Investigation of Surgical patients
M K ALAM MS; FRCS Edited by Dr Shaher Abbarah
ILOs
- Aims- Why investigate?
- Spectrum of investigations.
- Justify (indication) use of relevant investigations
- Complications.
Management of a clinical problem
Clinical presentation
- History
- Clinical examination
- Provisional/ working diagnosis/ DD
- Investigations
- Final diagnosis
- Treatment
What is Triple Assessment ?
Aims of investigation
- Support clinical suspicion
- Refute clinical suspicion
- Assess physiological impairment- risk to surgical treatment
- Detect asymptomatic disorders
- Screen - carcinoma breast, carcinoma colon etc.
“Always keep in consideration- risk & cost”
Hematological investigations
-
FBC or CBC: low Hb (anemia), MCV, MCHC (normocytic, microcytic), leukocytosis (infection)
-
Platelet count: Thrombocytopenia ( drug- heparin, ITP, autoimmune), Thrombocytosis ( post-splenectomy)
-
Coagulation profile: PT, INR, APTT Disordered in: chronic liver disease, jaundice, bleeding, medications
- PT assess the Extrinsic & common pathway
- PTT assess the Intrinsic & common pathway
CBC: complete blood count , FBC: Full blood count Warfarin follow up by INR Heparin follow up by PTT
Biochemical Investigations
- Na: 135-146 mmol/L- ↓ -water overload, SIADH ↑- fasting, vomiting, burn, Conn’s syndrome
