- Patient sitting
- Exposure- down to upper chest
- Stand in front & behind of the patient
Inspection (from front & sides)
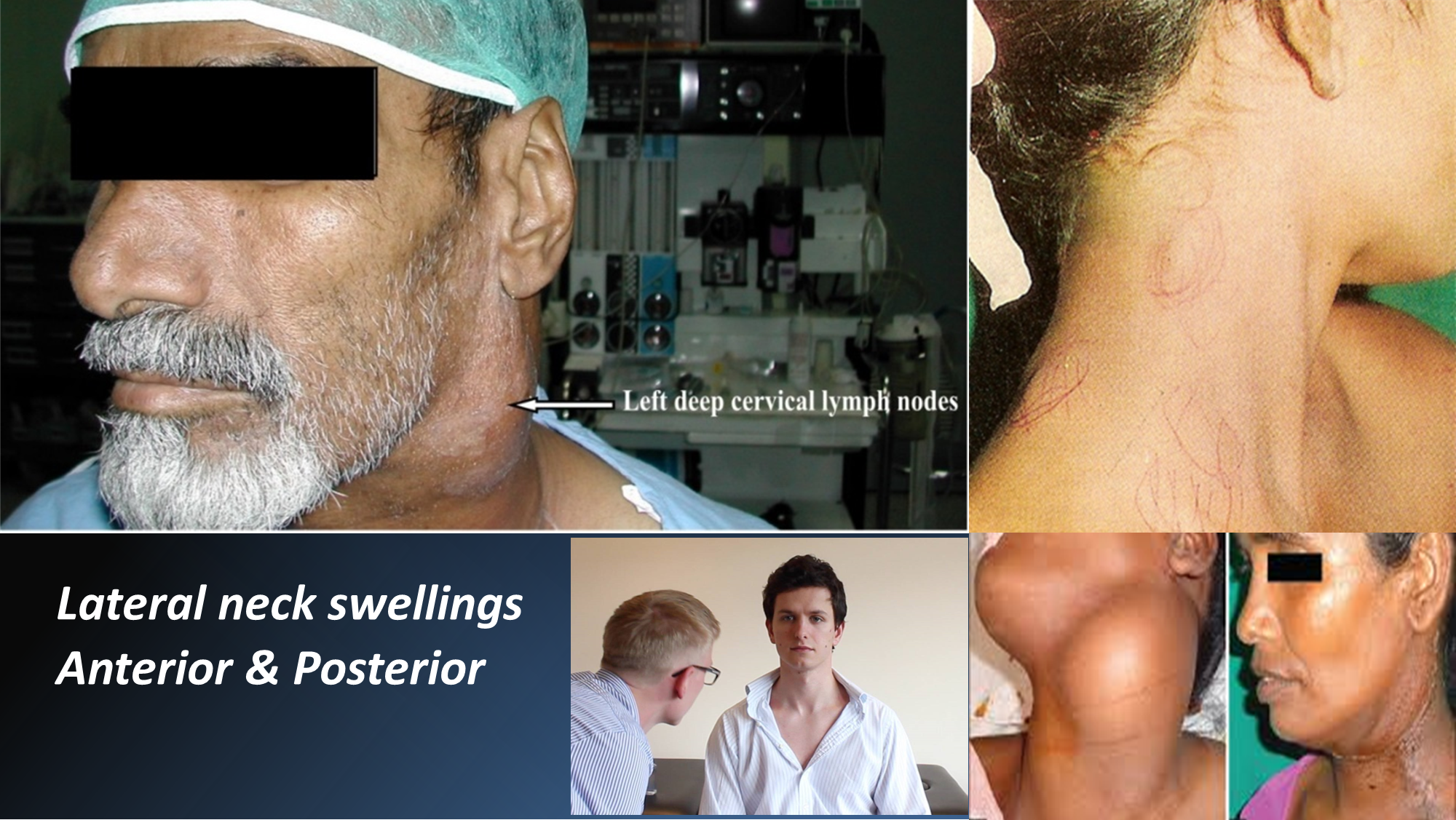
- Lump or lumps: location- anterior / posterior triangle
- Unilateral/bilateral
- Single/ multiple
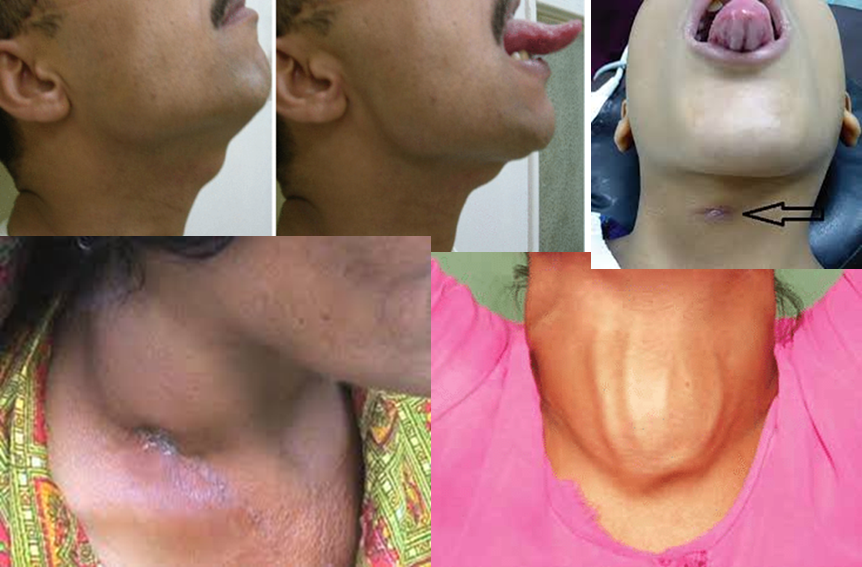
- Shape, size (butterfly shaped-thyroid)
