These are drugs that block voltage-gated Ca2+ channels.
Classification of CCBs according to therapeutic effect:
-
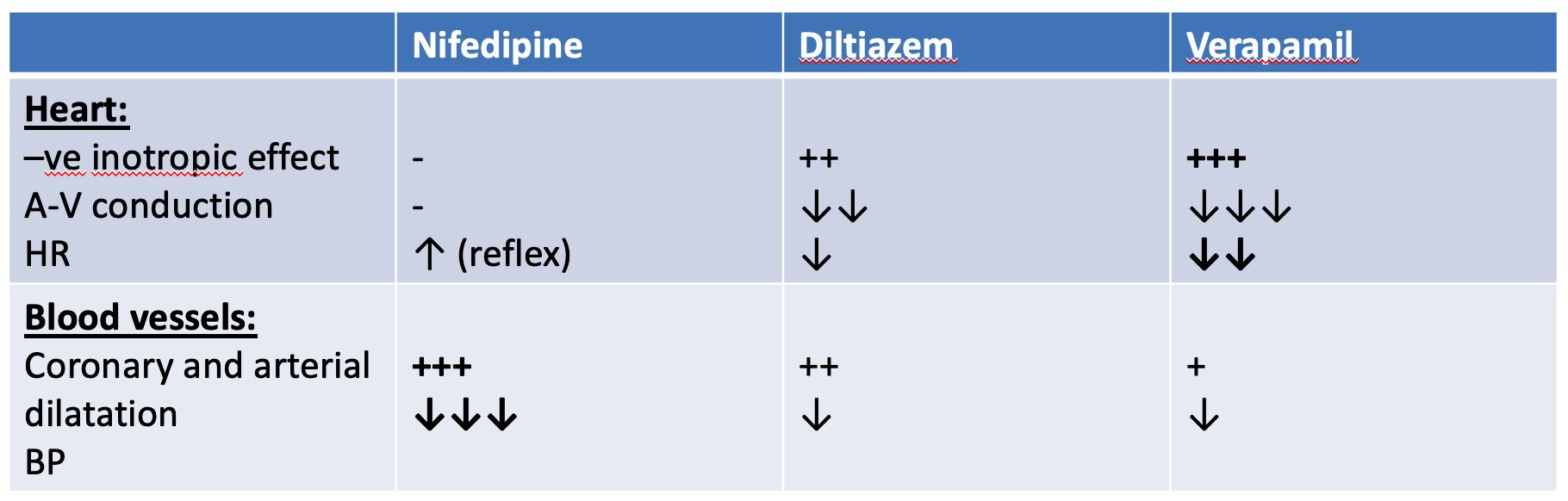
CCB with mainly cardiac effects: (Heart. SMF) ‘Lowers CO, HR, B.D., constipation, decrease insulin secretion; dangerous in DM2’ - verapamil,;
decreases insulin secretion - contraindicated in angina w/ diabetes- diltiazem (mainly on heart, little vascular effect). -
CCB with mainly vascular effects: (stim heart reflex tachy, ) - nifedipine, - amlodipine, - isradipine, - felodipine, - nimodipine
Other effects:
- Smooth muscles: they relax bronchial, GIT, and uterine smooth ms.
- Insulin release: verapamil ↓ insulin release (in high dose).
Therapeutic uses:
A. Cardio-selective CCBs (verapamil and diltiazem):
-
Ischemic heart disease: see Ischemic Heart Diseases
-
Cardiac arrhythmias: supraventricular tachycardia (SVT): Because they ↓ SAN activity and slow A-V conduction.
N.B. Nifedipine is contraindicated because it cause hypotension and reflex tachycardia.
-
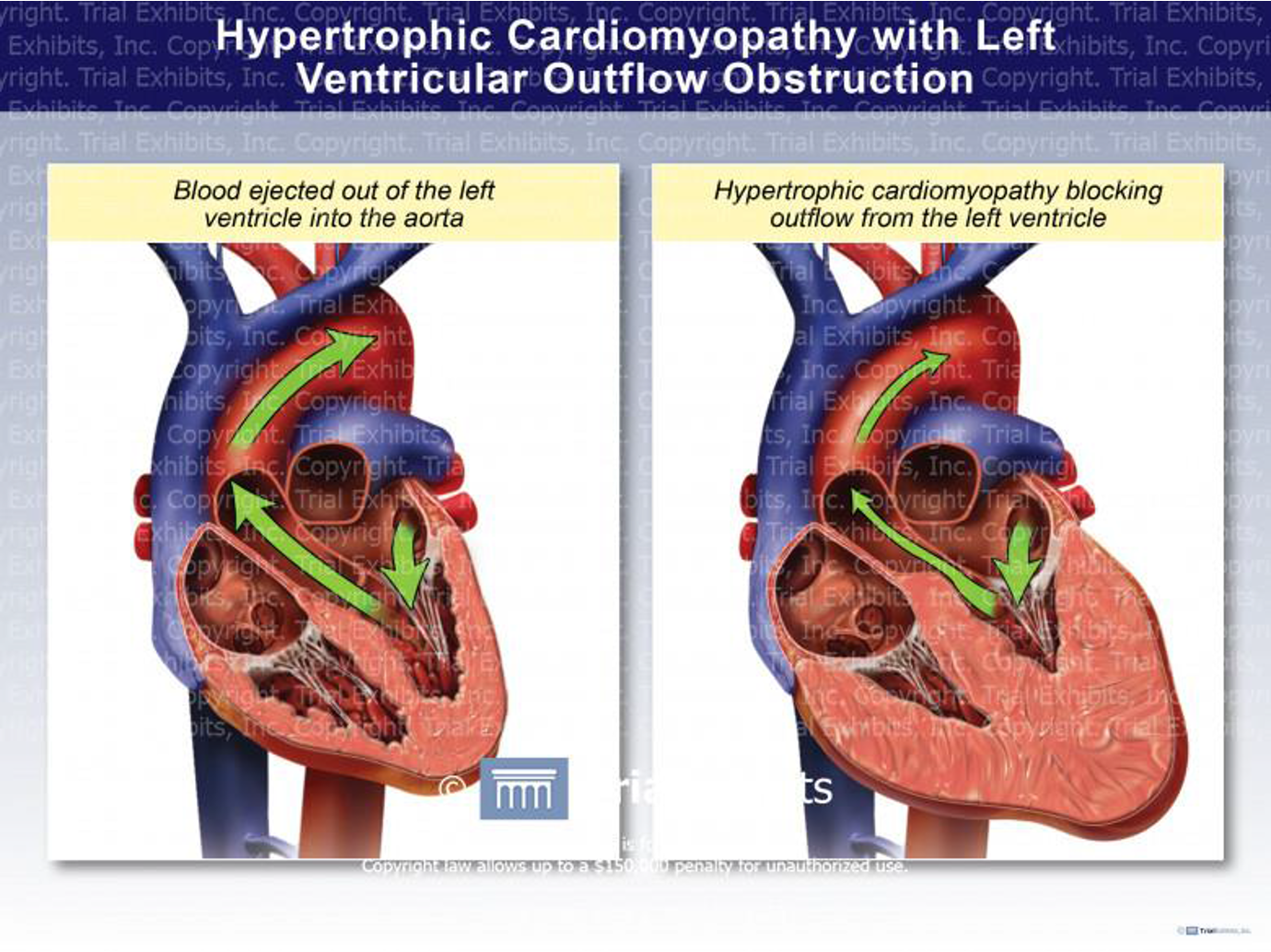
Hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy (IHSS): In hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy, the wall of the left ventricle and interventricular septum is much thickened leading to narrowing of the aortic outlet and obstruction of blood flow. This obstruction is increased by increasing contractility while decreasing contractility leads to decrease resistance to blood flow through the aortic outlet.
N.B. Nifedipine is contraindicated because it produces reflex tachycardia → worsening of the outflow obstruction.
-
Arterial hypertension: They cause VD due to ↓ Ca2+ influx in the vascular smooth muscles. They ↓ myocardial contractility and COP.
B. Vasculo-selective CCBs (Nifedipine and amlodipine):
- Arterial hypertension.
- Senile cerebral ischemia (nimodipine).; ((vasodilation of cerebral
- Peripheral vascular disease: to improve peripheral microcirculation.
Adverse effects:
1-Verapamil and diltiazem:
- Bradycardia and heart block.
- Worsening of CHF (due to their –ve inotropic effect).