- K: 3.5- 5.5 mmol/L- changes- vulnerable to arrhythmias ↑ met. acido, blood trans, crush injury, ↓ vom/diarrh, ileus, met alkalo, diuretics
- Urea: 2.6- 6.7 mmol/L- dehydration, renal insufficiency
- Creatinine: 60-120 mmol/L- marker of renal disease
- Glucose: 3.9-5.6 mmol/L- diabetes
- Total protein: 62-80 G/L
- Albumin: 35-50G/L- nutritional assessment Z
Low Albumin indicate post op morbidity and increase in complication Pre-albumin is acute indicator of nutritional status
-
Bilirubin <17 mmol/L- direct/ indirect type (jaundice)
-
ALP: 25-120 U/L- liver, bone, placenta & intestine Indicator of bile ducts obstruction, primary biliary cirrhosis, sclerosing cholangitis
-
AST: 10-40 U/L- liver, cardiac muscle, skeletal muscles, kidneys, brain, pancreas
-
ALT: 5-30U/L- liver, skeletal muscle,
-
GGT - (M-10-55, F 5-35 u/L) - ↑- bile duct injury
What are liver function test? ALT: more specific of Liver injury GGT: Gamma-Glutamyl Transferase, ALP: Alkaline phosphatase AST: Aspartate Aminotransferase (SGOT) ALT: Alanine Transaminase (SGPT)
-
LDH: 49-195U/L- found in most body tissues, ↑- liver disease, heart attack, anemia, muscle trauma, bone fractures, cancers, meningitis, encephalitis, HIV
-
Creatinine phosphokinase (CPK/ CK)- 24-195 U/L: Found in heart, skeletal muscles, brain CPK indicative of muscular damage. CK-MB - specific of myocardial muscle damage, CK-MM- specific of skeletal muscle damage
