Pregnancy Dermatoses CS-OSPE
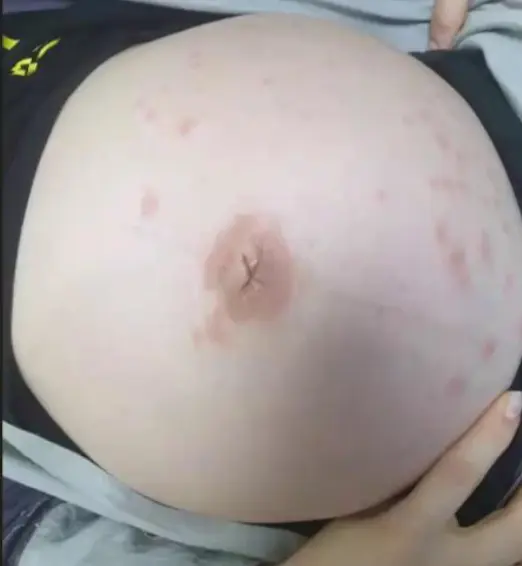
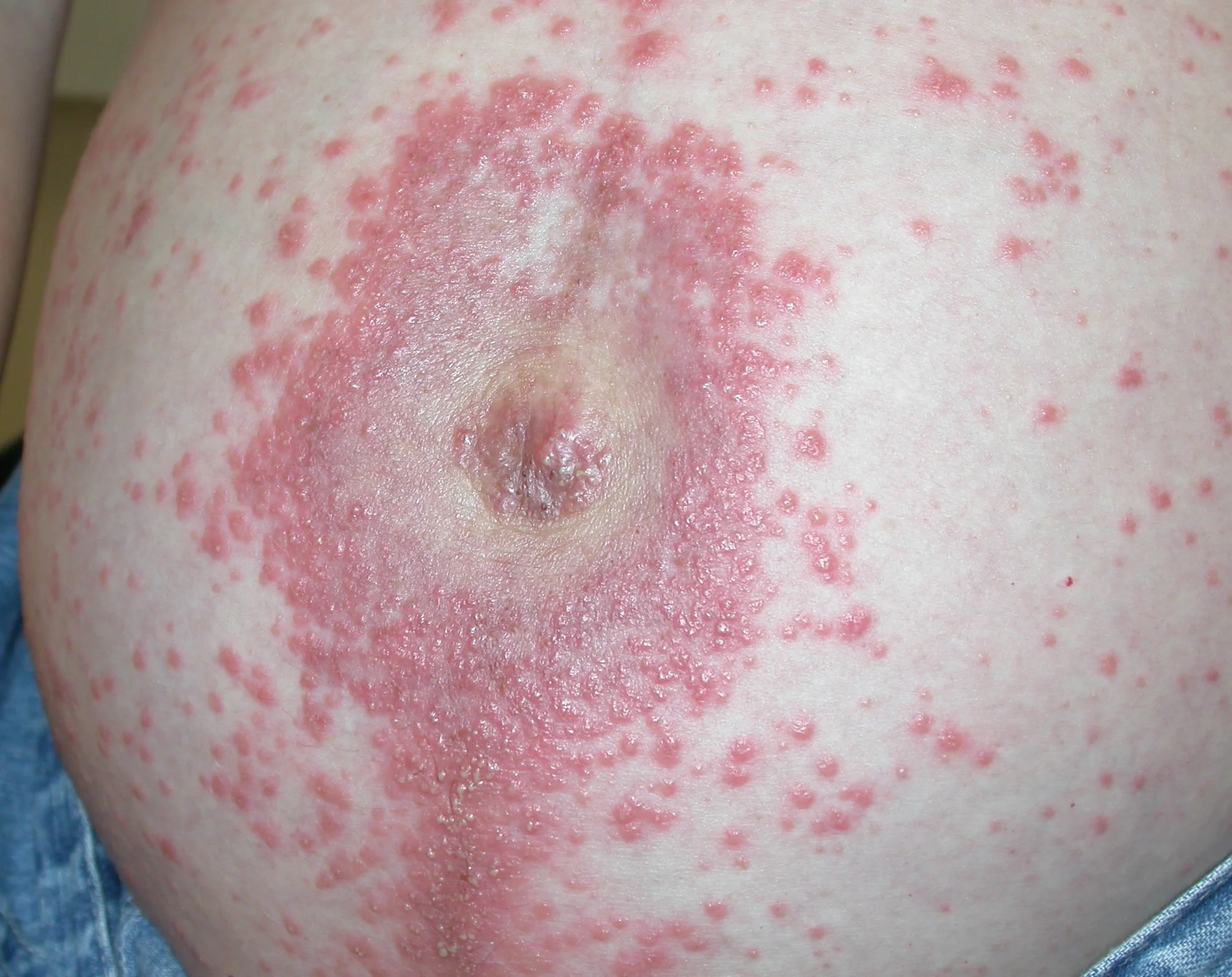
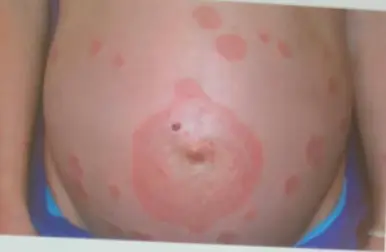
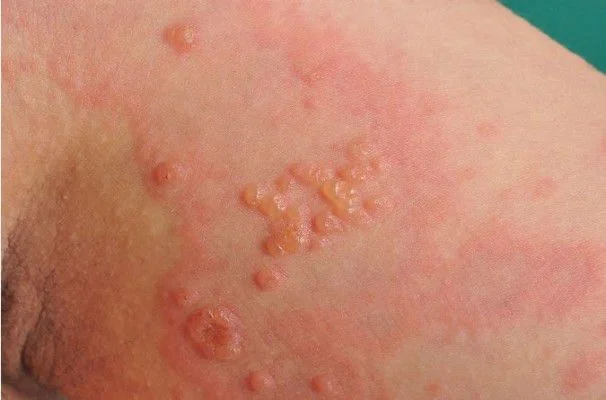
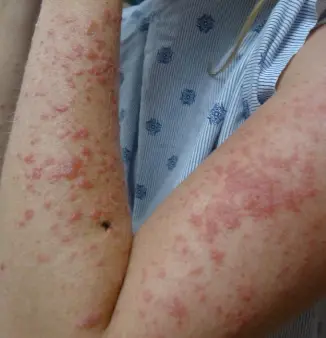
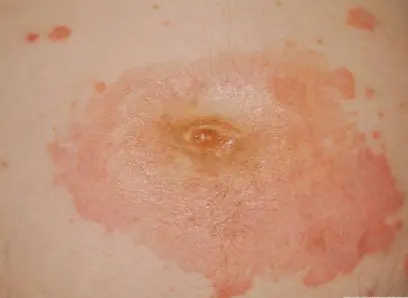
Pemphigoid Gestation / Herpes Gestationis (formerly Pemphigus Gestation)
Description/Clinical Features: Pregnant woman Itchy umbilicus, pruritic eruption Z On her 21 weeks of her pregnancy Involves the umbilicus Subepidermal Blister - Papule - Vesicles - Bullae A multipara lady on her 21 weeks of her pregnancy developed a pruritic eruption. A 35-year-old pregnant woman, G1P0, in her second trimester, presented to the ER with a widespread severe pruritic eruption that involved all the body. On examinations, a few bullae were found on her upper thighs. Her GP tried antipruritic treatments including antihistamines, emollients, and topical steroids without noticeable improvement.
- From the picture and description, what are important clinical features of this condition?
- Widespread pruritic eruption (papules, vesicles, bullae)
- Subepidermal blisters
- Often involves the umbilicus (a key differentiating feature from PUPPP, which usually spares the umbilicus)
- Commonly occurs in the second trimester of pregnancy
Diagnosis:
- Pemphigoid gestationis / Pemphigus gestation (also known as Herpes Gestationis)
Differential Diagnosis (DDx):
- PUPPP (Pruritic Urticarial Papules and Plaques of Pregnancy)
Pathology:
- Subepidermal with esenophiles.
- PB1,2 antigen and IgG .
Confirmatory Test: * Direct Immunofluorescence (DIF): Z * Expected finding: A linear band of C3 +/- IgG at the basement membrane zone.
Support Diagnosis:
- Umbilical involvement
-
- Direct Immunofluorescence
Treatment:
- Topical steroids mild cases Z
- Systemic steroid / Oral prednisone if severe (e.g., Prednisone), especially if topical steroids didn’t improve the patient or in severe/widespread cases. Z
Complications: Z
- Preterm labor / Preterm delivery
- Postpartum severe eruption may occur
- Low birth weight / Small-for-gestational age infants
- Fetus acquires it too / Blister in neonate
- Recurs in later pregnancy / Recurrency
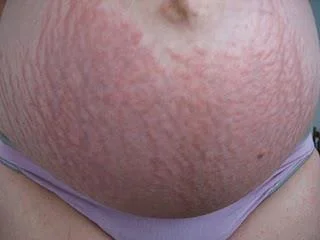
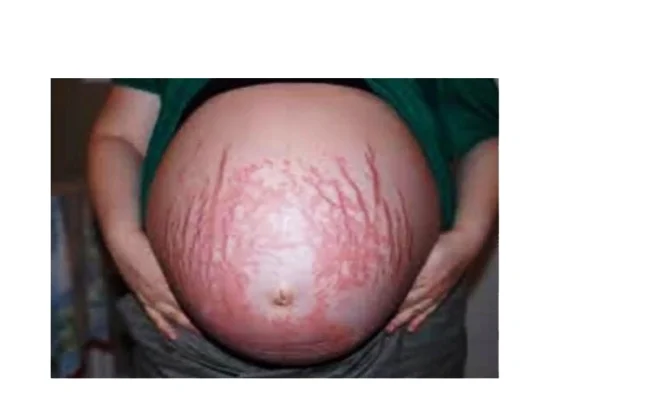
Pruritic Urticarial Papules and Plaques of Pregnancy (PUPPP)
Diagnosis:
- Pruritic urticarial papules and plaques of pregnancy (PUPPP)
Differential Diagnosis (DDx):
- Pemphigoid gestationis
Pathology:
- Hormonal
Characteristic:
- Does not involve the umbilicus, Abdominal striae with not involve the umbilicus, Erythematous urticarial papules surrounded by a pale halo.
