- is more common in female.
- It usually occur after the age of 40 years.
It is more vascular and enhances strongly with contrast
Mostly asymptomatic: General symptoms of CNS tumors (e.g., seizures and focal neurologic signs)
MRI (imaging modality of choice)
- Round, sharply demarcated space-occupying lesion with radiological features of an extra-axial tumor
- T1: isointense or hypointense
- T2: isointense or hyperintense
Contrast MRI findings
- Significant homogenous enhancement of the meningioma
- Dural tail sign.
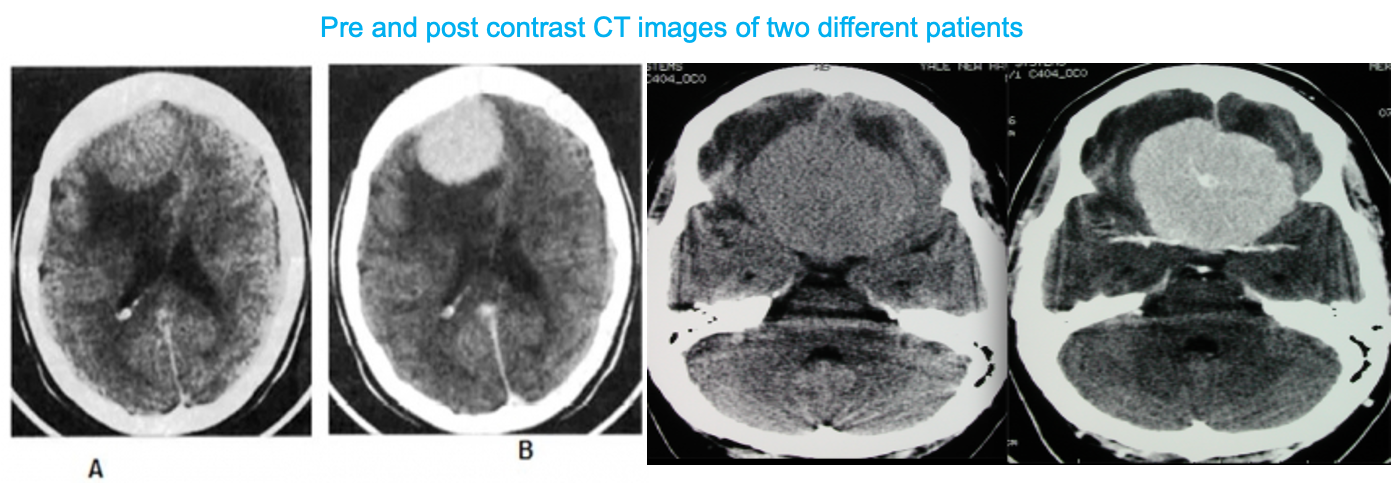
CT scan
CT scans performed to investigate unexplained headaches or seizures are usually the first to pick up incidental meningioma.
Findings
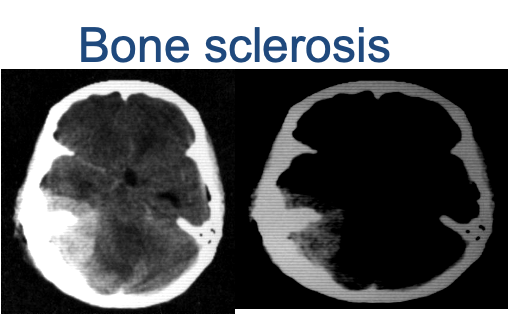
- Hyperdense or isodense well-demarcated extra-axial mass
- Possible calcifications
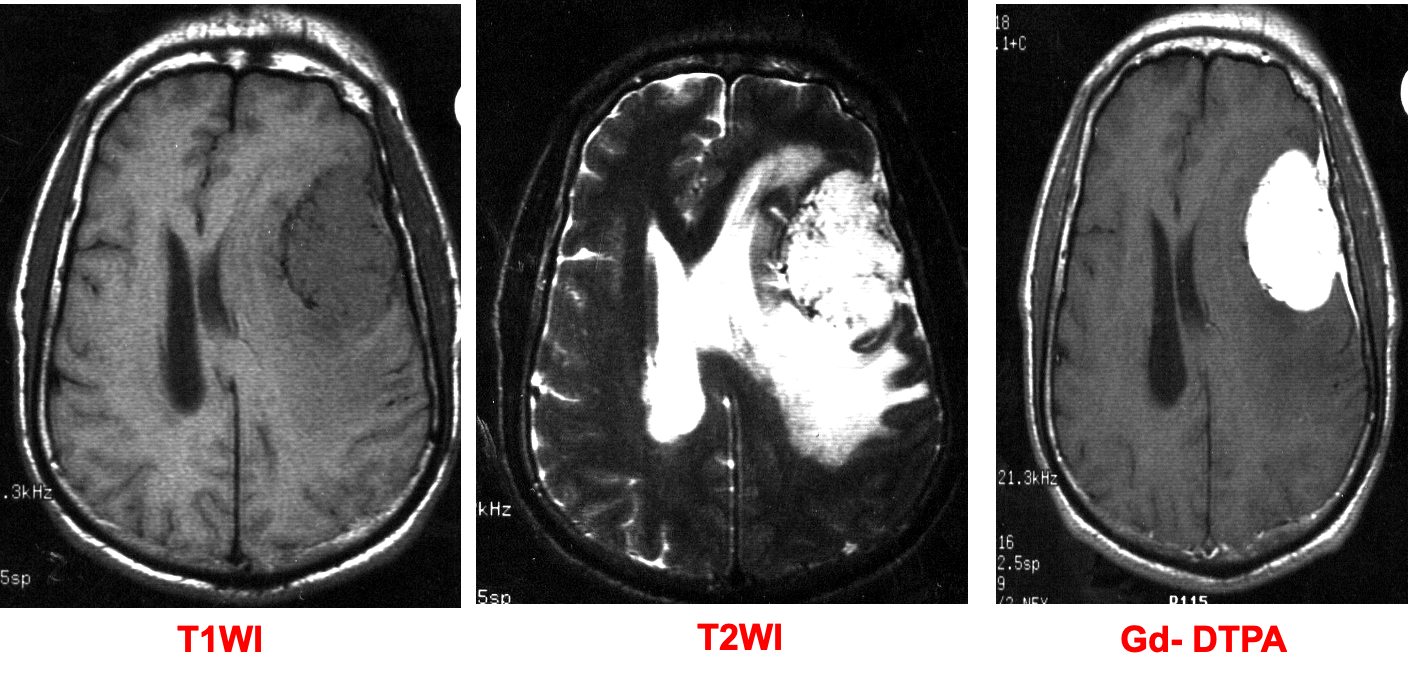 There is an oval mass in the left parietal region, with well-defined borders, appears hypointense to grey matter on the T1 & hyperintense on T2-weighted image. There is ipsilateral ventricular compression and contralateral shift of midline structures and both ventricles associated with perifocal edema. The lesion shows homogeneous enhancement on the contrast T1-weighted image and a dural tail
There is an oval mass in the left parietal region, with well-defined borders, appears hypointense to grey matter on the T1 & hyperintense on T2-weighted image. There is ipsilateral ventricular compression and contralateral shift of midline structures and both ventricles associated with perifocal edema. The lesion shows homogeneous enhancement on the contrast T1-weighted image and a dural tail