Respiratory distress in the newborn: Hyaline membrane disease:
Clinical features
- Maternal history of premature birth
- Onset of symptoms: usually immediately after birth but can occur up to 72 hours postpartum
- Signs of increased respiratory effort -Tachypnea -Nasal flaring and subcostal/intercostal and jugular retractions.
- Cyanosis
- Decreased breath sounds on auscultation
X-ray chest
- Interstitial pulmonary edema with perihilar streaking
- Diffuse, fine, reticulogranular (ground-glass) densities with low lung volumes and air bronchograms
- Atelectasis
X-ray chest (frontal view) of Neonatal respiratory distress syndrome
The lungs are opacified and have a granular appearance. Air bronchograms extend to the lung periphery. An endotracheal tube is well-positioned above the carina.
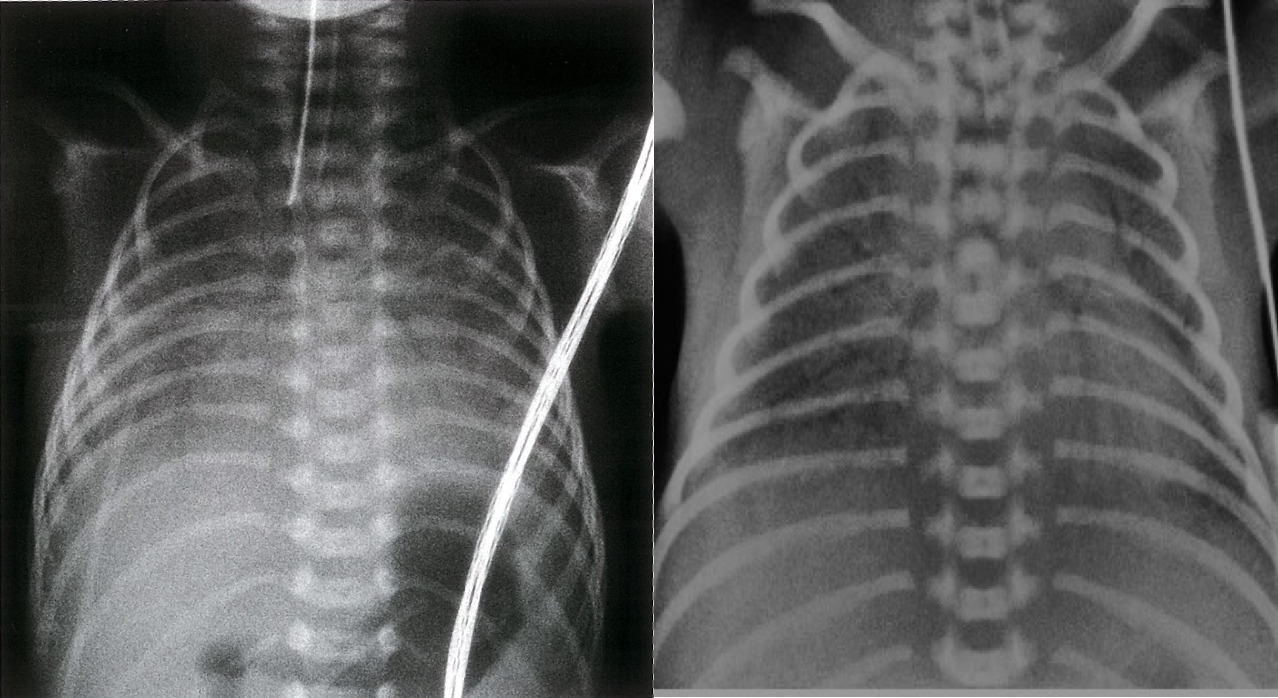
Neonatal respiratory distress syndrome (hyaline membrane disease). Posteroanterior film
showing the general granular opacity of the lungs typical of hyaline membrane disease. The vessels, the heart borders and the diaphragm outlines are indistinct and air bronchograms are visible. Note the uniformity of distribution of the changes in the lungs – an important diagnostic feature of hyaline membrane diseasev