Surgery & Clinical Medicine
Cervical Lymphadenopathy
Causes Y
1. Acute: a. Acute pyogenic lymphadenitis. b. Acute lymphatic leukemia. c. Acute infectious mononucleosis. (E.B. virus)
2. Chronic: **A. Inflammatory ** - Nonspecific—Chronic pyogenic lymph adenitis. - Specific—TB, syphilis, sarcoidosis.
B. Neoplastic (malignant) I. Primary: Lymphoma Hodgkin’s disease
- Lymphosarcoma.
- Reticulum cell sarcoma.
II. Secondary –Metastatic
- lymph node from a primary growth.
C. Autoimmune disorders, e.g. SLE, juvenile rheumatoid arthritis (Still’s disease).
Investigations:
- Blood-Complete blood count,
- chest -Xray.
- FNAC and biopsy of the enlarged lymph nodes. Initial Inv. - if not enough do exesional biopsy
OSCE
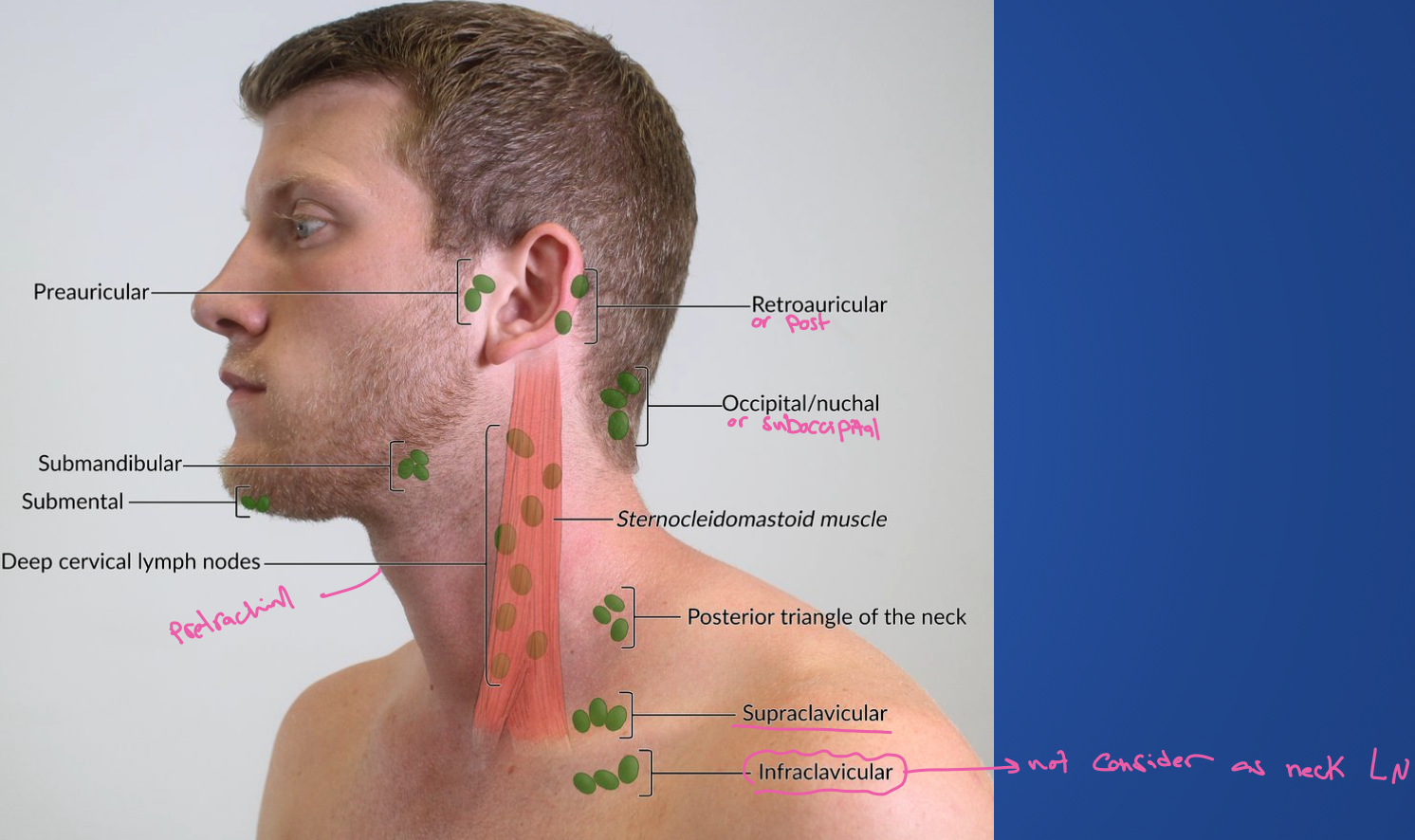
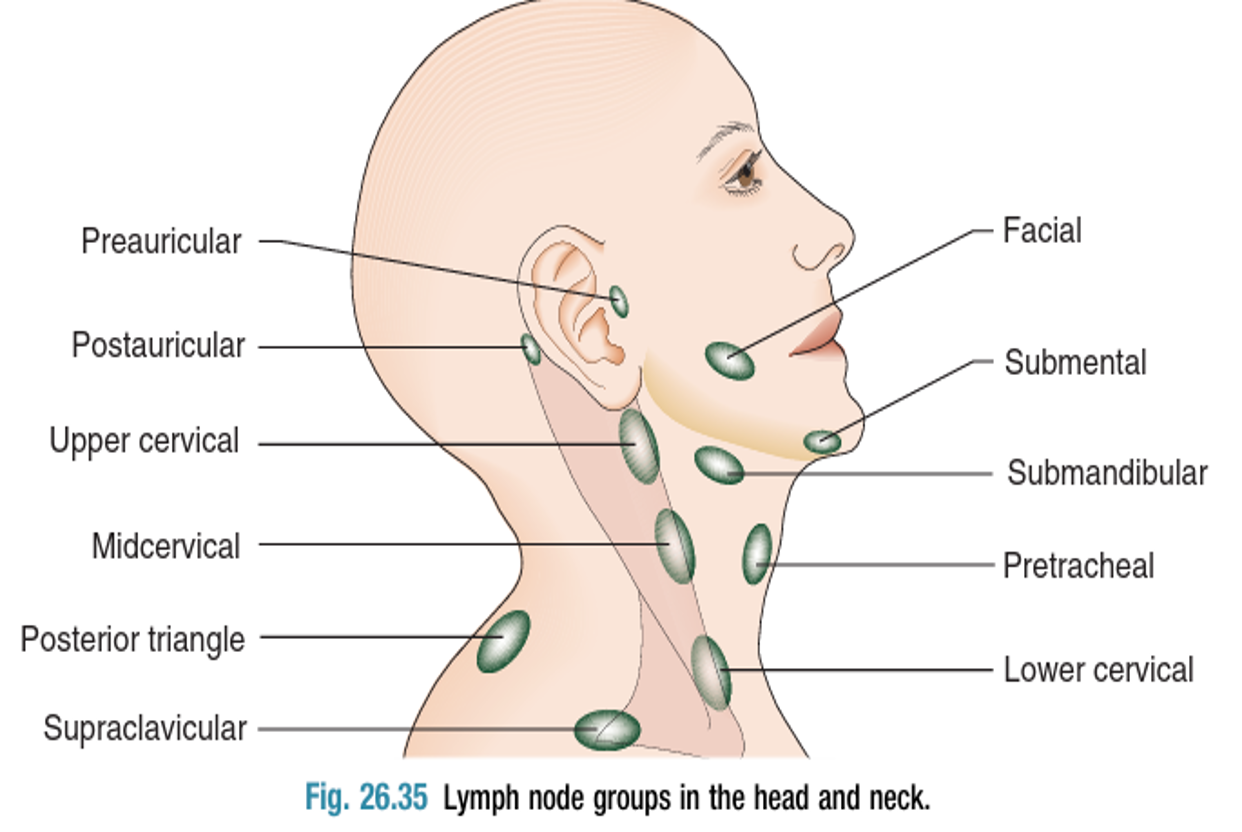
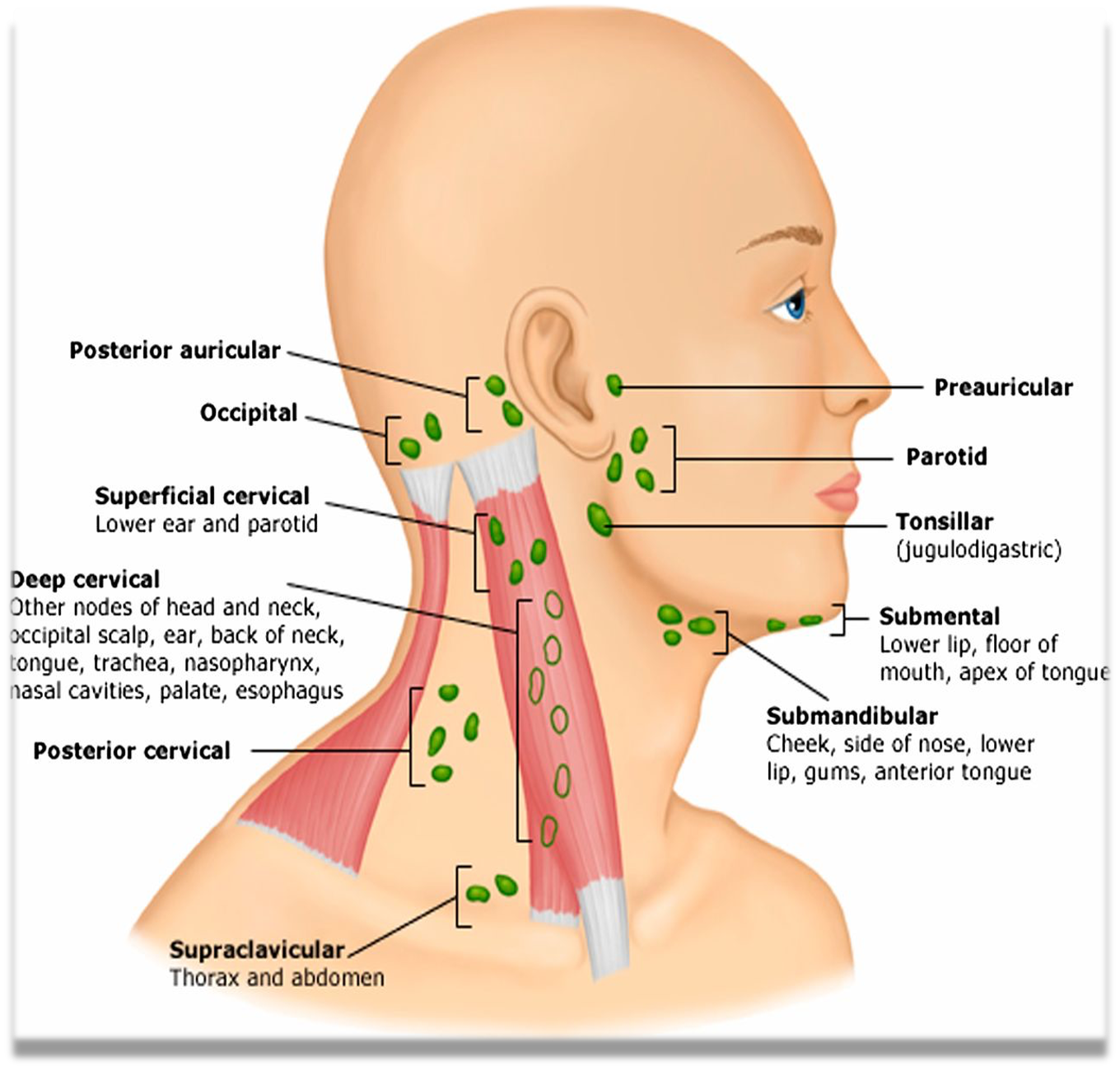 The jugulodigastric lymph node is commonly enlarged in both inflammatory and malignant conditions.
The jugulodigastric lymph node is commonly enlarged in both inflammatory and malignant conditions.