-
Amylase <100 u/L mild rise- non-specific- sialadenitis, perf. PU, cholecystitis, intestinal obstruction
-
Lipase: 0-160 U/L – specific for pancreatic disease
LDH: Lactate Dehydrogenase CK: Creatinine Kinase
Tumour markers
-
PSA- Prostate (Screening + Followup)
-
CEA- Colorectal (Followup) - (colonoscopy for screening)
-
α- fetoprotein (AFP)- Hepatocellular (Follow up) + (US/AFP screening)
-
β-hCG- Testicular (Non-seminoma no screening), gestational
-
CA 19-9- pancreas (monitor treatment), Colorectal
-
CA 125 - Ovarian (screening + Follow up)
-
CA 15-3 & CA 27.29- Breast (not very helpful, monitor treatment) (No screen/follow)
CEA: carcinoembryonic antigen CA: Cancer Antigen
lady 25 years old - one his friends has breast cancer, she came to screen for breast - give mammogram (less than 40 dont screen)
lady 40 years is done for screening for breast cancer - orr 10 years family hx age diagnosis
mamogram used for screening not gene study
Microbiological, serology, immunological investigations
- Urine
- Sputum
- Stool
- Hepatitis screening
- Antibiotic sensitivity
- Serology- antibodies against infection
- Immunology- autoantibodies- TSI-thyroid stimulating immunoglobulin, Anti-thyroglobulin antibody, anti-TPO- thyroid peroxidase
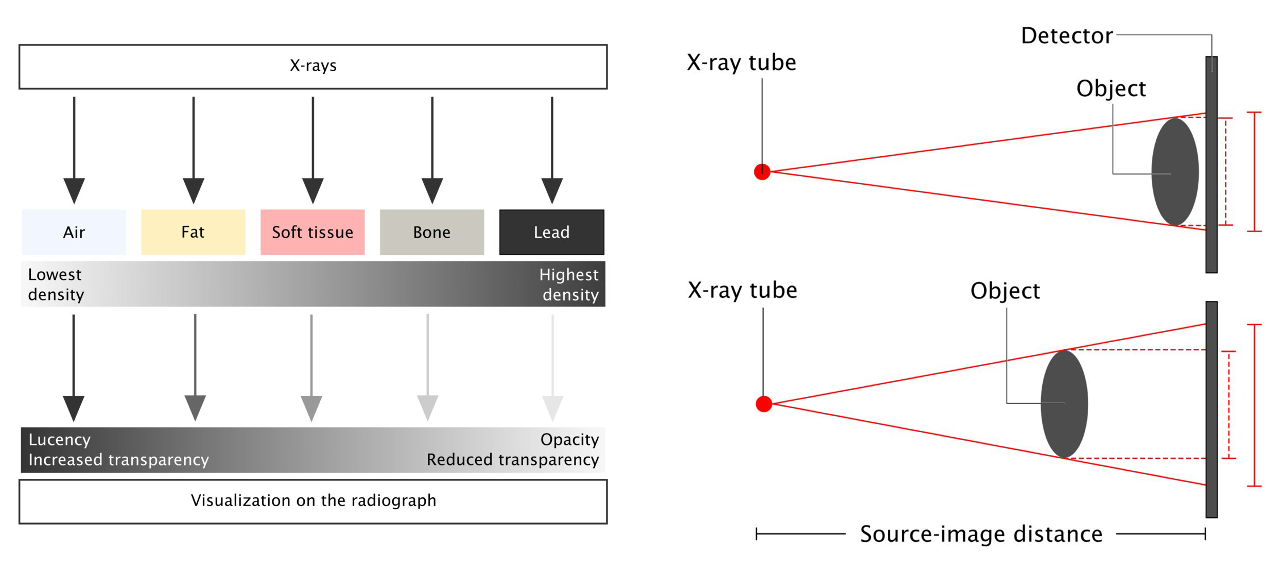
Imaging studies