Treatment:
- Topical steroid
- In severe case, oral prednisone
- Anti-histamine
What is false (regarding recurrence):
- Recurrence at next pregnancy (implies it usually does not recur)
Intense, non-remitting pruritus without skin lesions, itch is worse after a hot shower
Intrahepatic Cholestasis of Pregnancy (ICP)
Diagnosis Intrahepatic Cholestasis of Pregnancy (ICP)
Differential Diagnosis
- Alcoholic hepatitis
- Drug-induced hepatitis
- Biliary obstruction
- Primary biliary cirrhosis
Description No skin lesions
Pathophysiology Due to increased levels of estrogen
Estrogen Effects
- Promotes cholestasis
- Inhibits reuptake of bile acids into hepatocytes
- Inhibits bile transport proteins
Complications for the Mother
- Bleeding
- Intestinal malabsorption
- Cholelithiasis.
Complications for the Fetus
- Prematurity
- Fetal distress
- Death.
Goal of Treatment
- Decrease circulating bile acids
- Reduce symptoms
- Prevent maternal and fetal complications
Management
- Full history
- Examination
- Education
- Ursodeoxycholic acid
- Vitamin K supplementation
- When cholestasis is severe, delivery is considered earlier if fetal lung maturity is established
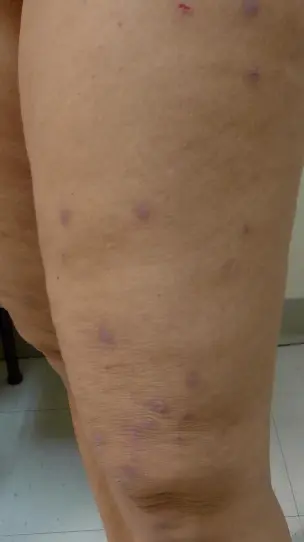
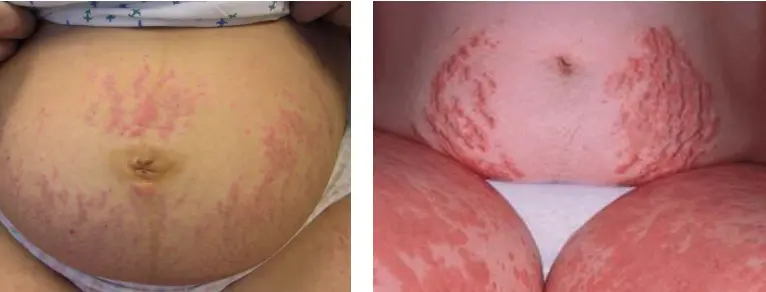
Atopic eruption of pregnancy
How does it clinically present?
- Lichenified papules over the legs, some of which are excoriated
What is the treatment?
- Topical steroids.
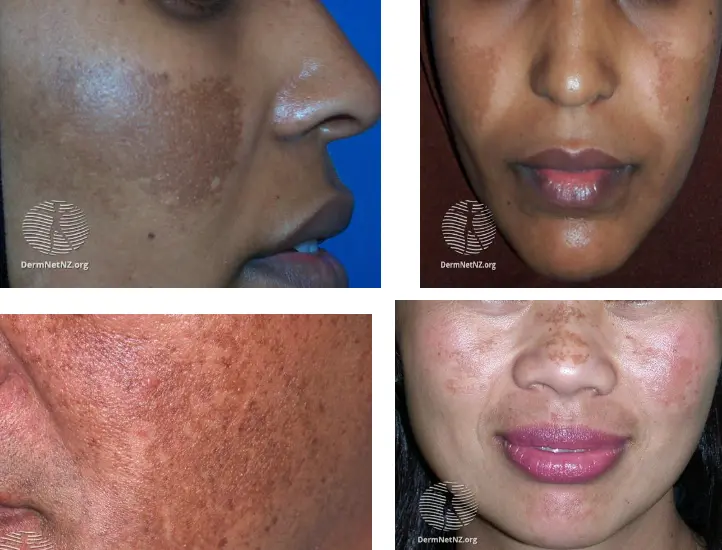
Melasma
What is the diagnosis?
- Melasma.
What is the clinical presentation?
- bilateral, blotchy, symmetrical brownish facial pigmentation.
What is the underlying pathology?
- Overproduction of melanin.
What is the recommended treatment?
- Sunscreen.
- Discontinue hormonal contraception if possible.
- Cosmetic camouflage.
- Kligman regime (Hydroquinone, tretinoin, moderate potency topical steroid).