Children with tonsillitis, young adults with glandular fever or Hodgkin’s disease, middle aged adults with cancers of the oral cavity and oropharynx can all present with lymphadenopathy at this site.
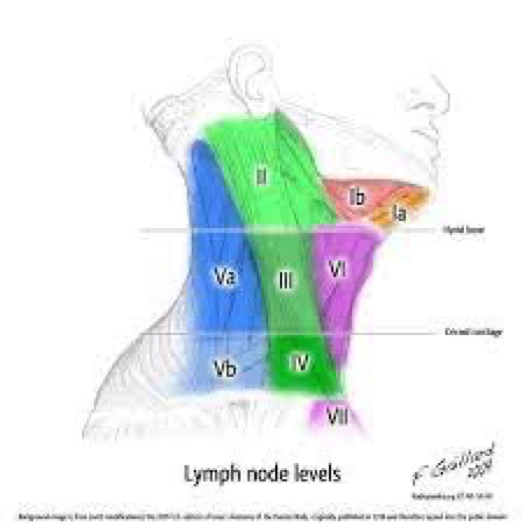
-
I- submental submandibular
-
II, III, IV - Sternoclediomastoid
-
VI - Pre Sterno
-
V- Post Sterno
-
VII - Sternum
Oncological levels of the neck lymph nodes Level 1 divided by digastric muscle to level IA and IB