Plain x-ray- CXR, AXR, tomograms
OSPE Z
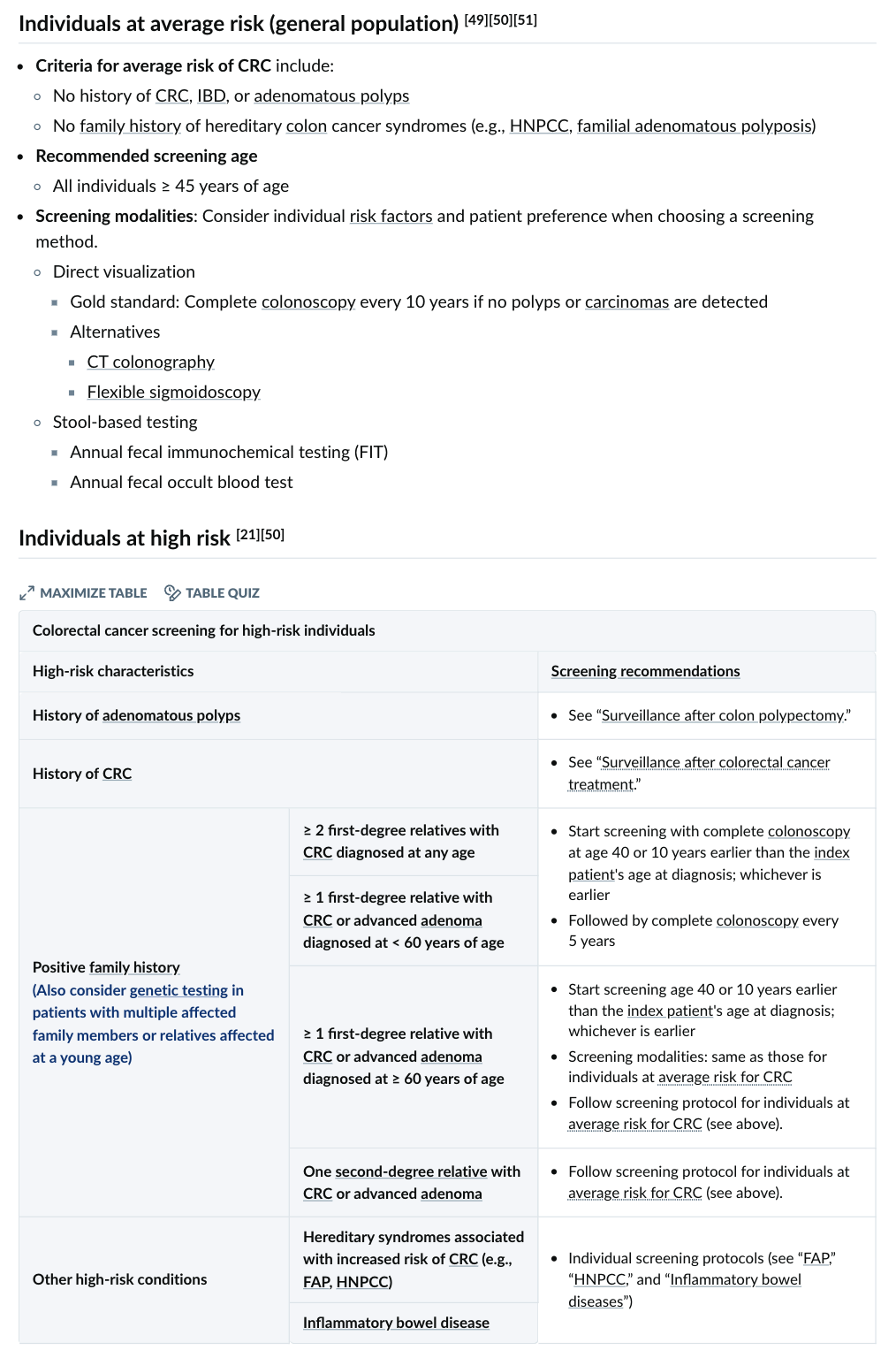
 Modality: plain x-ray
Findings: air under diaphram / multiple air fluid levels
Differentials: perforation / obstruction
Modality: plain x-ray
Findings: air under diaphram / multiple air fluid levels
Differentials: perforation / obstruction
Side effects of radiation:
- Induction of malignancy
- Genetic mutation
 Modality:
Findings:
Differentials:
Modality:
Findings:
Differentials:
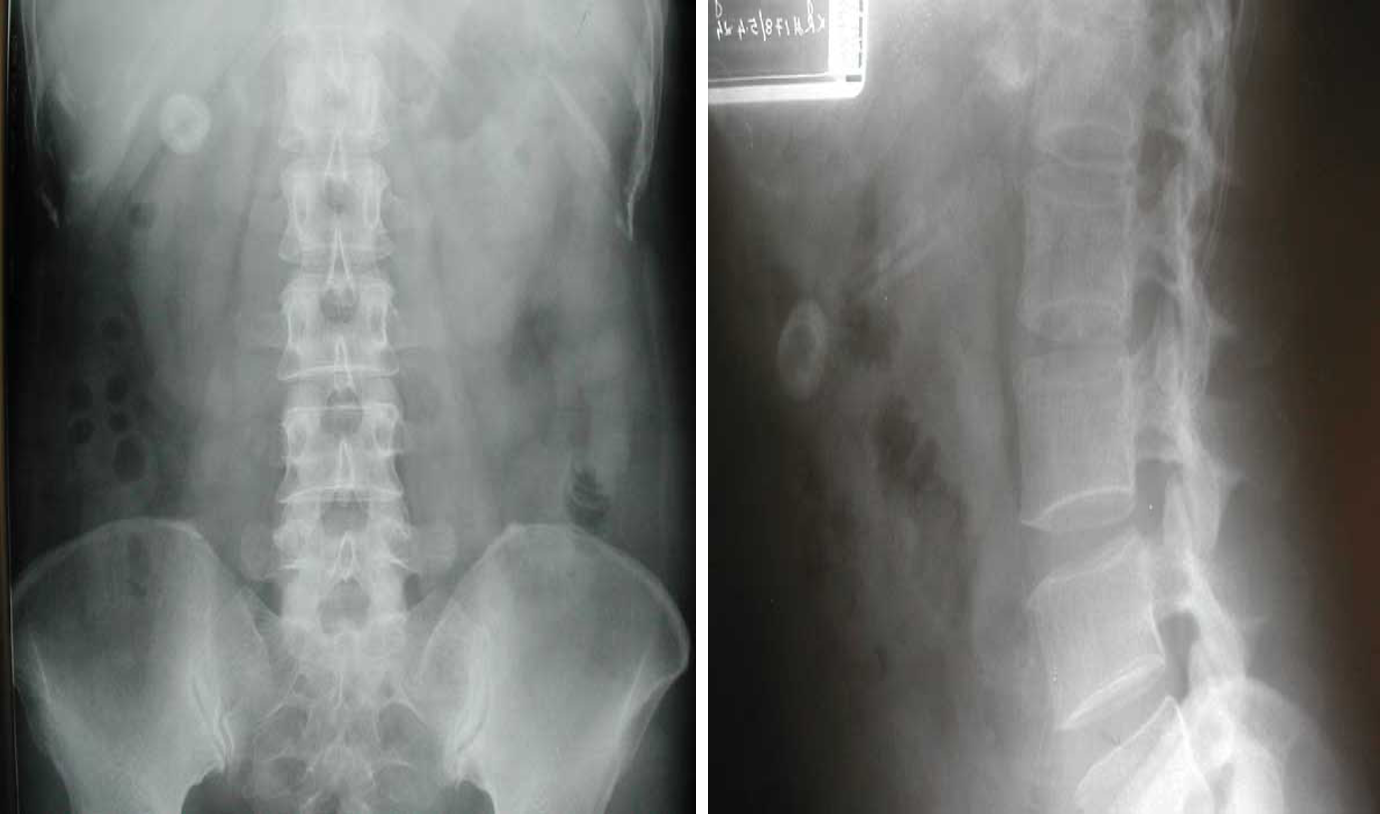 Modality: plain x-ray
Findings: radiopaque
Differentials: gallbladder
Modality: plain x-ray
Findings: radiopaque
Differentials: gallbladder
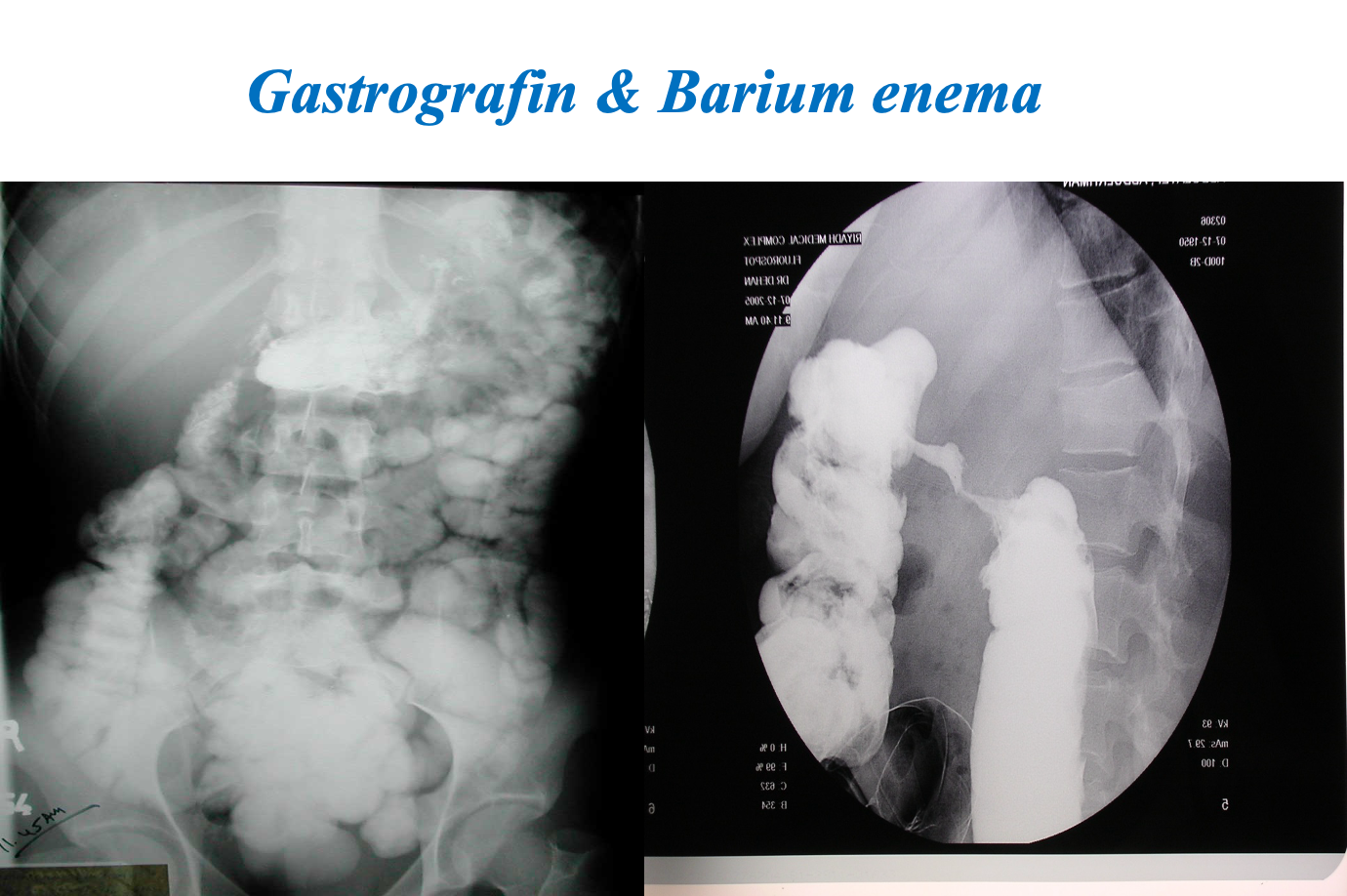
Contrast Imaging
-
Gastrograffin swallow, Barium meal / enema
- Visualize GI tract
- Single/ double contrast
- Inferior to endoscopy
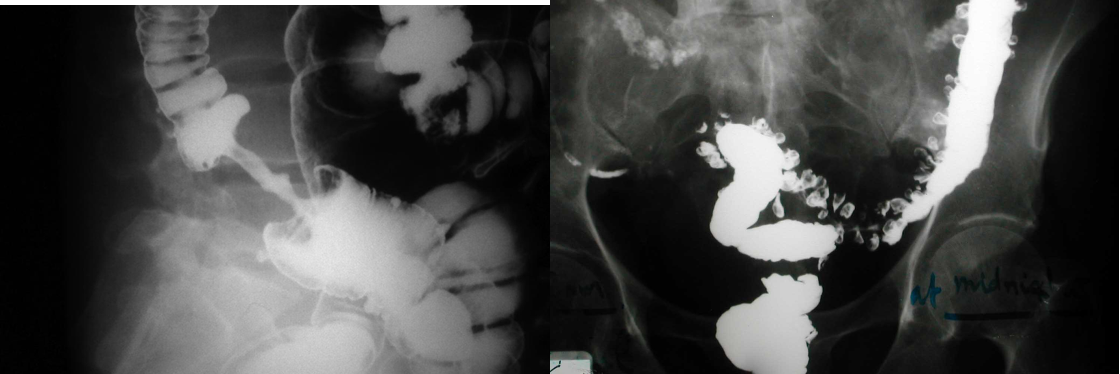
Modality: Gastrography swallow / Barium Enema Findings: apple core / out pouching lesions Differentials: colon cancer / diverticulum
40 yrs old man presents to ER w/ acute adominal pain - hx of gallbladder stone - which of the following
- initial test = ERECT CHEST X-RAY - to exclude perforation
- FIRST CHOICE = U/S
Imaging studies- Ultrasound
- Safe
- Low cost
- Operator dependent
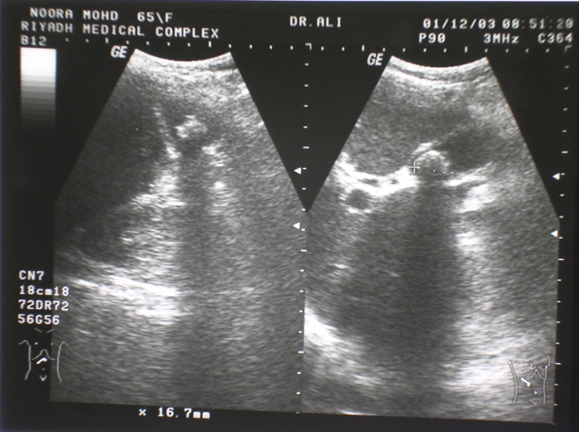
Investigation of first choice: biliary dis. & gynaecology.
