It is a combination of trimethoprim & S. methoxazole:
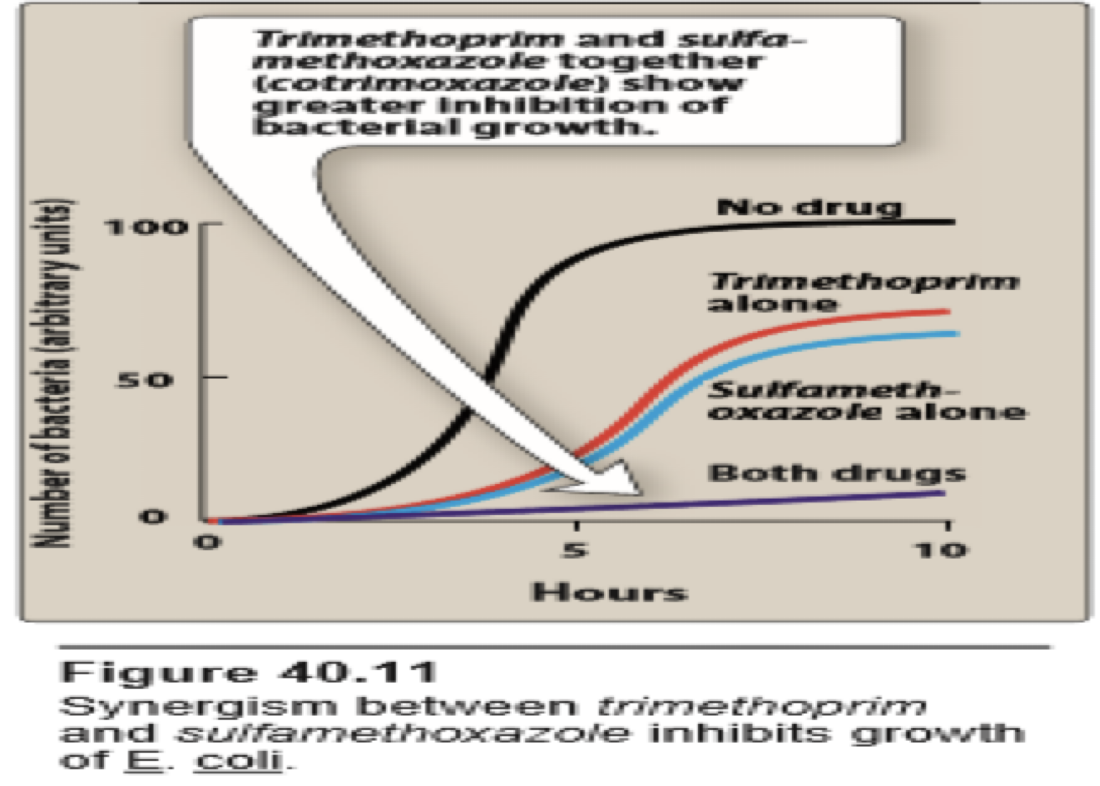
Either drug alone is bacteriostatic, but in combination co-trimoxazole is Cidal (because it inhibits two successive steps of the enzymatic pathway for the synthesis of folinic acid), less bacterial resistance develops and bacteria which were not sensitive to sulfonamides become sensitive e.g. Salmonella, Proteus.
The combination drug
trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (TMP/SMX) is the most widely used folate antagonist, active against both bacterial and parasitic/fungal infections. ((by inhibit newly formed folic acid, and inhibits rapidly of storaged folic acid - generally static of both drugs))
The combination was selected because of: the synergistic activity and the similarity in the half-lives of the two drugs.
Effect of it is synergestic - greater than sum - potentiates and overcomes Example : 1+1 = 4 | Drugs: TMP:SMZ = 1 : 5 It is effective against salmonella, shigella, staphylococci, proteus, E.coli, haemophilus, Neisseria (Pseudomonas is usually insensitive).
