Middle Ear
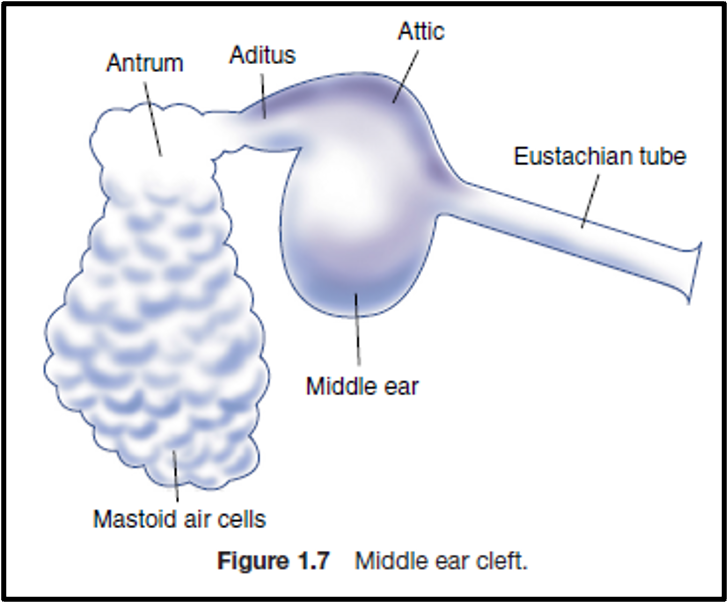
The middle ear, together with the eustachian tube, aditus, antrum, and mastoid air cells, is called the middle ear cleft.
- Lined by mucous membrane and filled with air.
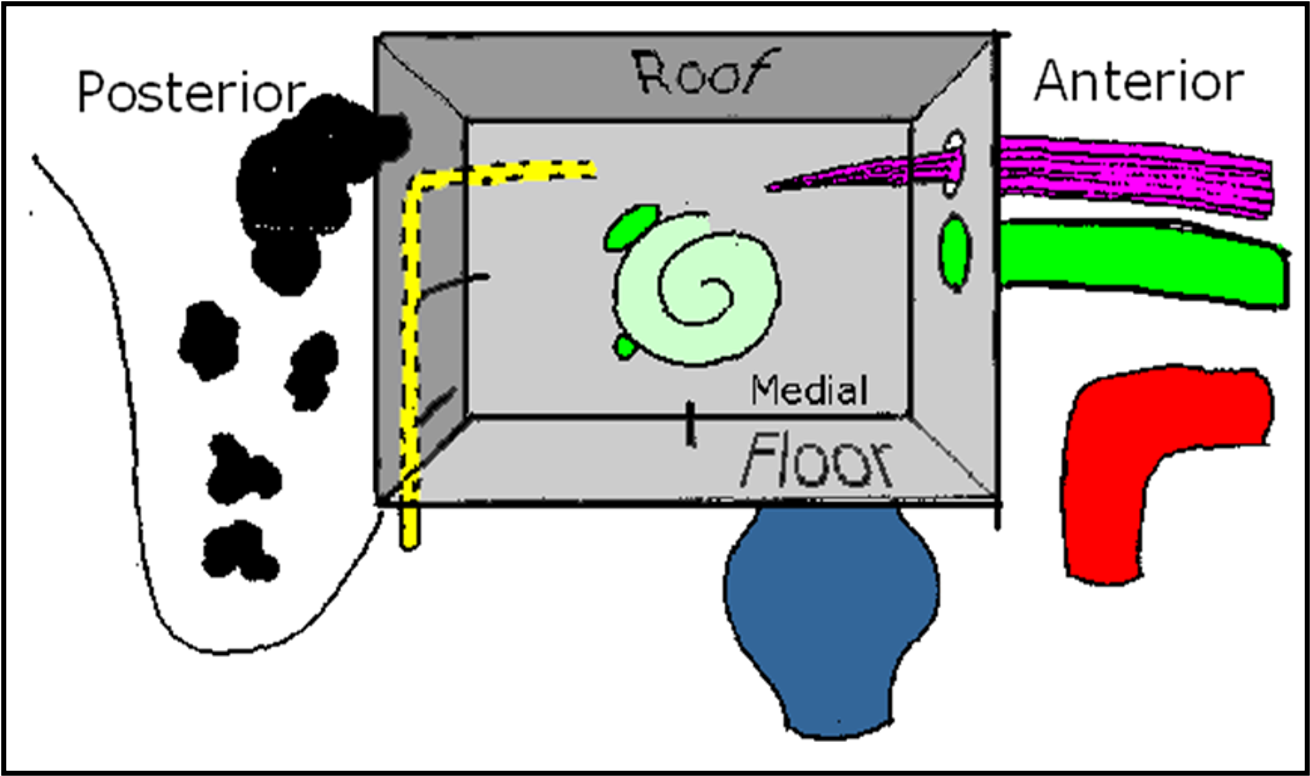
- Six walls:
- Lateral
- Medial
- Anterior
- Posterior
- Floor
- Roof
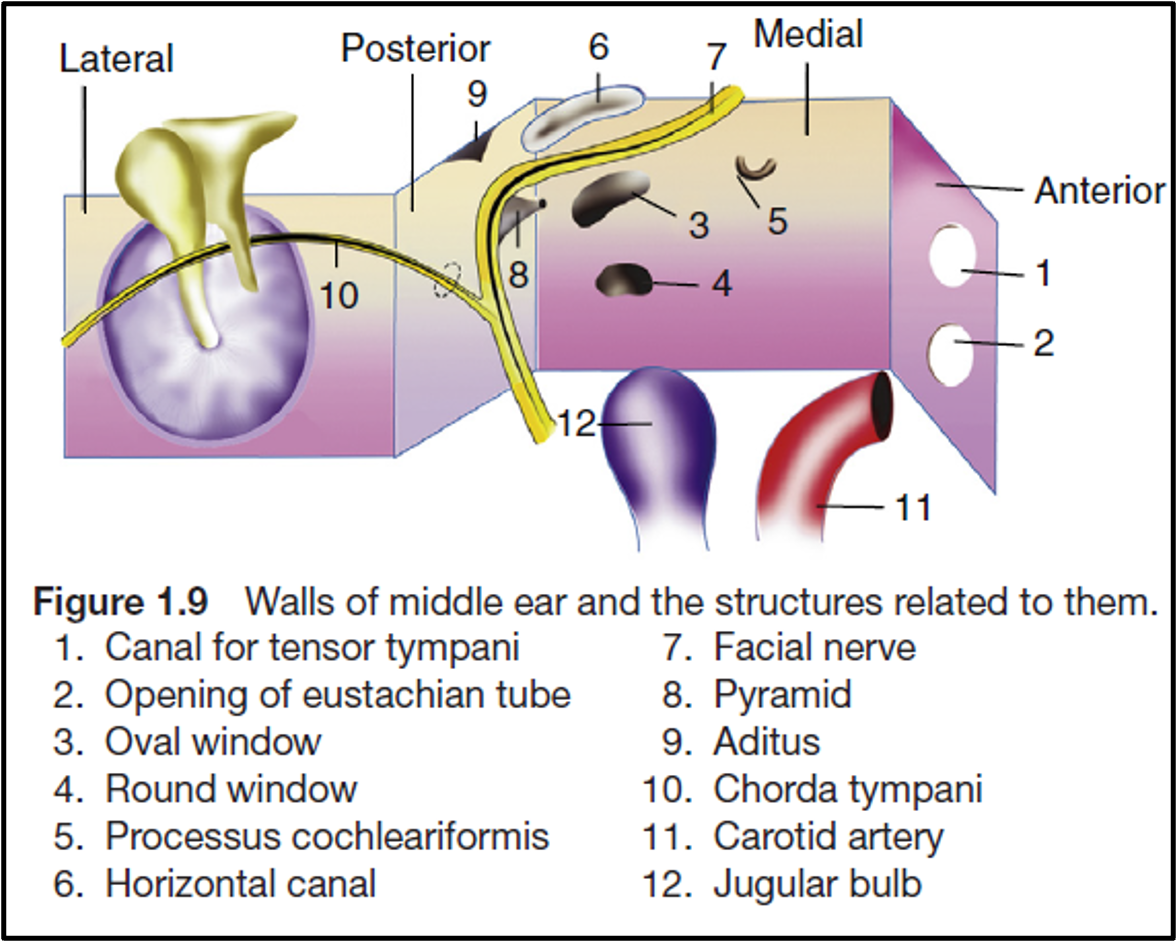
Walls of Middle Ear
- Roof: Tegmen tympani (thin plate of bone).
- Floor: Jugular bulb.
- Anterior Wall: Internal carotid artery, eustachian tube, and tensor tympani muscle.
- Posterior Wall: Pyramid, aditus, facial nerve.
- Medial Wall: Promontory (due to the basal coil of the cochlea), oval window, round window, facial nerve, lateral semicircular canal.
- Lateral Wall: Tympanic membrane and bony outer attic wall (scutum).