Imaging studies- CT scan
- Oral, IV contrast
- Used for: Abdomen, chest , brain, vascular and urinary tract.
- Side effects: Anaphylactic reaction, renal injury, radiation
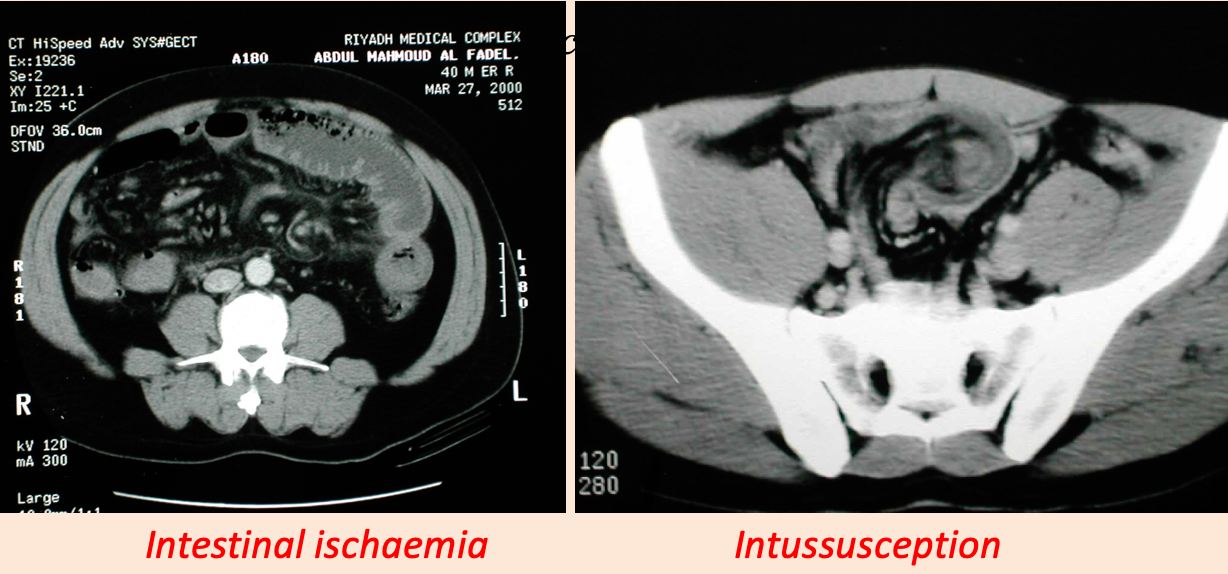
What is the relation of Metformin and the IV contrast ?
Before CT
- Wear hospital gown
- Take off jewelry/metal objects
- NPO ?
- If IV contrast needed, Renal profile needed
- Consent
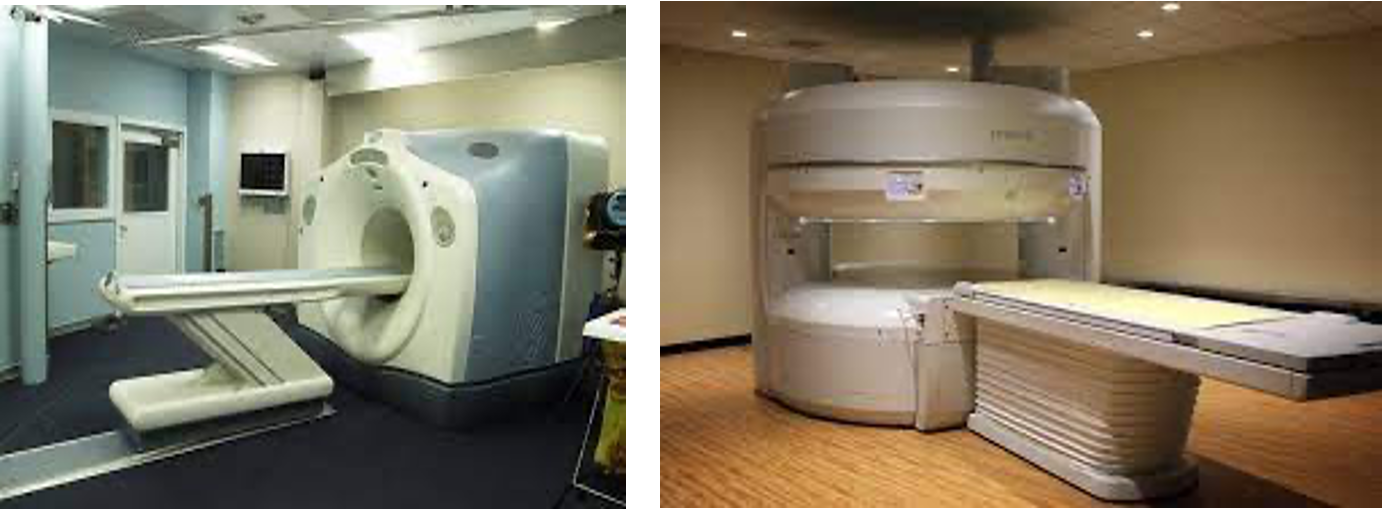
Imagi˚ng studies - MRI
- Good images: Soft tissue (better than CT) Blood vessel (MRI angiogram)
- No known deleterious effect
- No radiation
- Slow and expensive.
