Internal Medicine
NSTEMI & UNSTABLE ANGINA
Investigations and Treatment
High risk patient who are likely to progress to MI require urgent coronary angiography in less than 72 Hours
Who are high risk patient ?
- Increased Troponin
- Dynamic ST or T wave changes
- Previous MI
- PCI within last 6 months
- Previous CABG
Medical Treatment Unstable Angina & NSTEMI
- O2 ⇒
- Morphine and anti emetic ⇒
- Aspirin ⇒
- Clopidrogrel (Plavix )- anti platelet agent OR : Dual AP therapy with Aspirin & Prasugrel or ticagrelor ⇒
- Enoxaprin- low molecular heparin ⇒
- Beta blocker ⇒
- (Bisoprolol) ⇒
- ACE-Inhibitors ⇒
- Nitrates ⇒
- Statins ⇒
Thera
Unstable angina may present by one of the following:
- ~ Angina at rest
- ~ Crescendo angina (increased frequency and severity)
- ~ Angina of recent onset (within 4-6 weeks)
It may be due to:
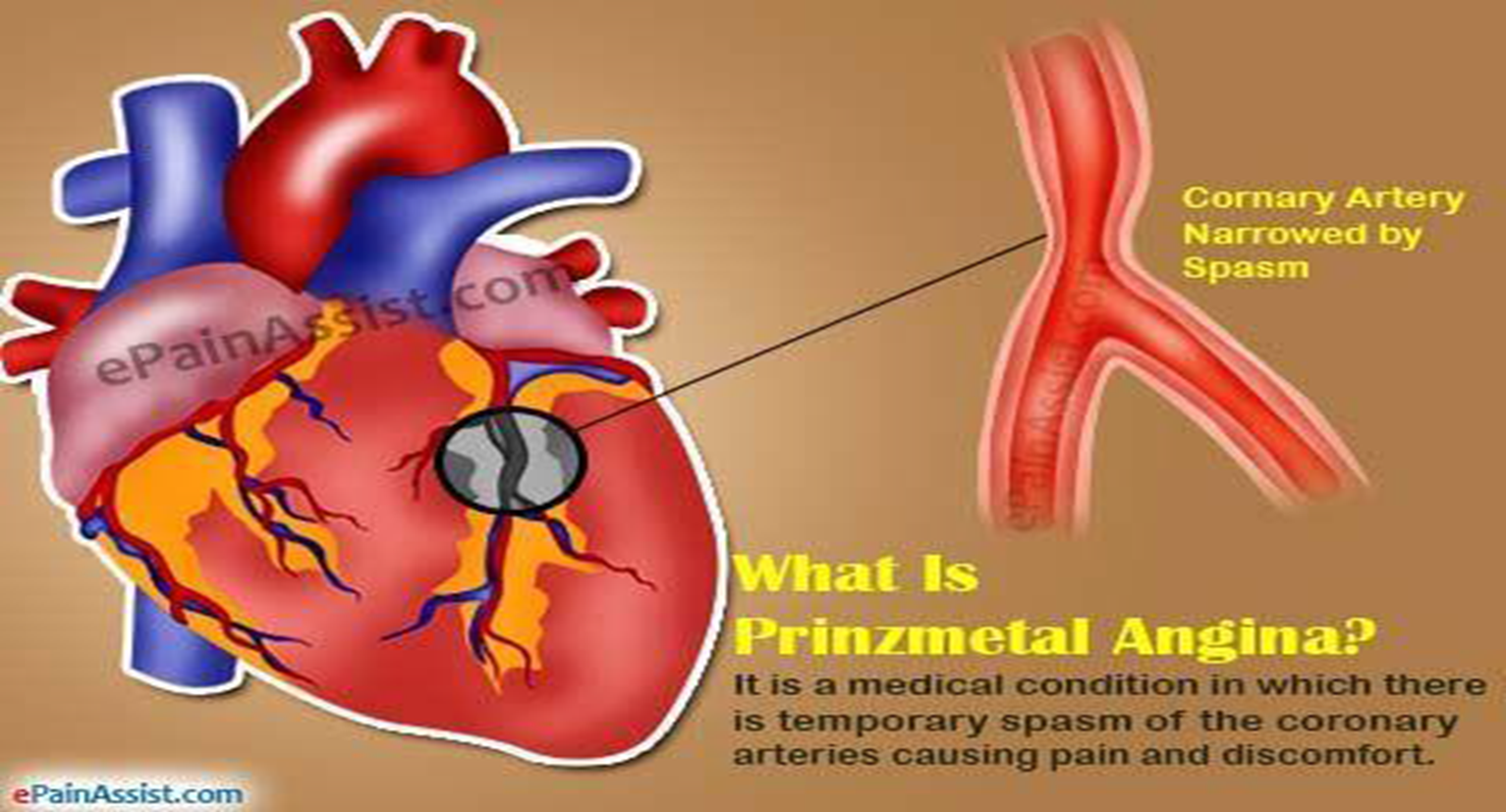
• Non-occlusive coronary thrombus on top of atheroma. • Coronary artery spasm (Prinzmetal’s angina).
Unstable angina (UA) is considered to be present in patients with: ischemic symptoms suggestive of an ACS without elevation in biomarkers with or without ECG changes indicative of ischemia.
Diagnosis:
- ECG: shows changes in 30-50%.
- Cardiac enzymes: are not elevated distinguished from acute MI.
- Coronary angiography.