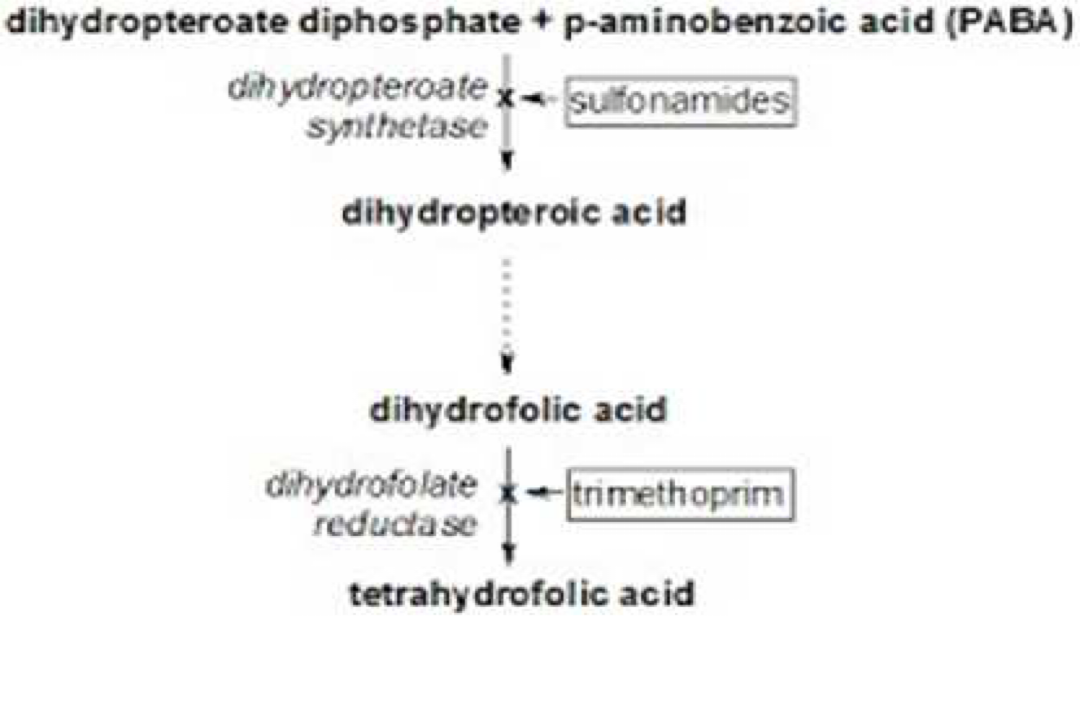
Mechanism of action
Sulphamethoxazole acts on the first step in the folic acid synthesis pathway(see before).
Trimethoprim acts on the second step in the folic acid synthetic pathway(see before). This step occurs in man, but the sensitivity of the enzyme that is inhibited is much greater in bacteria than in man, therefore, the drug is relatively safe.
These drugs inhibit steps in the folate biosynthesis pathway, depleting the pool of nucleosides and ultimately leading to inhibition of DNA synthesis in susceptible organisms.
Cotrimoxazole has a broader spectrum of antibacterial action than the sulfa drugs alone . It is effective in treating= uses
- Used in treatment of uncomplicated lower UTIs and prophylaxis against recurrent UTIs and respiratory tract infections,
- Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia tretment and prophylaxis
- toxoplasmosis,
- salmonella infections (typhoid fever) resistant to ampicillin or chloramphenicol.
- community-acquired skin and soft tissue infections caused by methicillin-resistant S aureus infections (MRSA).
