clinical examinations are:
Preparation for Examination
- Permission
- Privacy
- Nurse presence
- General precautions
Observe while taking history General health Mental state- anxiety, nervousness, agitated
General Examination
- Agitated, nervous or lethargic patient
- Temperature
- Pulse: Tachycardia, bradycardia, water hammer pulse
- BP & RR
- Palm: Moist, sweaty (hyperthyroid)
- Skin: Dry (hypothyroid)
Other Signs
- Tremor: Arm out in front, elbow & wrist straight, finger straight & separated ( out stretched hands)
- Protruded unsupported tongue.
- Thyrotoxicosis- fine fast tremor
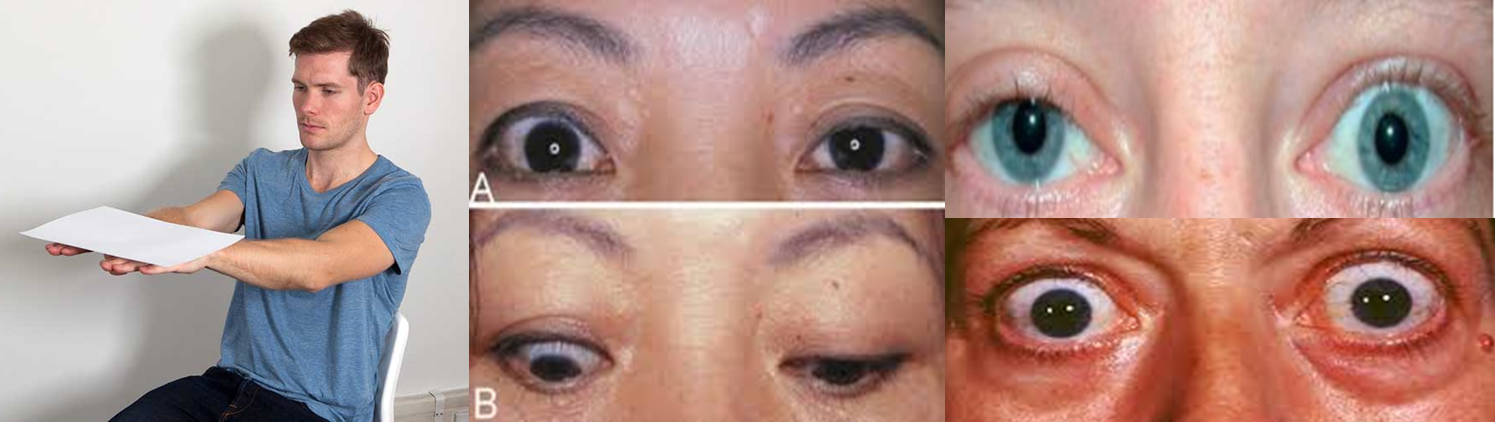
Eye Manifestations:
Signs How to detect it? A- Infrequent blinking. By Inspection B- Apparent rim of sclera above cornea. By Inspection C- Staring look & Lid lag (von Graefe’s sign): upper eyelid fails to follow the eye ball moving downwards
- Lid retraction: Upper lid- higher than normal. Lower lid- normal position D- Lack of wrinkling of forehead on looking up. E- Lack of convergence:
In brief: How to examine eye signs?
- Inspect & comment on infrequent blinking & Exophthalmos.
- Then fix patient head & move your finger to detect lid lag, lack of wrinkling on looking upwards& lack of convergence.
- N.B: Also, you must examine the scalp for metastatic masses.
Eye signs in thyrotoxicosis (hyperthyroidism):
From front: Sclera becomes visible above & below or only below A. Ruler test: Ruler cannot touch both Supra orbital & infra orbital ridges
B. Navzenger’s method: Stand behind the patient and look to his eyes from above , normally you cannot see patient’s eyes
C. Russel Frazer test: Normally, there is a groove between eye ball & supra orbital margin, Loss of this groove → True exophthalmos.
Complete General Examination
- CVS- sinus tachycardia/ fibrillation
- Respiratory system: Tumor, TB
- Abdomen: Hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, other mass, testis
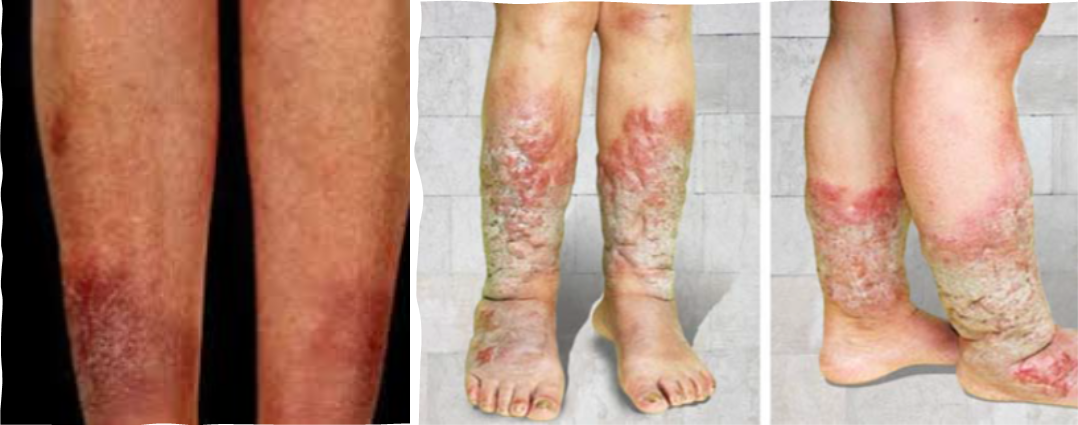
- Extremity- proximal muscle weakness, pretibial myxedema (thyroid dermopathy) – localized lesions of the skin from the deposition of hyaluronic acid