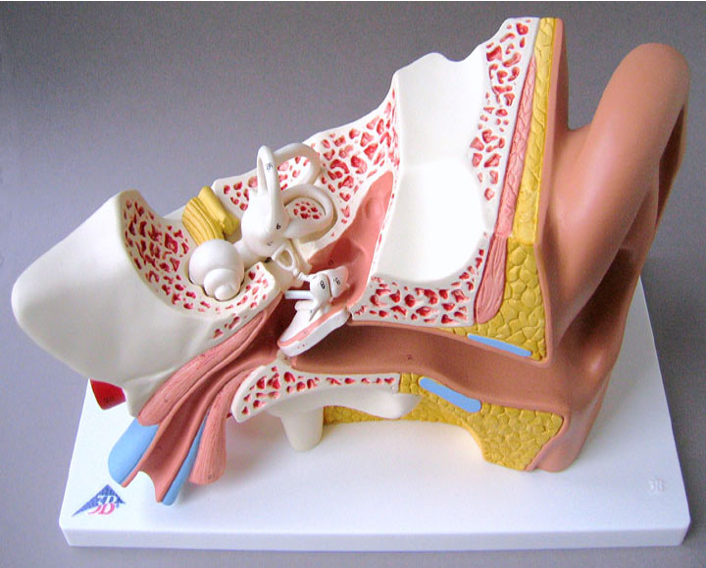
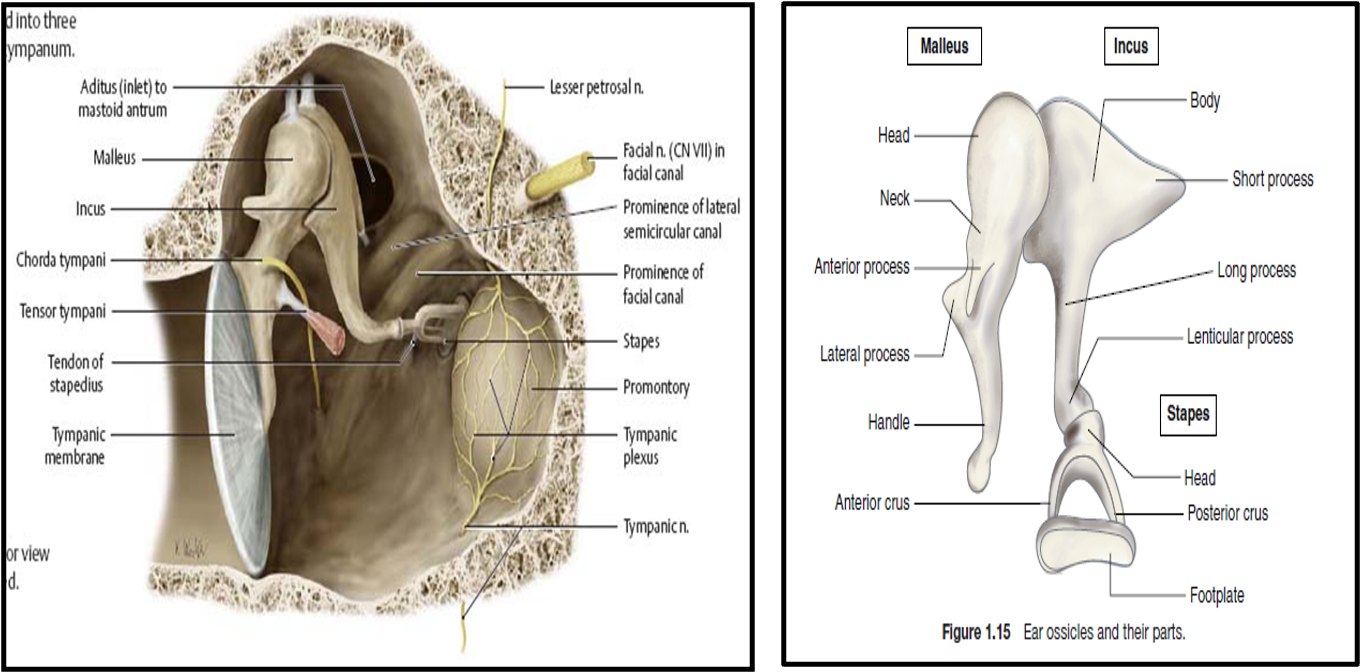
Contents of Middle Ear
- Ossicles:
- Malleus
- Incus
- Stapes
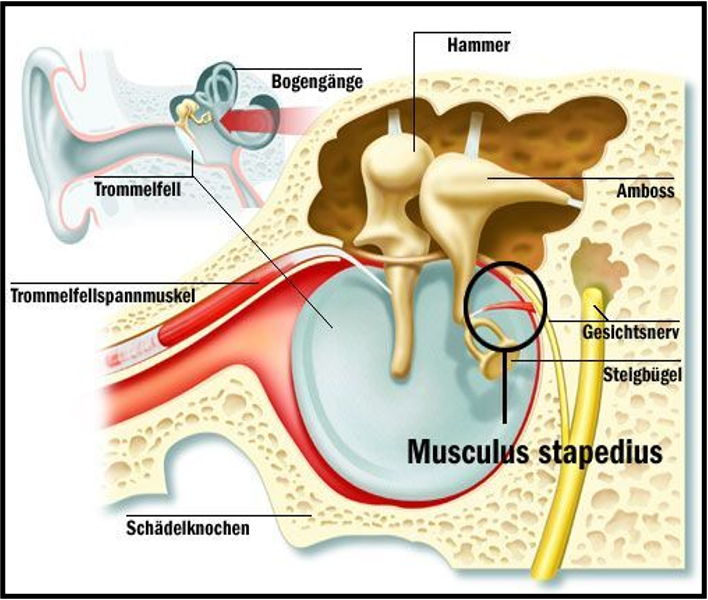
- Intratympanic Muscles:
- Tensor tympani
- Stapedius
- Nerves:
- Chorda tympani
- Tympanic plexus
Tensor Tympani and Stapedius Muscles
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve Supply | Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tensor Tympani | Eustachian tube | Attached to malleus | Trigeminal nerve (V) | Tenses the tympanic membrane, dampens sound vibrations |