- TMP/SMX is also an alternative therapy for bacterial prostatitis,
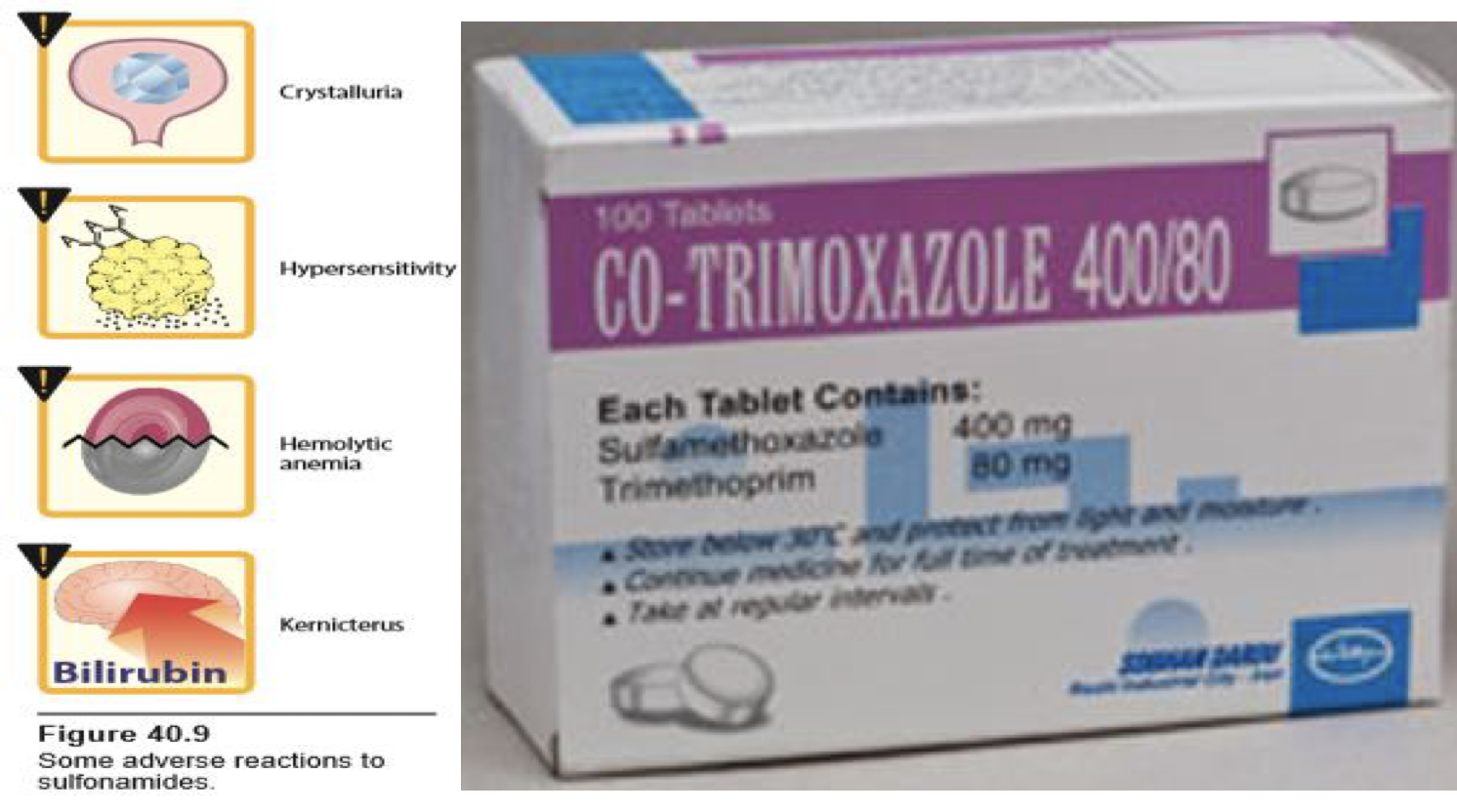
Adverse effects
Like sulfonamides and trimethoprim
TMP/SMX can cause both true and pseudo-renal failure. Crystalluria and acute interstitial nephritis (AIN) caused by the SMX component can lead to acute renal failure; however, the blockade of creatinine secretion by TMP can cause an increase in serum creatinine without a true decline in glomerular filtration rate. TMP can also cause hyperkalemia in a fashion similar to the potassium-sparing diuretics (e.g., triamterene).