- Ask to swallow- goitre moves
Inspection- neck swellings
- Tongue protrusion: Thyroglossal cyst - moves up & Thyroid, LN- no movement
- Skin changes: discoloration
- Sinuses- tuberculous / scar
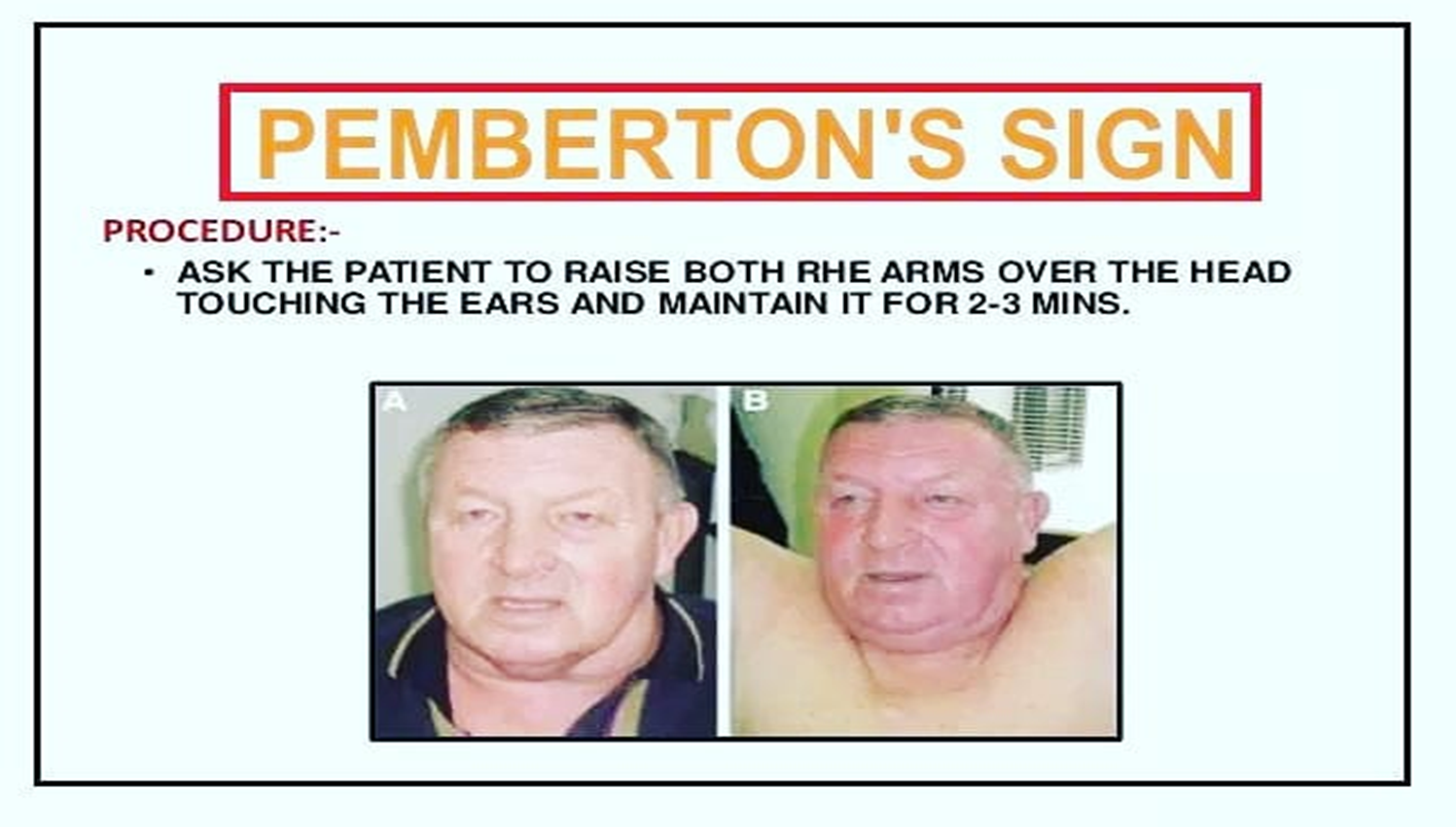
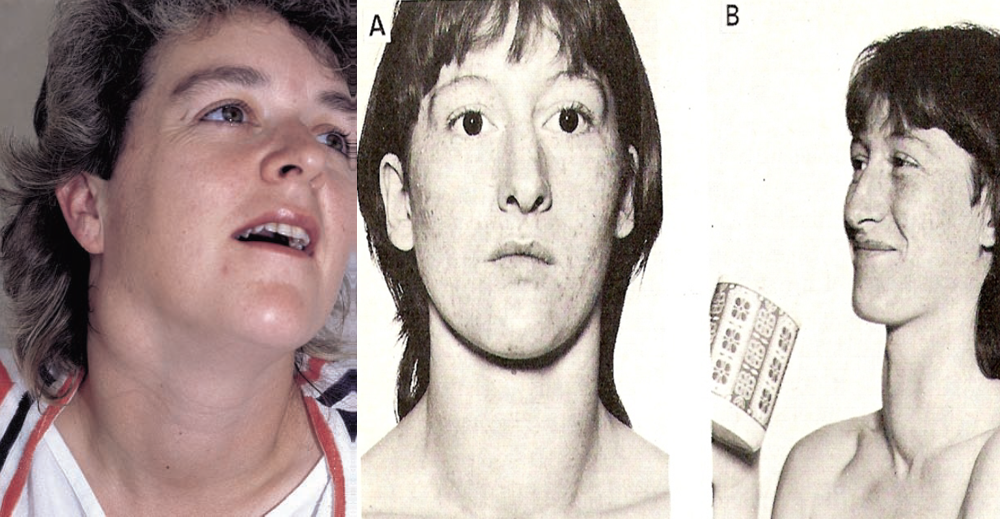
- Neck veins distension- Pemberton’s sign & retrosternal thyroid extension
Pemberton’s sign is used to evaluate venous obstruction in patients with goiters. The sign is positive when bilateral arm elevation causes facial plethora. It has been attributed to a “cork effect” resulting from the thyroid obstructing the thoracic inlet, thereby increasing pressure on the venous system.