- ↓ insulin release and worsening of DM2.
- Constipation and reversible hepatotoxicity.
- Ankle edema (less common than with nifedipine).
2-Nifedipine:
- Hypotension and reflex tachycardia. Can be prevented by;___
- Gingival hyperplasia.
- Ankle edema (due to VD). How to treat ankle edema if occurred from CCBs? - Minimize sodium intake. - Avoid prolonged standing. - Mild diuretics. - Stop CCBs if the above measures failed.
Contraindications and precautions:
1- Verapamil:
- Heart failure.
- Bradycardia, heart block, or sick sinus syndrome (SSS).
- With β-blockers: because both β-blockers and verapamil have –ve inotropic and chronotropic effects, this will cause severe cardiac depression (nifedipine is the drug of choice if β-blockers are used with CCBs because it doesn’t cause bradycardia).
- With digitalis: because digitalis also ↓ A-V conduction and HR.
2-Nifedipine:
- Severe heart failure.
- Hypotension.
- Hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy (IHSS)
- Unstable angina (for fear of reflex tachycardia).
Calcium channel blockers (CCBs)
- These are drugs that block voltage-gated Ca2+ channels.
- Classification of CCBs according to therapeutic effect:
- CCB with mainly cardiac effects: verapamil, diltiazem (???????).
- CCB with mainly vascular effects: nifedipine, amlodipine, isradipine, felodipine, nimodipine
Pharmacokinetics: X
- Oral absorption is nearly complete.
- Plasma protein binding is 70-98% … - Metabolism: verapamil and diltiazem are metabolized into active metabolites. - In older patients and in patients with liver cirrhosis the dose should be decreased.
CCBs IHD
- They ↓ myocardial contractility and myocardial O2 demand.
- They ↓ coronary vascular resistance and increase coronary blood flow.
- They dilate epicardial coronary vessels.
- ↓ myocardial cell necrosis.
N.B. Although nifedipine is coronary dilator, it has some disadvantages in angina: It may cause hypotension and reflex tachycardia.
Diltiazem , Verapamil should be used when B Blockers are contraindicated (asthma peripheral vascular disease) or cause side effects (impotence, depression).