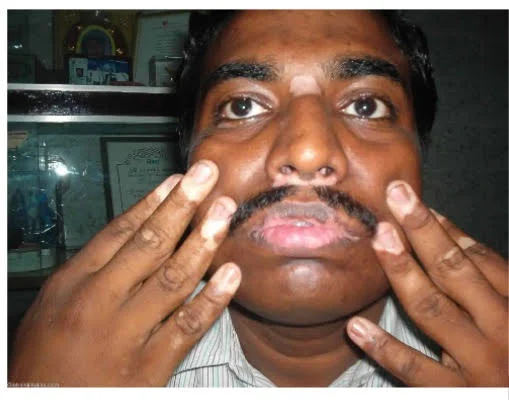
Ali is a 30 Y/O teacher develop these skin lesions. Started to appear as small macules then within five months expanded as current patches on the distal and proximal digits & face.
Acrofacial Vitiligo
- What is the clinical type of disease Ali develop?
- Acrofacial vitiligo
- Which of the following diseases Ali has a high liability to develop?
- Alopecia areata and Addison disease
- What is the possible treatment?
- Excimer laser, topical steroids, depigmentation
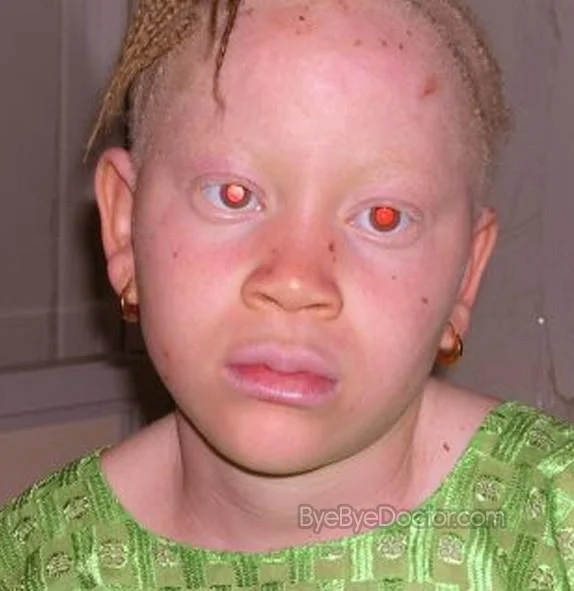
Albinism vs Vitiligo
- What is the condition?
- Albinism
- Pathogenesis:
- Absence of tyrosinase enzyme → no melanin
- What disease might happen to this patient?
- SCC
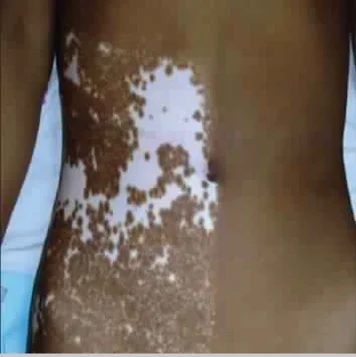
Vitiligo (Segmental Type)
- What is the diagnosis?
- Vitiligo
- What is the type?
- Segmental
- Which of the following may be used? PUVA