- Contraindications
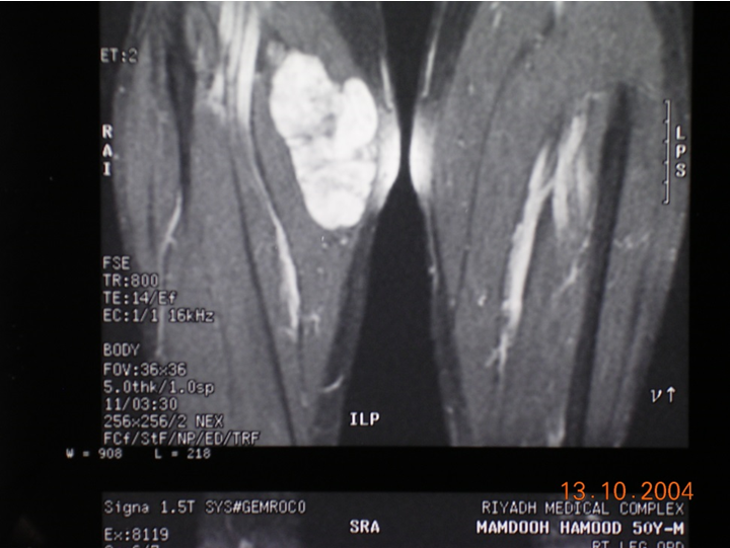
Absolute: ferromagnetic implants
MRI use electromagnetic fields and radio waves rather than ionizing radiation
Ionizing radiation is radiation that contains enough energy to liberate electrons from atomic orbit, which ionizes them. , which can create damaging free radicals (x-ray)
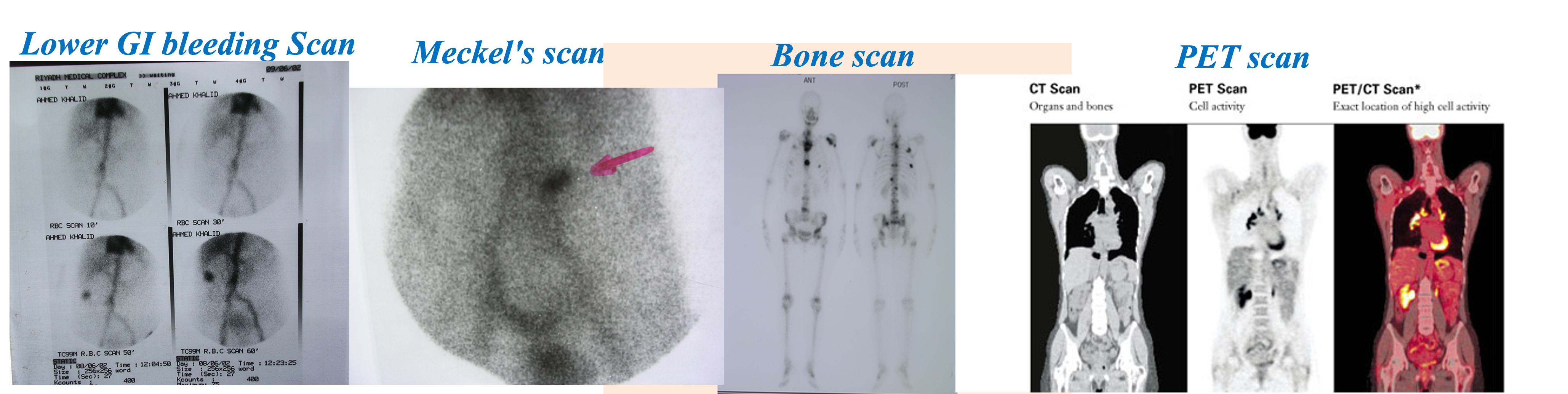
Imaging studies – Isotope scan
- Isotope scan: More information about function than structure. I131,Tc99, I123, Ga67, Th201- incorporated into other molecule to localize target organ.
- Detected by gamma camera.
- Bone metastasis, renal function, foci of infection, GI bleeding, infarction of myocardium, sentinel node detection
- PET scan: Expensive. Use: Brain physiology, tumour detection , cardiac physiology
Technetium-99 Tagged RBC scan can detect bleeding rate of 0.1 ml/hr
PET: positron emission tomography
Endoscopy
- Precise diagnosis: GI, pancreatic, biliary, bronchus, urinary tract
- Cytology/ biopsy.
- Minimally invasive therapy: laparoscopy, arthroscopy, ERCP.