| Stapedius | Pyramid on posterior wall of tympanic cavity | Attached to stapes | Facial nerve (VII) | Dampens excessive sound vibrations |
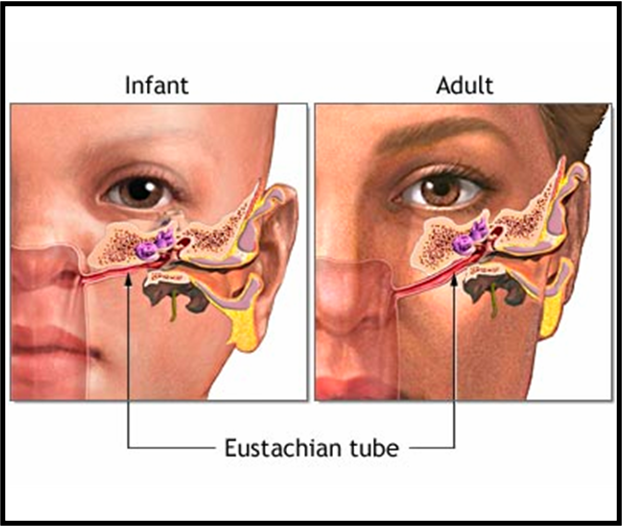
Eustachian Tube
- Posterior 1/3rd: Osseous, opens into the middle ear.
- Anterior 2/3rd: Membranous, opens into the nasopharynx.
- Length:
- At birth: 17–18 mm, more horizontal.
- Adult: 3.5 cm, angulated.
- Muscles:
- Tensor veli palatini
- Levator veli palatini
- Salpingopharyngeus
- Function: The middle ear is aerated through the eustachian tube to keep it at the same pressure as that of the ear canal
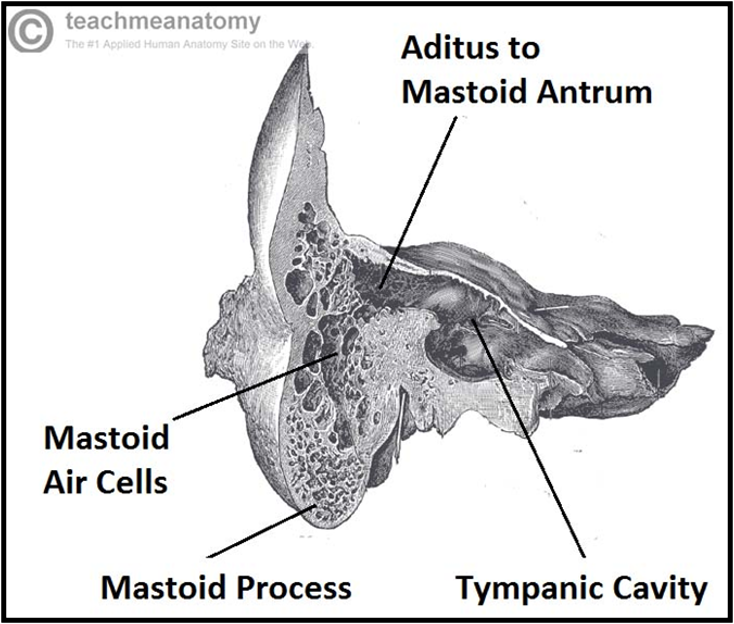
Mastoid
- Consists of bone cortex with a “honeycomb” of air cells underneath.