- Disadvantages: Unpleasant, uncomfortable (sedation/ anesthesia)
- Complications: Infection, perforation, aspiration, bleeding, cardiac arrhythmias, respiratory arrest
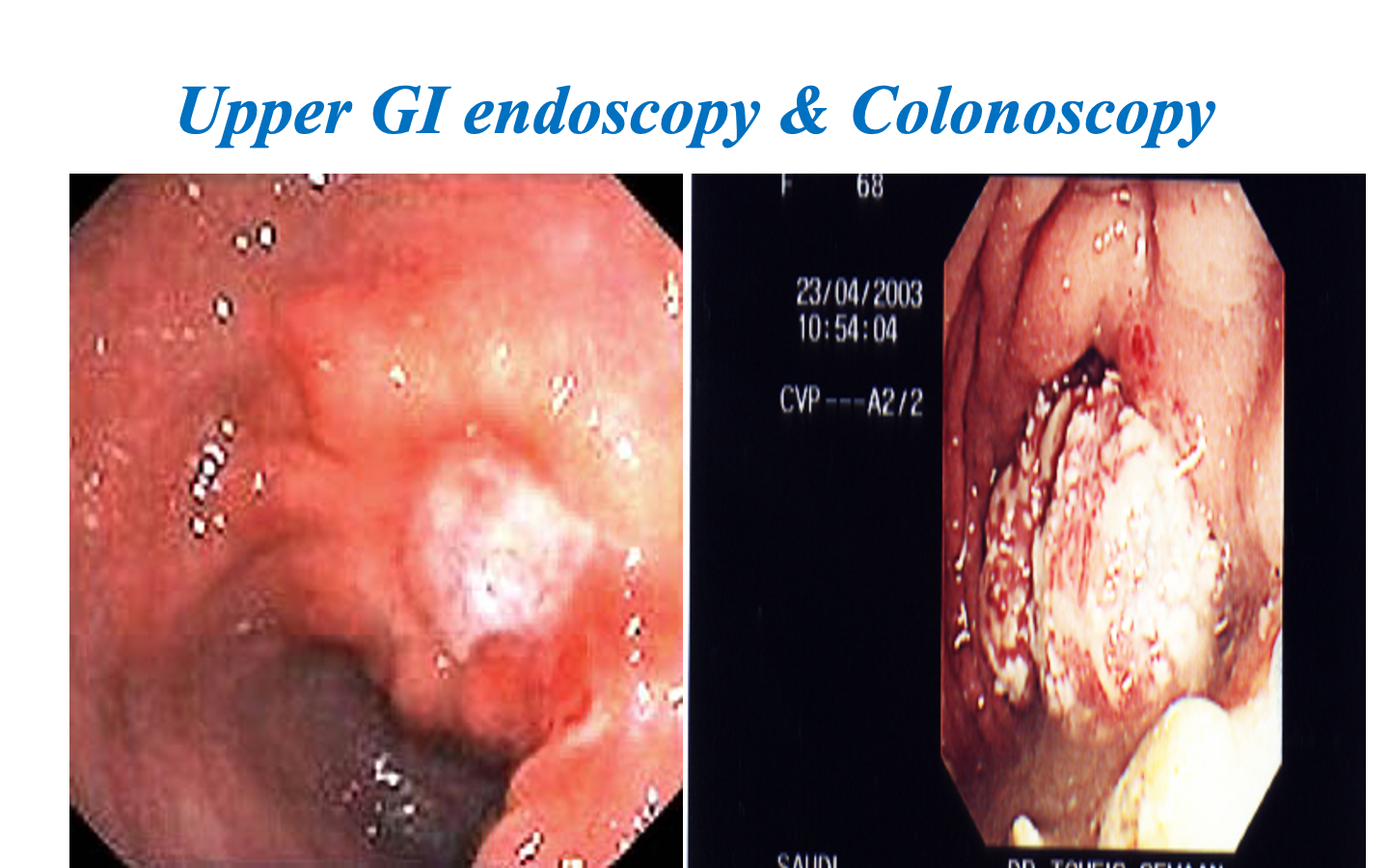
ERCP: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography
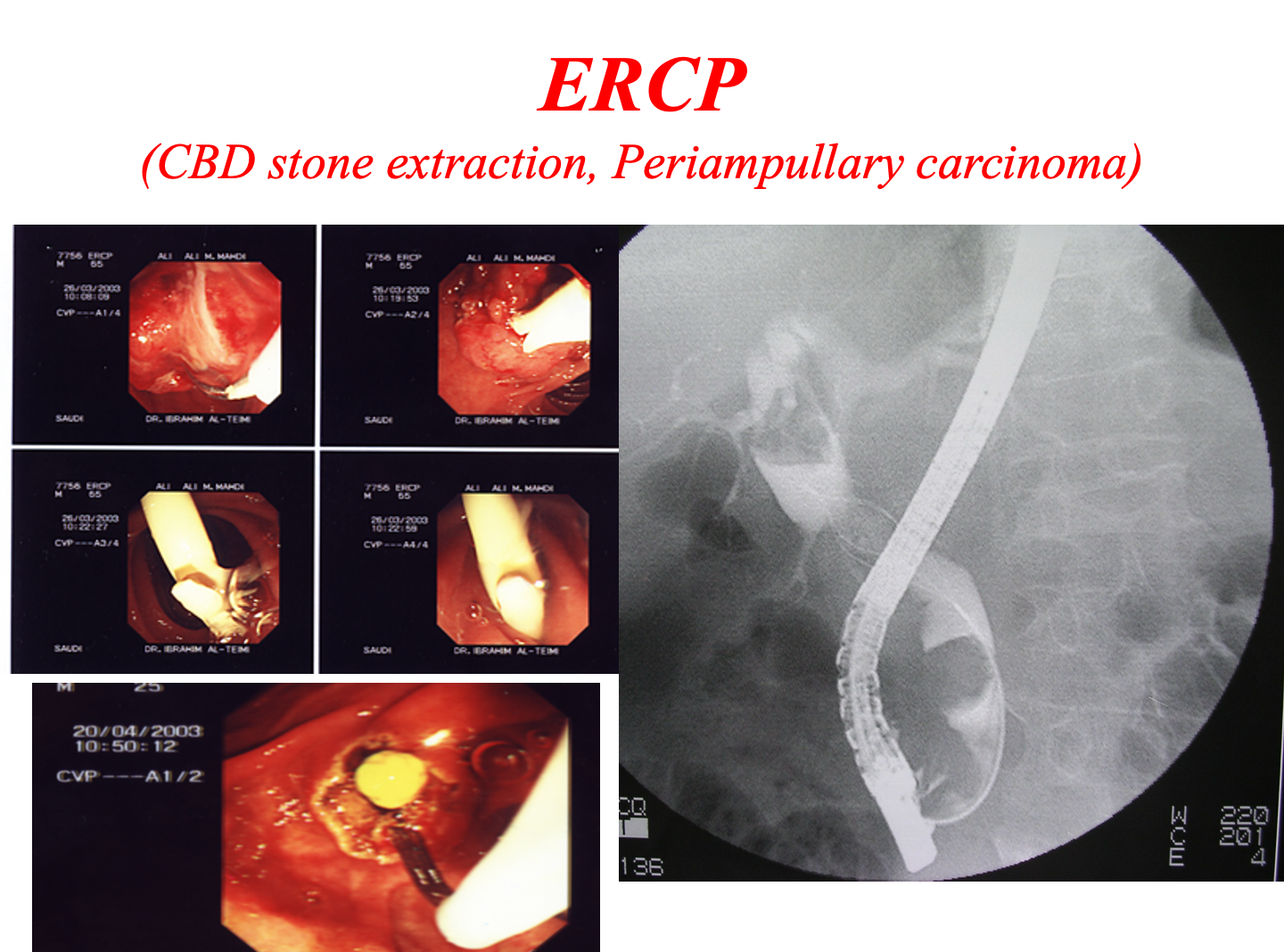
Tissue sampling
- Body fluids- pleura, peritoneum, sputum , urine.
- Smears, brush cytology
- FNAC Z (Shows abnormality only without margin)
- Core biopsy Z (basement membrane differentiation)
- Open biopsy (incision/ excision)
- Frozen section biopsy: Biopsy material frozen in liquid nitrogen, sliced, stained & reported in minutes
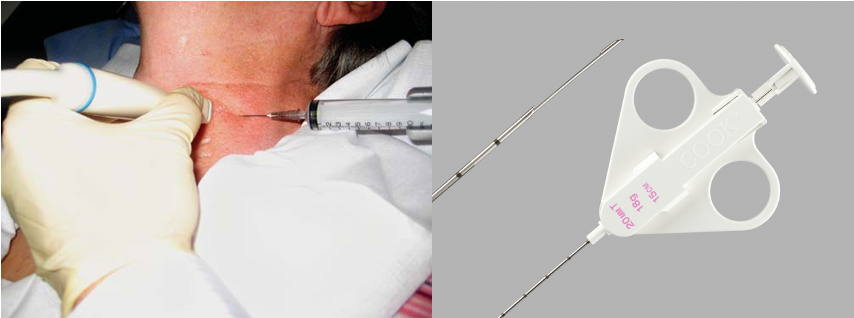
Z Fine Needle Aspiration: A thin, hollow needle is used to collect a sample of cells from a mass or lesion for analysis. (Less invasive procedure). Commonly used in thyroid nodule
Core Needle Biopsy: A hollow needle is used to collect a sample of tissue for evaluation of its histopathological features. Commonly used to assess suspicious breast lesion
Open Biopsy: Incisional or Excisional
Function tests
- Cardiac evaluation: ECG, Thallium scan, Echocardiography
- Respiratory function: ABG (risk pCO2 > 45 mmHg) FVC & FEV1 ( risk- < 70% of predicted)
- Renal function: Lab, Scintigraphic renography- DMSA, MAG3, DTPA
- Endocrine function- lab, isotope scan
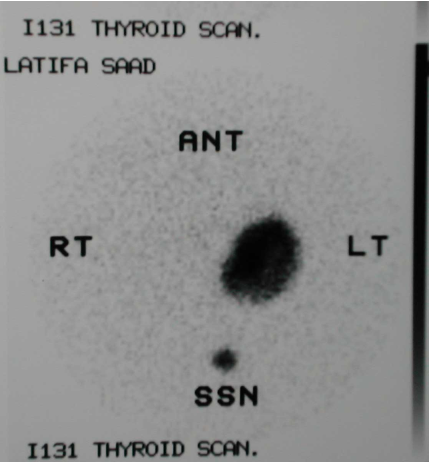 DMSA: Dimercaptosuccinic acid scintigraphy
DTPA: Diethylene-triamine-penta-acetic acid
MAG: Mercaptoacetyle triglycine
DMSA: Dimercaptosuccinic acid scintigraphy
DTPA: Diethylene-triamine-penta-acetic acid
MAG: Mercaptoacetyle triglycine
Screening
- Screening for malignant disease ((((FOB))), FIT replacing FOB, mammography, PSA, endoscopy)
- Screening for surgical disease (one-t aneurysm AAA - ultrasonography in men ages 65 to 75 years who have ever smoked.
 FOBT: Fecal Occult Blood Test False positive in?
“Ever smoker”: who smoke 100 cigarettes during his/her lifetime
FOBT: Fecal Occult Blood Test False positive in?
“Ever smoker”: who smoke 100 cigarettes during his/her lifetime
FIT: Fecal Immunohistochemical test
Colonoscopy for colon cancer starting age at recommended at general 45 on recent suggestion - 40 family hx or 10 years earlier Mammogram for breast cancer starting age at 40